Longxiang Tang
RePlan: Reasoning-guided Region Planning for Complex Instruction-based Image Editing
Dec 18, 2025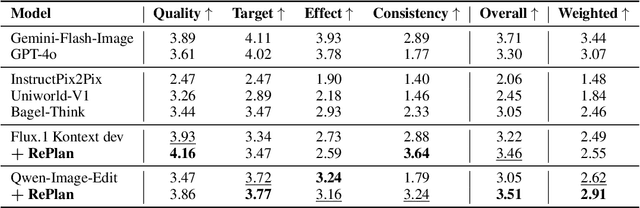
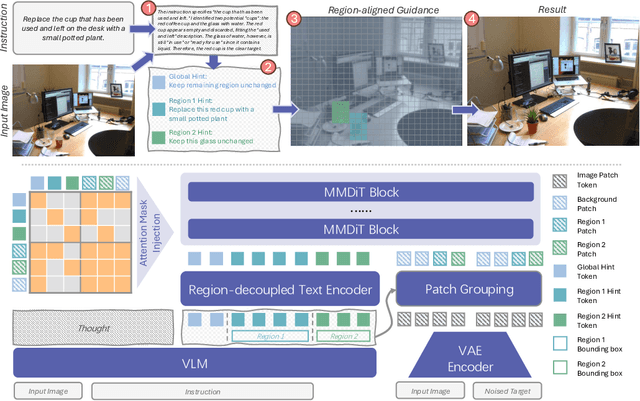

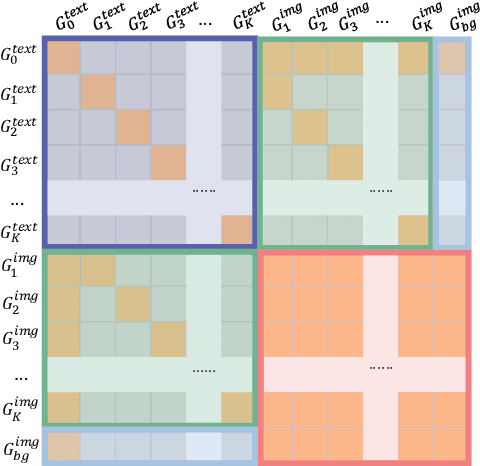
Abstract:Instruction-based image editing enables natural-language control over visual modifications, yet existing models falter under Instruction-Visual Complexity (IV-Complexity), where intricate instructions meet cluttered or ambiguous scenes. We introduce RePlan (Region-aligned Planning), a plan-then-execute framework that couples a vision-language planner with a diffusion editor. The planner decomposes instructions via step-by-step reasoning and explicitly grounds them to target regions; the editor then applies changes using a training-free attention-region injection mechanism, enabling precise, parallel multi-region edits without iterative inpainting. To strengthen planning, we apply GRPO-based reinforcement learning using 1K instruction-only examples, yielding substantial gains in reasoning fidelity and format reliability. We further present IV-Edit, a benchmark focused on fine-grained grounding and knowledge-intensive edits. Across IV-Complex settings, RePlan consistently outperforms strong baselines trained on far larger datasets, improving regional precision and overall fidelity. Our project page: https://replan-iv-edit.github.io
Segment Concealed Objects with Incomplete Supervision
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Incompletely-Supervised Concealed Object Segmentation (ISCOS) involves segmenting objects that seamlessly blend into their surrounding environments, utilizing incompletely annotated data, such as weak and semi-annotations, for model training. This task remains highly challenging due to (1) the limited supervision provided by the incompletely annotated training data, and (2) the difficulty of distinguishing concealed objects from the background, which arises from the intrinsic similarities in concealed scenarios. In this paper, we introduce the first unified method for ISCOS to address these challenges. To tackle the issue of incomplete supervision, we propose a unified mean-teacher framework, SEE, that leverages the vision foundation model, ``\emph{Segment Anything Model (SAM)}'', to generate pseudo-labels using coarse masks produced by the teacher model as prompts. To mitigate the effect of low-quality segmentation masks, we introduce a series of strategies for pseudo-label generation, storage, and supervision. These strategies aim to produce informative pseudo-labels, store the best pseudo-labels generated, and select the most reliable components to guide the student model, thereby ensuring robust network training. Additionally, to tackle the issue of intrinsic similarity, we design a hybrid-granularity feature grouping module that groups features at different granularities and aggregates these results. By clustering similar features, this module promotes segmentation coherence, facilitating more complete segmentation for both single-object and multiple-object images. We validate the effectiveness of our approach across multiple ISCOS tasks, and experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance. Furthermore, SEE can serve as a plug-and-play solution, enhancing the performance of existing models.
* IEEE TPAMI
AliTok: Towards Sequence Modeling Alignment between Tokenizer and Autoregressive Model
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive image generation aims to predict the next token based on previous ones. However, existing image tokenizers encode tokens with bidirectional dependencies during the compression process, which hinders the effective modeling by autoregressive models. In this paper, we propose a novel Aligned Tokenizer (AliTok), which utilizes a causal decoder to establish unidirectional dependencies among encoded tokens, thereby aligning the token modeling approach between the tokenizer and autoregressive model. Furthermore, by incorporating prefix tokens and employing two-stage tokenizer training to enhance reconstruction consistency, AliTok achieves great reconstruction performance while being generation-friendly. On ImageNet-256 benchmark, using a standard decoder-only autoregressive model as the generator with only 177M parameters, AliTok achieves a gFID score of 1.50 and an IS of 305.9. When the parameter count is increased to 662M, AliTok achieves a gFID score of 1.35, surpassing the state-of-the-art diffusion method with 10x faster sampling speed. The code and weights are available at https://github.com/ali-vilab/alitok.
UnfoldIR: Rethinking Deep Unfolding Network in Illumination Degradation Image Restoration
May 10, 2025Abstract:Deep unfolding networks (DUNs) are widely employed in illumination degradation image restoration (IDIR) to merge the interpretability of model-based approaches with the generalization of learning-based methods. However, the performance of DUN-based methods remains considerably inferior to that of state-of-the-art IDIR solvers. Our investigation indicates that this limitation does not stem from structural shortcomings of DUNs but rather from the limited exploration of the unfolding structure, particularly for (1) constructing task-specific restoration models, (2) integrating advanced network architectures, and (3) designing DUN-specific loss functions. To address these issues, we propose a novel DUN-based method, UnfoldIR, for IDIR tasks. UnfoldIR first introduces a new IDIR model with dedicated regularization terms for smoothing illumination and enhancing texture. We unfold the iterative optimized solution of this model into a multistage network, with each stage comprising a reflectance-assisted illumination correction (RAIC) module and an illumination-guided reflectance enhancement (IGRE) module. RAIC employs a visual state space (VSS) to extract non-local features, enforcing illumination smoothness, while IGRE introduces a frequency-aware VSS to globally align similar textures, enabling mildly degraded regions to guide the enhancement of details in more severely degraded areas. This suppresses noise while enhancing details. Furthermore, given the multistage structure, we propose an inter-stage information consistent loss to maintain network stability in the final stages. This loss contributes to structural preservation and sustains the model's performance even in unsupervised settings. Experiments verify our effectiveness across 5 IDIR tasks and 3 downstream problems.
UniAnimate-DiT: Human Image Animation with Large-Scale Video Diffusion Transformer
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:This report presents UniAnimate-DiT, an advanced project that leverages the cutting-edge and powerful capabilities of the open-source Wan2.1 model for consistent human image animation. Specifically, to preserve the robust generative capabilities of the original Wan2.1 model, we implement Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) technique to fine-tune a minimal set of parameters, significantly reducing training memory overhead. A lightweight pose encoder consisting of multiple stacked 3D convolutional layers is designed to encode motion information of driving poses. Furthermore, we adopt a simple concatenation operation to integrate the reference appearance into the model and incorporate the pose information of the reference image for enhanced pose alignment. Experimental results show that our approach achieves visually appearing and temporally consistent high-fidelity animations. Trained on 480p (832x480) videos, UniAnimate-DiT demonstrates strong generalization capabilities to seamlessly upscale to 720P (1280x720) during inference. The training and inference code is publicly available at https://github.com/ali-vilab/UniAnimate-DiT.
Hybrid-Level Instruction Injection for Video Token Compression in Multi-modal Large Language Models
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Recent Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have been challenged by the computational overhead resulting from massive video frames, often alleviated through compression strategies. However, the visual content is not equally contributed to user instructions, existing strategies (\eg, average pool) inevitably lead to the loss of potentially useful information. To tackle this, we propose the Hybrid-level Instruction Injection Strategy for Conditional Token Compression in MLLMs (HICom), utilizing the instruction as a condition to guide the compression from both local and global levels. This encourages the compression to retain the maximum amount of user-focused information while reducing visual tokens to minimize computational burden. Specifically, the instruction condition is injected into the grouped visual tokens at the local level and the learnable tokens at the global level, and we conduct the attention mechanism to complete the conditional compression. From the hybrid-level compression, the instruction-relevant visual parts are highlighted while the temporal-spatial structure is also preserved for easier understanding of LLMs. To further unleash the potential of HICom, we introduce a new conditional pre-training stage with our proposed dataset HICom-248K. Experiments show that our HICom can obtain distinguished video understanding ability with fewer tokens, increasing the performance by 2.43\% average on three multiple-choice QA benchmarks and saving 78.8\% tokens compared with the SOTA method. The code is available at https://github.com/lntzm/HICom.
Does Your Vision-Language Model Get Lost in the Long Video Sampling Dilemma?
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:The rise of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) has significantly advanced video understanding. However, efficiently processing long videos remains a challenge due to the ``Sampling Dilemma'': low-density sampling risks missing critical information, while high-density sampling introduces redundancy. To address this issue, we introduce LSDBench, the first benchmark designed to evaluate LVLMs on long-video tasks by constructing high Necessary Sampling Density (NSD) questions, where NSD represents the minimum sampling density required to accurately answer a given question. LSDBench focuses on dense, short-duration actions to rigorously assess the sampling strategies employed by LVLMs. To tackle the challenges posed by high-NSD questions, we propose a novel Reasoning-Driven Hierarchical Sampling (RHS) framework, which combines global localization of question-relevant cues with local dense sampling for precise inference. Additionally, we develop a lightweight Semantic-Guided Frame Selector to prioritize informative frames, enabling RHS to achieve comparable or superior performance with significantly fewer sampled frames. Together, our LSDBench and RHS framework address the unique challenges of high-NSD long-video tasks, setting a new standard for evaluating and improving LVLMs in this domain.
DreamRelation: Relation-Centric Video Customization
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Relational video customization refers to the creation of personalized videos that depict user-specified relations between two subjects, a crucial task for comprehending real-world visual content. While existing methods can personalize subject appearances and motions, they still struggle with complex relational video customization, where precise relational modeling and high generalization across subject categories are essential. The primary challenge arises from the intricate spatial arrangements, layout variations, and nuanced temporal dynamics inherent in relations; consequently, current models tend to overemphasize irrelevant visual details rather than capturing meaningful interactions. To address these challenges, we propose DreamRelation, a novel approach that personalizes relations through a small set of exemplar videos, leveraging two key components: Relational Decoupling Learning and Relational Dynamics Enhancement. First, in Relational Decoupling Learning, we disentangle relations from subject appearances using relation LoRA triplet and hybrid mask training strategy, ensuring better generalization across diverse relationships. Furthermore, we determine the optimal design of relation LoRA triplet by analyzing the distinct roles of the query, key, and value features within MM-DiT's attention mechanism, making DreamRelation the first relational video generation framework with explainable components. Second, in Relational Dynamics Enhancement, we introduce space-time relational contrastive loss, which prioritizes relational dynamics while minimizing the reliance on detailed subject appearances. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DreamRelation outperforms state-of-the-art methods in relational video customization. Code and models will be made publicly available.
Gamma: Toward Generic Image Assessment with Mixture of Assessment Experts
Mar 09, 2025



Abstract:Image assessment aims to evaluate the quality and aesthetics of images and has been applied across various scenarios, such as natural and AIGC scenes. Existing methods mostly address these sub-tasks or scenes individually. While some works attempt to develop unified image assessment models, they have struggled to achieve satisfactory performance or cover a broad spectrum of assessment scenarios. In this paper, we present \textbf{Gamma}, a \textbf{G}eneric im\textbf{A}ge assess\textbf{M}ent model using \textbf{M}ixture of \textbf{A}ssessment Experts, which can effectively assess images from diverse scenes through mixed-dataset training. Achieving unified training in image assessment presents significant challenges due to annotation biases across different datasets. To address this issue, we first propose a Mixture of Assessment Experts (MoAE) module, which employs shared and adaptive experts to dynamically learn common and specific knowledge for different datasets, respectively. In addition, we introduce a Scene-based Differential Prompt (SDP) strategy, which uses scene-specific prompts to provide prior knowledge and guidance during the learning process, further boosting adaptation for various scenes. Our Gamma model is trained and evaluated on 12 datasets spanning 6 image assessment scenarios. Extensive experiments show that our unified Gamma outperforms other state-of-the-art mixed-training methods by significant margins while covering more scenes. Code: https://github.com/zht8506/Gamma.
Integrating Extra Modality Helps Segmentor Find Camouflaged Objects Well
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Camouflaged Object Segmentation (COS) remains a challenging problem due to the subtle visual differences between camouflaged objects and backgrounds. Owing to the exceedingly limited visual cues available from visible spectrum, previous RGB single-modality approaches often struggle to achieve satisfactory results, prompting the exploration of multimodal data to enhance detection accuracy. In this work, we present UniCOS, a novel framework that effectively leverages diverse data modalities to improve segmentation performance. UniCOS comprises two key components: a multimodal segmentor, UniSEG, and a cross-modal knowledge learning module, UniLearner. UniSEG employs a state space fusion mechanism to integrate cross-modal features within a unified state space, enhancing contextual understanding and improving robustness to integration of heterogeneous data. Additionally, it includes a fusion-feedback mechanism that facilitate feature extraction. UniLearner exploits multimodal data unrelated to the COS task to improve the segmentation ability of the COS models by generating pseudo-modal content and cross-modal semantic associations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniSEG outperforms existing Multimodal COS (MCOS) segmentors, regardless of whether real or pseudo-multimodal COS data is available. Moreover, in scenarios where multimodal COS data is unavailable but multimodal non-COS data is accessible, UniLearner effectively exploits these data to enhance segmentation performance. Our code will be made publicly available on \href{https://github.com/cnyvfang/UniCOS}{GitHub}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge