Chaojie Mao
DenseGRPO: From Sparse to Dense Reward for Flow Matching Model Alignment
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Recent GRPO-based approaches built on flow matching models have shown remarkable improvements in human preference alignment for text-to-image generation. Nevertheless, they still suffer from the sparse reward problem: the terminal reward of the entire denoising trajectory is applied to all intermediate steps, resulting in a mismatch between the global feedback signals and the exact fine-grained contributions at intermediate denoising steps. To address this issue, we introduce \textbf{DenseGRPO}, a novel framework that aligns human preference with dense rewards, which evaluates the fine-grained contribution of each denoising step. Specifically, our approach includes two key components: (1) we propose to predict the step-wise reward gain as dense reward of each denoising step, which applies a reward model on the intermediate clean images via an ODE-based approach. This manner ensures an alignment between feedback signals and the contributions of individual steps, facilitating effective training; and (2) based on the estimated dense rewards, a mismatch drawback between the uniform exploration setting and the time-varying noise intensity in existing GRPO-based methods is revealed, leading to an inappropriate exploration space. Thus, we propose a reward-aware scheme to calibrate the exploration space by adaptively adjusting a timestep-specific stochasticity injection in the SDE sampler, ensuring a suitable exploration space at all timesteps. Extensive experiments on multiple standard benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed DenseGRPO and highlight the critical role of the valid dense rewards in flow matching model alignment.
Unison: A Fully Automatic, Task-Universal, and Low-Cost Framework for Unified Understanding and Generation
Dec 08, 2025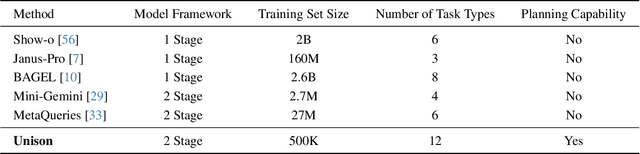
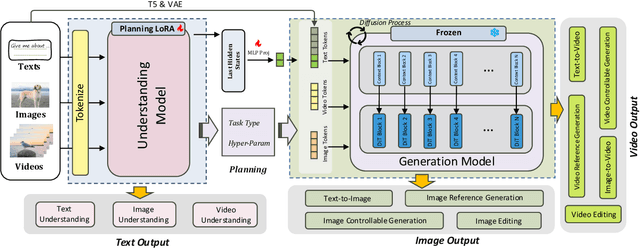
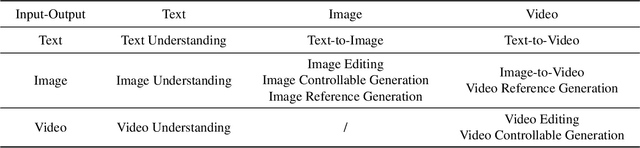

Abstract:Unified understanding and generation is a highly appealing research direction in multimodal learning. There exist two approaches: one trains a transformer via an auto-regressive paradigm, and the other adopts a two-stage scheme connecting pre-trained understanding and generative models for alignment fine-tuning. The former demands massive data and computing resources unaffordable for ordinary researchers. Though the latter requires a lower training cost, existing works often suffer from limited task coverage or poor generation quality. Both approaches lack the ability to parse input meta-information (such as task type, image resolution, video duration, etc.) and require manual parameter configuration that is tedious and non-intelligent. In this paper, we propose Unison which adopts the two-stage scheme while preserving the capabilities of the pre-trained models well. With an extremely low training cost, we cover a variety of multimodal understanding tasks, including text, image, and video understanding, as well as diverse generation tasks, such as text-to-visual content generation, editing, controllable generation, and IP-based reference generation. We also equip our model with the ability to automatically parse user intentions, determine the target task type, and accurately extract the meta-information required for the corresponding task. This enables full automation of various multimodal tasks without human intervention. Experiments demonstrate that, under a low-cost setting of only 500k training samples and 50 GPU hours, our model can accurately and automatically identify tasks and extract relevant parameters, and achieve superior performance across a variety of understanding and generation tasks.
Wan: Open and Advanced Large-Scale Video Generative Models
Mar 26, 2025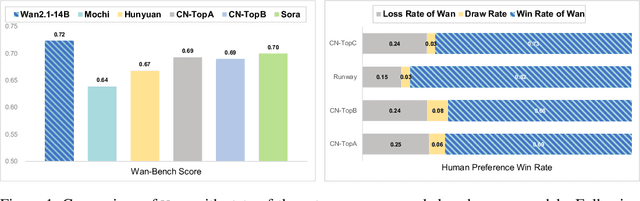



Abstract:This report presents Wan, a comprehensive and open suite of video foundation models designed to push the boundaries of video generation. Built upon the mainstream diffusion transformer paradigm, Wan achieves significant advancements in generative capabilities through a series of innovations, including our novel VAE, scalable pre-training strategies, large-scale data curation, and automated evaluation metrics. These contributions collectively enhance the model's performance and versatility. Specifically, Wan is characterized by four key features: Leading Performance: The 14B model of Wan, trained on a vast dataset comprising billions of images and videos, demonstrates the scaling laws of video generation with respect to both data and model size. It consistently outperforms the existing open-source models as well as state-of-the-art commercial solutions across multiple internal and external benchmarks, demonstrating a clear and significant performance superiority. Comprehensiveness: Wan offers two capable models, i.e., 1.3B and 14B parameters, for efficiency and effectiveness respectively. It also covers multiple downstream applications, including image-to-video, instruction-guided video editing, and personal video generation, encompassing up to eight tasks. Consumer-Grade Efficiency: The 1.3B model demonstrates exceptional resource efficiency, requiring only 8.19 GB VRAM, making it compatible with a wide range of consumer-grade GPUs. Openness: We open-source the entire series of Wan, including source code and all models, with the goal of fostering the growth of the video generation community. This openness seeks to significantly expand the creative possibilities of video production in the industry and provide academia with high-quality video foundation models. All the code and models are available at https://github.com/Wan-Video/Wan2.1.
ICE-Bench: A Unified and Comprehensive Benchmark for Image Creating and Editing
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Image generation has witnessed significant advancements in the past few years. However, evaluating the performance of image generation models remains a formidable challenge. In this paper, we propose ICE-Bench, a unified and comprehensive benchmark designed to rigorously assess image generation models. Its comprehensiveness could be summarized in the following key features: (1) Coarse-to-Fine Tasks: We systematically deconstruct image generation into four task categories: No-ref/Ref Image Creating/Editing, based on the presence or absence of source images and reference images. And further decompose them into 31 fine-grained tasks covering a broad spectrum of image generation requirements, culminating in a comprehensive benchmark. (2) Multi-dimensional Metrics: The evaluation framework assesses image generation capabilities across 6 dimensions: aesthetic quality, imaging quality, prompt following, source consistency, reference consistency, and controllability. 11 metrics are introduced to support the multi-dimensional evaluation. Notably, we introduce VLLM-QA, an innovative metric designed to assess the success of image editing by leveraging large models. (3) Hybrid Data: The data comes from real scenes and virtual generation, which effectively improves data diversity and alleviates the bias problem in model evaluation. Through ICE-Bench, we conduct a thorough analysis of existing generation models, revealing both the challenging nature of our benchmark and the gap between current model capabilities and real-world generation requirements. To foster further advancements in the field, we will open-source ICE-Bench, including its dataset, evaluation code, and models, thereby providing a valuable resource for the research community.
VACE: All-in-One Video Creation and Editing
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Diffusion Transformer has demonstrated powerful capability and scalability in generating high-quality images and videos. Further pursuing the unification of generation and editing tasks has yielded significant progress in the domain of image content creation. However, due to the intrinsic demands for consistency across both temporal and spatial dynamics, achieving a unified approach for video synthesis remains challenging. We introduce VACE, which enables users to perform Video tasks within an All-in-one framework for Creation and Editing. These tasks include reference-to-video generation, video-to-video editing, and masked video-to-video editing. Specifically, we effectively integrate the requirements of various tasks by organizing video task inputs, such as editing, reference, and masking, into a unified interface referred to as the Video Condition Unit (VCU). Furthermore, by utilizing a Context Adapter structure, we inject different task concepts into the model using formalized representations of temporal and spatial dimensions, allowing it to handle arbitrary video synthesis tasks flexibly. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the unified model of VACE achieves performance on par with task-specific models across various subtasks. Simultaneously, it enables diverse applications through versatile task combinations. Project page: https://ali-vilab.github.io/VACE-Page/.
ACE++: Instruction-Based Image Creation and Editing via Context-Aware Content Filling
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:We report ACE++, an instruction-based diffusion framework that tackles various image generation and editing tasks. Inspired by the input format for the inpainting task proposed by FLUX.1-Fill-dev, we improve the Long-context Condition Unit (LCU) introduced in ACE and extend this input paradigm to any editing and generation tasks. To take full advantage of image generative priors, we develop a two-stage training scheme to minimize the efforts of finetuning powerful text-to-image diffusion models like FLUX.1-dev. In the first stage, we pre-train the model using task data with the 0-ref tasks from the text-to-image model. There are many models in the community based on the post-training of text-to-image foundational models that meet this training paradigm of the first stage. For example, FLUX.1-Fill-dev deals primarily with painting tasks and can be used as an initialization to accelerate the training process. In the second stage, we finetune the above model to support the general instructions using all tasks defined in ACE. To promote the widespread application of ACE++ in different scenarios, we provide a comprehensive set of models that cover both full finetuning and lightweight finetuning, while considering general applicability and applicability in vertical scenarios. The qualitative analysis showcases the superiority of ACE++ in terms of generating image quality and prompt following ability. Code and models will be available on the project page: https://ali-vilab. github.io/ACE_plus_page/.
BACON: Supercharge Your VLM with Bag-of-Concept Graph to Mitigate Hallucinations
Jul 03, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents Bag-of-Concept Graph (BACON) to gift models with limited linguistic abilities to taste the privilege of Vision Language Models (VLMs) and boost downstream tasks such as detection, visual question answering (VQA), and image generation. Since the visual scenes in physical worlds are structured with complex relations between objects, BACON breaks down annotations into basic minimum elements and presents them in a graph structure. Element-wise style enables easy understanding, and structural composition liberates difficult locating. Careful prompt design births the BACON captions with the help of public-available VLMs and segmentation methods. In this way, we gather a dataset with 100K annotated images, which endow VLMs with remarkable capabilities, such as accurately generating BACON, transforming prompts into BACON format, envisioning scenarios in the style of BACONr, and dynamically modifying elements within BACON through interactive dialogue and more. Wide representative experiments, including detection, VQA, and image generation tasks, tell BACON as a lifeline to achieve previous out-of-reach tasks or excel in their current cutting-edge solutions.
StyleBooth: Image Style Editing with Multimodal Instruction
Apr 18, 2024
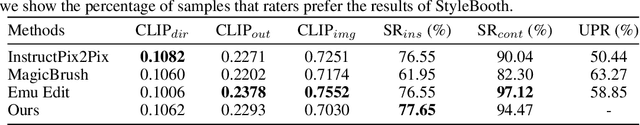
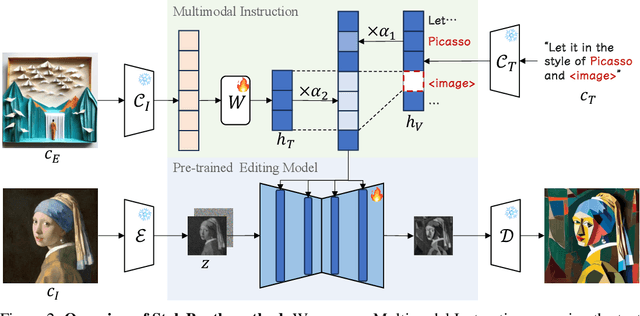

Abstract:Given an original image, image editing aims to generate an image that align with the provided instruction. The challenges are to accept multimodal inputs as instructions and a scarcity of high-quality training data, including crucial triplets of source/target image pairs and multimodal (text and image) instructions. In this paper, we focus on image style editing and present StyleBooth, a method that proposes a comprehensive framework for image editing and a feasible strategy for building a high-quality style editing dataset. We integrate encoded textual instruction and image exemplar as a unified condition for diffusion model, enabling the editing of original image following multimodal instructions. Furthermore, by iterative style-destyle tuning and editing and usability filtering, the StyleBooth dataset provides content-consistent stylized/plain image pairs in various categories of styles. To show the flexibility of StyleBooth, we conduct experiments on diverse tasks, such as text-based style editing, exemplar-based style editing and compositional style editing. The results demonstrate that the quality and variety of training data significantly enhance the ability to preserve content and improve the overall quality of generated images in editing tasks. Project page can be found at https://ali-vilab.github.io/stylebooth-page/.
Locate, Assign, Refine: Taming Customized Image Inpainting with Text-Subject Guidance
Mar 28, 2024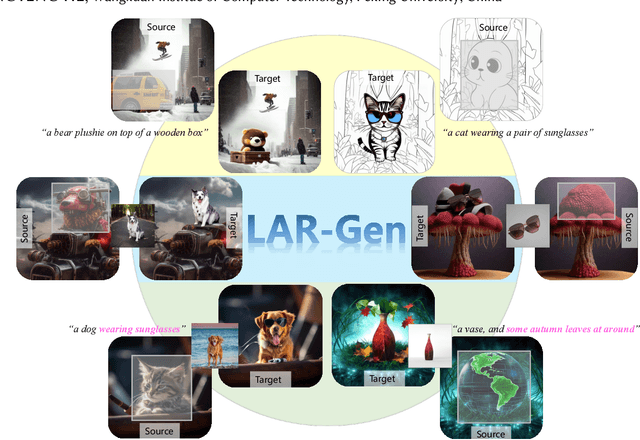
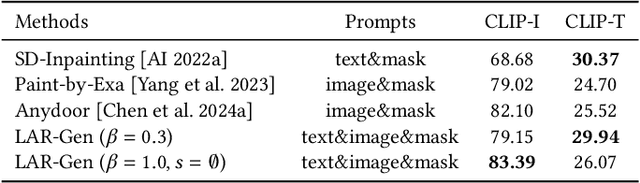
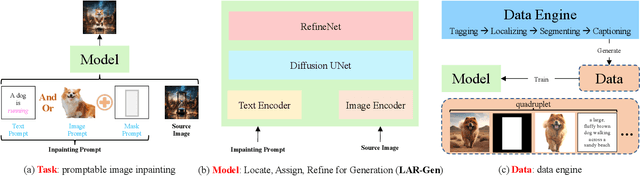
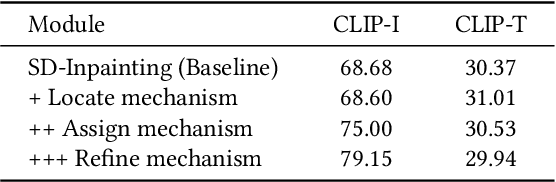
Abstract:Prior studies have made significant progress in image inpainting guided by either text or subject image. However, the research on editing with their combined guidance is still in the early stages. To tackle this challenge, we present LAR-Gen, a novel approach for image inpainting that enables seamless inpainting of masked scene images, incorporating both the textual prompts and specified subjects. Our approach adopts a coarse-to-fine manner to ensure subject identity preservation and local semantic coherence. The process involves (i) Locate: concatenating the noise with masked scene image to achieve precise regional editing, (ii) Assign: employing decoupled cross-attention mechanism to accommodate multi-modal guidance, and (iii) Refine: using a novel RefineNet to supplement subject details. Additionally, to address the issue of scarce training data, we introduce a novel data construction pipeline. This pipeline extracts substantial pairs of data consisting of local text prompts and corresponding visual instances from a vast image dataset, leveraging publicly available large models. Extensive experiments and varied application scenarios demonstrate the superiority of LAR-Gen in terms of both identity preservation and text semantic consistency. Project page can be found at \url{https://ali-vilab.github.io/largen-page/}.
Res-Attn : An Enhanced Res-Tuning Approach with Lightweight Attention Mechanism
Dec 28, 2023Abstract:Res-Tuning introduces a flexible and efficient paradigm for model tuning, showing that tuners decoupled from the backbone network can achieve performance comparable to traditional methods. Existing methods commonly construct the tuner as a set of trainable low-rank decomposition matrices, positing that a low-rank subspace suffices for adapting pre-trained foundational models to new scenarios. In this work, we present an advanced, efficient tuner augmented with low-rank attention, termed Res-Attn , which also adheres to the Res-Tuning framework. Res-Attn utilizes a parallel multi-head attention module equipped with low-rank projections for query, key, and value to execute streamlined attention operations. Through training this lightweight attention module, Res-Attn facilitates adaptation to new scenarios. Our extensive experiments across a range of discriminative and generative tasks showcase the superior performance of our method when compared to existing alternatives
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge