Yun Zheng
GenAgent: Scaling Text-to-Image Generation via Agentic Multimodal Reasoning
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:We introduce GenAgent, unifying visual understanding and generation through an agentic multimodal model. Unlike unified models that face expensive training costs and understanding-generation trade-offs, GenAgent decouples these capabilities through an agentic framework: understanding is handled by the multimodal model itself, while generation is achieved by treating image generation models as invokable tools. Crucially, unlike existing modular systems constrained by static pipelines, this design enables autonomous multi-turn interactions where the agent generates multimodal chains-of-thought encompassing reasoning, tool invocation, judgment, and reflection to iteratively refine outputs. We employ a two-stage training strategy: first, cold-start with supervised fine-tuning on high-quality tool invocation and reflection data to bootstrap agent behaviors; second, end-to-end agentic reinforcement learning combining pointwise rewards (final image quality) and pairwise rewards (reflection accuracy), with trajectory resampling for enhanced multi-turn exploration. GenAgent significantly boosts base generator(FLUX.1-dev) performance on GenEval++ (+23.6\%) and WISE (+14\%). Beyond performance gains, our framework demonstrates three key properties: 1) cross-tool generalization to generators with varying capabilities, 2) test-time scaling with consistent improvements across interaction rounds, and 3) task-adaptive reasoning that automatically adjusts to different tasks. Our code will be available at \href{https://github.com/deep-kaixun/GenAgent}{this url}.
ShowTable: Unlocking Creative Table Visualization with Collaborative Reflection and Refinement
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:While existing generation and unified models excel at general image generation, they struggle with tasks requiring deep reasoning, planning, and precise data-to-visual mapping abilities beyond general scenarios. To push beyond the existing limitations, we introduce a new and challenging task: creative table visualization, requiring the model to generate an infographic that faithfully and aesthetically visualizes the data from a given table. To address this challenge, we propose ShowTable, a pipeline that synergizes MLLMs with diffusion models via a progressive self-correcting process. The MLLM acts as the central orchestrator for reasoning the visual plan and judging visual errors to provide refined instructions, the diffusion execute the commands from MLLM, achieving high-fidelity results. To support this task and our pipeline, we introduce three automated data construction pipelines for training different modules. Furthermore, we introduce TableVisBench, a new benchmark with 800 challenging instances across 5 evaluation dimensions, to assess performance on this task. Experiments demonstrate that our pipeline, instantiated with different models, significantly outperforms baselines, highlighting its effective multi-modal reasoning, generation, and error correction capabilities.
ChronoTailor: Harnessing Attention Guidance for Fine-Grained Video Virtual Try-On
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Video virtual try-on aims to seamlessly replace the clothing of a person in a source video with a target garment. Despite significant progress in this field, existing approaches still struggle to maintain continuity and reproduce garment details. In this paper, we introduce ChronoTailor, a diffusion-based framework that generates temporally consistent videos while preserving fine-grained garment details. By employing a precise spatio-temporal attention mechanism to guide the integration of fine-grained garment features, ChronoTailor achieves robust try-on performance. First, ChronoTailor leverages region-aware spatial guidance to steer the evolution of spatial attention and employs an attention-driven temporal feature fusion mechanism to generate more continuous temporal features. This dual approach not only enables fine-grained local editing but also effectively mitigates artifacts arising from video dynamics. Second, ChronoTailor integrates multi-scale garment features to preserve low-level visual details and incorporates a garment-pose feature alignment to ensure temporal continuity during dynamic motion. Additionally, we collect StyleDress, a new dataset featuring intricate garments, varied environments, and diverse poses, offering advantages over existing public datasets, and will be publicly available for research. Extensive experiments show that ChronoTailor maintains spatio-temporal continuity and preserves garment details during motion, significantly outperforming previous methods.
Aligned Better, Listen Better for Audio-Visual Large Language Models
Apr 02, 2025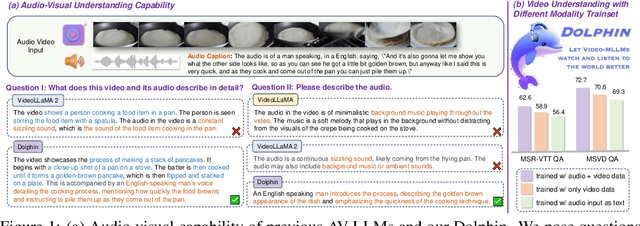
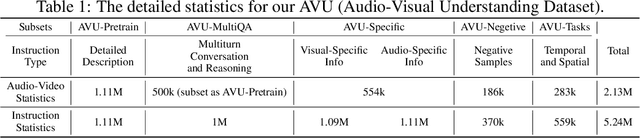
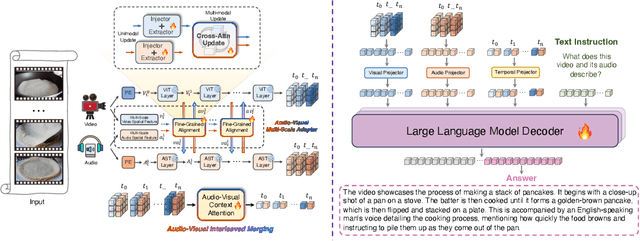
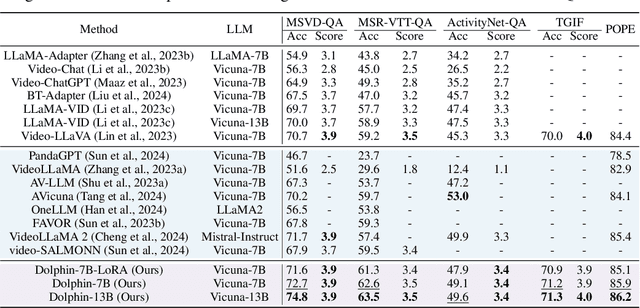
Abstract:Audio is essential for multimodal video understanding. On the one hand, video inherently contains audio, which supplies complementary information to vision. Besides, video large language models (Video-LLMs) can encounter many audio-centric settings. However, existing Video-LLMs and Audio-Visual Large Language Models (AV-LLMs) exhibit deficiencies in exploiting audio information, leading to weak understanding and hallucinations. To solve the issues, we delve into the model architecture and dataset. (1) From the architectural perspective, we propose a fine-grained AV-LLM, namely Dolphin. The concurrent alignment of audio and visual modalities in both temporal and spatial dimensions ensures a comprehensive and accurate understanding of videos. Specifically, we devise an audio-visual multi-scale adapter for multi-scale information aggregation, which achieves spatial alignment. For temporal alignment, we propose audio-visual interleaved merging. (2) From the dataset perspective, we curate an audio-visual caption and instruction-tuning dataset, called AVU. It comprises 5.2 million diverse, open-ended data tuples (video, audio, question, answer) and introduces a novel data partitioning strategy. Extensive experiments show our model not only achieves remarkable performance in audio-visual understanding, but also mitigates potential hallucinations.
Wan: Open and Advanced Large-Scale Video Generative Models
Mar 26, 2025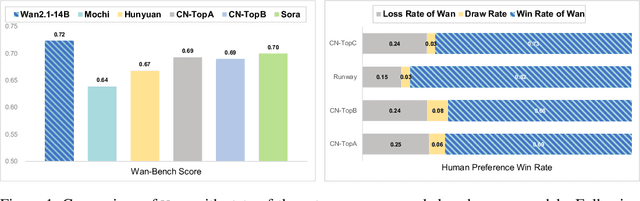



Abstract:This report presents Wan, a comprehensive and open suite of video foundation models designed to push the boundaries of video generation. Built upon the mainstream diffusion transformer paradigm, Wan achieves significant advancements in generative capabilities through a series of innovations, including our novel VAE, scalable pre-training strategies, large-scale data curation, and automated evaluation metrics. These contributions collectively enhance the model's performance and versatility. Specifically, Wan is characterized by four key features: Leading Performance: The 14B model of Wan, trained on a vast dataset comprising billions of images and videos, demonstrates the scaling laws of video generation with respect to both data and model size. It consistently outperforms the existing open-source models as well as state-of-the-art commercial solutions across multiple internal and external benchmarks, demonstrating a clear and significant performance superiority. Comprehensiveness: Wan offers two capable models, i.e., 1.3B and 14B parameters, for efficiency and effectiveness respectively. It also covers multiple downstream applications, including image-to-video, instruction-guided video editing, and personal video generation, encompassing up to eight tasks. Consumer-Grade Efficiency: The 1.3B model demonstrates exceptional resource efficiency, requiring only 8.19 GB VRAM, making it compatible with a wide range of consumer-grade GPUs. Openness: We open-source the entire series of Wan, including source code and all models, with the goal of fostering the growth of the video generation community. This openness seeks to significantly expand the creative possibilities of video production in the industry and provide academia with high-quality video foundation models. All the code and models are available at https://github.com/Wan-Video/Wan2.1.
Hybrid-Level Instruction Injection for Video Token Compression in Multi-modal Large Language Models
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Recent Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have been challenged by the computational overhead resulting from massive video frames, often alleviated through compression strategies. However, the visual content is not equally contributed to user instructions, existing strategies (\eg, average pool) inevitably lead to the loss of potentially useful information. To tackle this, we propose the Hybrid-level Instruction Injection Strategy for Conditional Token Compression in MLLMs (HICom), utilizing the instruction as a condition to guide the compression from both local and global levels. This encourages the compression to retain the maximum amount of user-focused information while reducing visual tokens to minimize computational burden. Specifically, the instruction condition is injected into the grouped visual tokens at the local level and the learnable tokens at the global level, and we conduct the attention mechanism to complete the conditional compression. From the hybrid-level compression, the instruction-relevant visual parts are highlighted while the temporal-spatial structure is also preserved for easier understanding of LLMs. To further unleash the potential of HICom, we introduce a new conditional pre-training stage with our proposed dataset HICom-248K. Experiments show that our HICom can obtain distinguished video understanding ability with fewer tokens, increasing the performance by 2.43\% average on three multiple-choice QA benchmarks and saving 78.8\% tokens compared with the SOTA method. The code is available at https://github.com/lntzm/HICom.
Rethinking Video Tokenization: A Conditioned Diffusion-based Approach
Mar 05, 2025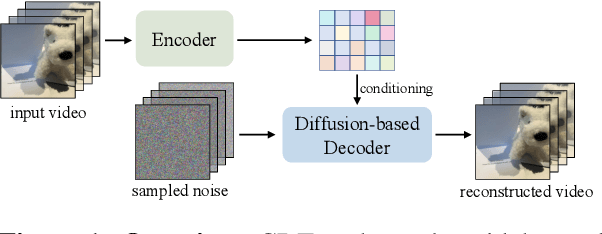
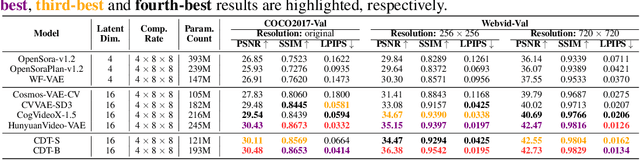
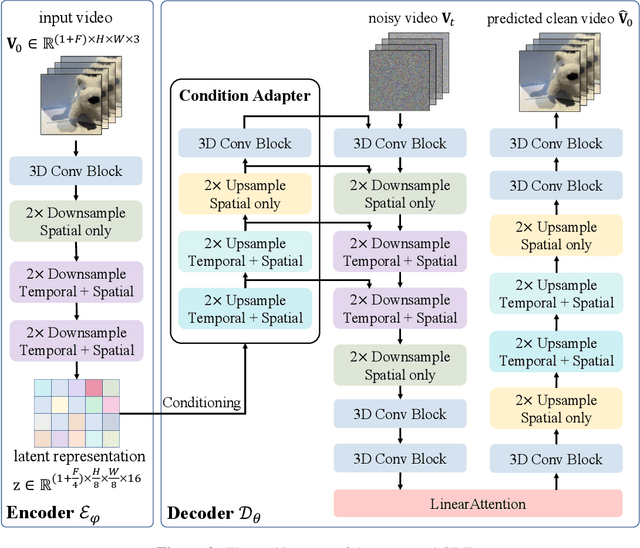
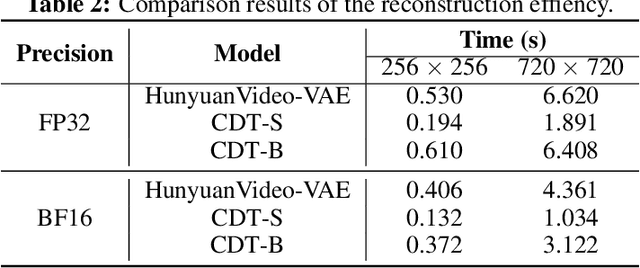
Abstract:Video tokenizers, which transform videos into compact latent representations, are key to video generation. Existing video tokenizers are based on the VAE architecture and follow a paradigm where an encoder compresses videos into compact latents, and a deterministic decoder reconstructs the original videos from these latents. In this paper, we propose a novel \underline{\textbf{C}}onditioned \underline{\textbf{D}}iffusion-based video \underline{\textbf{T}}okenizer entitled \textbf{\ourmethod}, which departs from previous methods by replacing the deterministic decoder with a 3D causal diffusion model. The reverse diffusion generative process of the decoder is conditioned on the latent representations derived via the encoder. With a feature caching and sampling acceleration, the framework efficiently reconstructs high-fidelity videos of arbitrary lengths. Results show that {\ourmethod} achieves state-of-the-art performance in video reconstruction tasks using just a single-step sampling. Even a smaller version of {\ourmethod} still achieves reconstruction results on par with the top two baselines. Furthermore, the latent video generation model trained using {\ourmethod} also shows superior performance.
UFO: A Unified Approach to Fine-grained Visual Perception via Open-ended Language Interface
Mar 04, 2025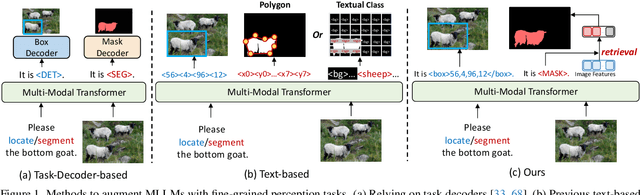
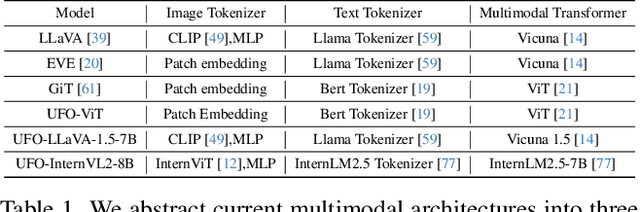
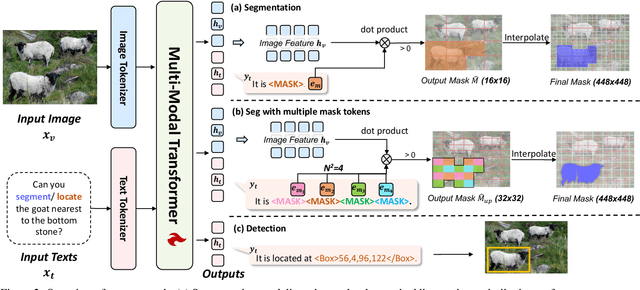
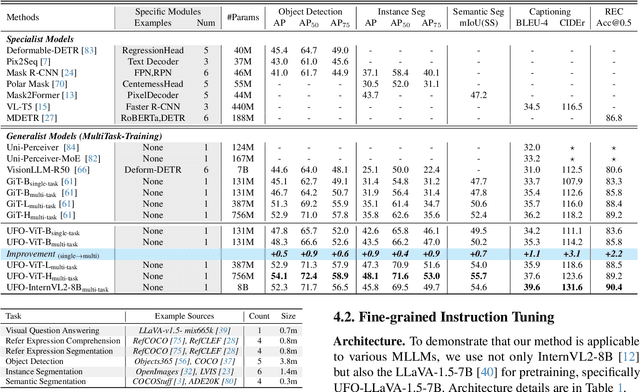
Abstract:Generalist models have achieved remarkable success in both language and vision-language tasks, showcasing the potential of unified modeling. However, effectively integrating fine-grained perception tasks like detection and segmentation into these models remains a significant challenge. This is primarily because these tasks often rely heavily on task-specific designs and architectures that can complicate the modeling process. To address this challenge, we present \ours, a framework that \textbf{U}nifies \textbf{F}ine-grained visual perception tasks through an \textbf{O}pen-ended language interface. By transforming all perception targets into the language space, \ours unifies object-level detection, pixel-level segmentation, and image-level vision-language tasks into a single model. Additionally, we introduce a novel embedding retrieval approach that relies solely on the language interface to support segmentation tasks. Our framework bridges the gap between fine-grained perception and vision-language tasks, significantly simplifying architectural design and training strategies while achieving comparable or superior performance to methods with intricate task-specific designs. After multi-task training on five standard visual perception datasets, \ours outperforms the previous state-of-the-art generalist models by 12.3 mAP on COCO instance segmentation and 3.3 mIoU on ADE20K semantic segmentation. Furthermore, our method seamlessly integrates with existing MLLMs, effectively combining fine-grained perception capabilities with their advanced language abilities, thereby enabling more challenging tasks such as reasoning segmentation. Code and models are available at https://github.com/nnnth/UFO.
What Is a Good Caption? A Comprehensive Visual Caption Benchmark for Evaluating Both Correctness and Coverage of MLLMs
Feb 19, 2025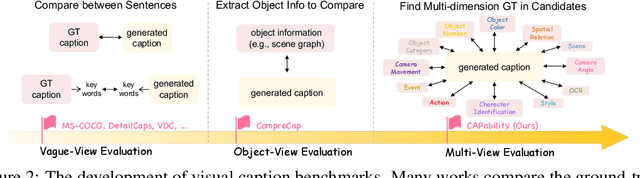
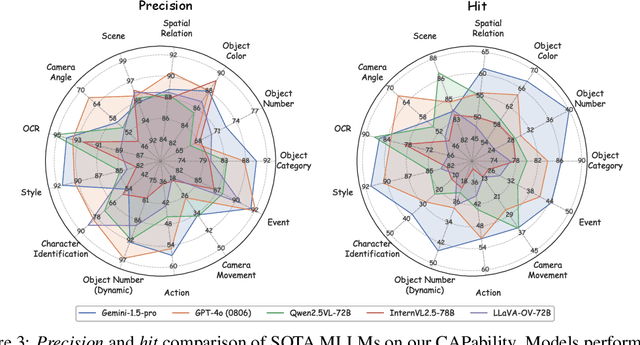

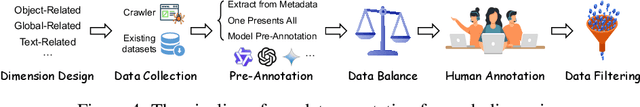
Abstract:Recent advancements in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have rendered traditional visual captioning benchmarks obsolete, as they primarily evaluate short descriptions with outdated metrics. While recent benchmarks address these limitations by decomposing captions into visual elements and adopting model-based evaluation, they remain incomplete-overlooking critical aspects, while providing vague, non-explanatory scores. To bridge this gap, we propose CV-CapBench, a Comprehensive Visual Caption Benchmark that systematically evaluates caption quality across 6 views and 13 dimensions. CV-CapBench introduces precision, recall, and hit rate metrics for each dimension, uniquely assessing both correctness and coverage. Experiments on leading MLLMs reveal significant capability gaps, particularly in dynamic and knowledge-intensive dimensions. These findings provide actionable insights for future research. The code and data will be released.
ContextHOI: Spatial Context Learning for Human-Object Interaction Detection
Dec 12, 2024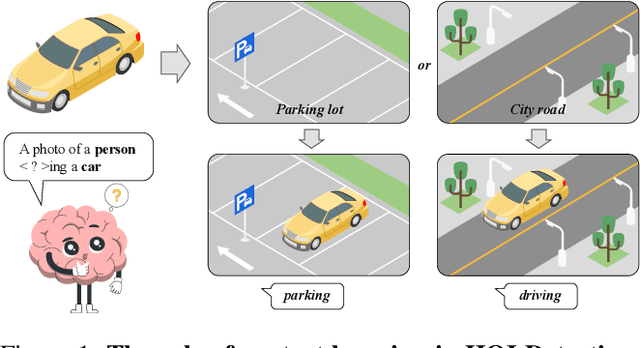
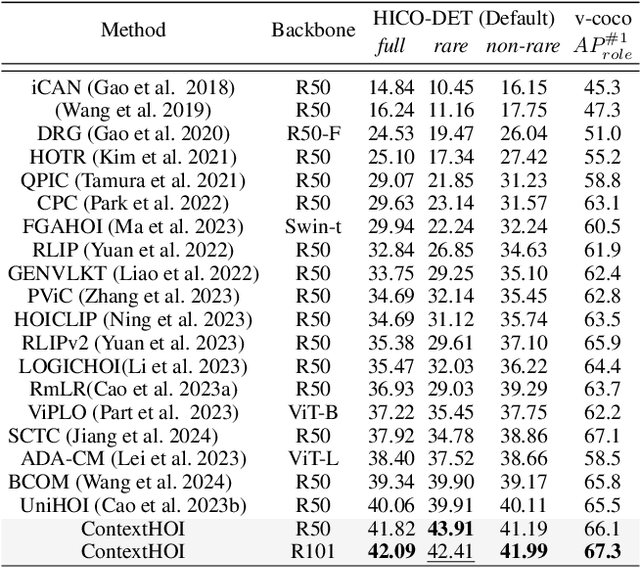
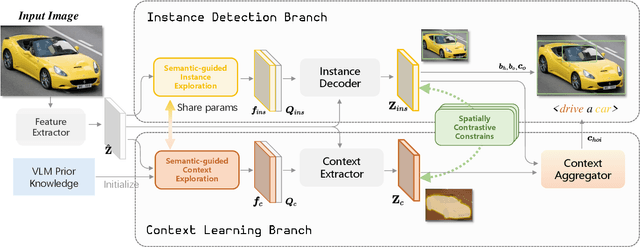
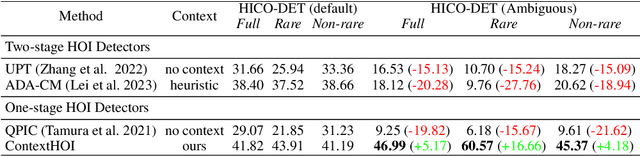
Abstract:Spatial contexts, such as the backgrounds and surroundings, are considered critical in Human-Object Interaction (HOI) recognition, especially when the instance-centric foreground is blurred or occluded. Recent advancements in HOI detectors are usually built upon detection transformer pipelines. While such an object-detection-oriented paradigm shows promise in localizing objects, its exploration of spatial context is often insufficient for accurately recognizing human actions. To enhance the capabilities of object detectors for HOI detection, we present a dual-branch framework named ContextHOI, which efficiently captures both object detection features and spatial contexts. In the context branch, we train the model to extract informative spatial context without requiring additional hand-craft background labels. Furthermore, we introduce context-aware spatial and semantic supervision to the context branch to filter out irrelevant noise and capture informative contexts. ContextHOI achieves state-of-the-art performance on the HICO-DET and v-coco benchmarks. For further validation, we construct a novel benchmark, HICO-ambiguous, which is a subset of HICO-DET that contains images with occluded or impaired instance cues. Extensive experiments across all benchmarks, complemented by visualizations, underscore the enhancements provided by ContextHOI, especially in recognizing interactions involving occluded or blurred instances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge