Xiangteng He
ICE-Bench: A Unified and Comprehensive Benchmark for Image Creating and Editing
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Image generation has witnessed significant advancements in the past few years. However, evaluating the performance of image generation models remains a formidable challenge. In this paper, we propose ICE-Bench, a unified and comprehensive benchmark designed to rigorously assess image generation models. Its comprehensiveness could be summarized in the following key features: (1) Coarse-to-Fine Tasks: We systematically deconstruct image generation into four task categories: No-ref/Ref Image Creating/Editing, based on the presence or absence of source images and reference images. And further decompose them into 31 fine-grained tasks covering a broad spectrum of image generation requirements, culminating in a comprehensive benchmark. (2) Multi-dimensional Metrics: The evaluation framework assesses image generation capabilities across 6 dimensions: aesthetic quality, imaging quality, prompt following, source consistency, reference consistency, and controllability. 11 metrics are introduced to support the multi-dimensional evaluation. Notably, we introduce VLLM-QA, an innovative metric designed to assess the success of image editing by leveraging large models. (3) Hybrid Data: The data comes from real scenes and virtual generation, which effectively improves data diversity and alleviates the bias problem in model evaluation. Through ICE-Bench, we conduct a thorough analysis of existing generation models, revealing both the challenging nature of our benchmark and the gap between current model capabilities and real-world generation requirements. To foster further advancements in the field, we will open-source ICE-Bench, including its dataset, evaluation code, and models, thereby providing a valuable resource for the research community.
Firzen: Firing Strict Cold-Start Items with Frozen Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Graphs for Recommendation
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Recommendation models utilizing unique identities (IDs) to represent distinct users and items have dominated the recommender systems literature for over a decade. Since multi-modal content of items (e.g., texts and images) and knowledge graphs (KGs) may reflect the interaction-related users' preferences and items' characteristics, they have been utilized as useful side information to further improve the recommendation quality. However, the success of such methods often limits to either warm-start or strict cold-start item recommendation in which some items neither appear in the training data nor have any interactions in the test stage: (1) Some fail to learn the embedding of a strict cold-start item since side information is only utilized to enhance the warm-start ID representations; (2) The others deteriorate the performance of warm-start recommendation since unrelated multi-modal content or entities in KGs may blur the final representations. In this paper, we propose a unified framework incorporating multi-modal content of items and KGs to effectively solve both strict cold-start and warm-start recommendation termed Firzen, which extracts the user-item collaborative information over frozen heterogeneous graph (collaborative knowledge graph), and exploits the item-item semantic structures and user-user behavioral association over frozen homogeneous graphs (item-item relation graph and user-user co-occurrence graph). Furthermore, we build four unified strict cold-start evaluation benchmarks based on publicly available Amazon datasets and a real-world industrial dataset from Weixin Channels via rearranging the interaction data and constructing KGs. Extensive empirical results demonstrate that our model yields significant improvements for strict cold-start recommendation and outperforms or matches the state-of-the-art performance in the warm-start scenario.
Towards Video Anomaly Retrieval from Video Anomaly Detection: New Benchmarks and Model
Jul 24, 2023



Abstract:Video anomaly detection (VAD) has been paid increasing attention due to its potential applications, its current dominant tasks focus on online detecting anomalies% at the frame level, which can be roughly interpreted as the binary or multiple event classification. However, such a setup that builds relationships between complicated anomalous events and single labels, e.g., ``vandalism'', is superficial, since single labels are deficient to characterize anomalous events. In reality, users tend to search a specific video rather than a series of approximate videos. Therefore, retrieving anomalous events using detailed descriptions is practical and positive but few researches focus on this. In this context, we propose a novel task called Video Anomaly Retrieval (VAR), which aims to pragmatically retrieve relevant anomalous videos by cross-modalities, e.g., language descriptions and synchronous audios. Unlike the current video retrieval where videos are assumed to be temporally well-trimmed with short duration, VAR is devised to retrieve long untrimmed videos which may be partially relevant to the given query. To achieve this, we present two large-scale VAR benchmarks, UCFCrime-AR and XDViolence-AR, constructed on top of prevalent anomaly datasets. Meanwhile, we design a model called Anomaly-Led Alignment Network (ALAN) for VAR. In ALAN, we propose an anomaly-led sampling to focus on key segments in long untrimmed videos. Then, we introduce an efficient pretext task to enhance semantic associations between video-text fine-grained representations. Besides, we leverage two complementary alignments to further match cross-modal contents. Experimental results on two benchmarks reveal the challenges of VAR task and also demonstrate the advantages of our tailored method.
PosterLayout: A New Benchmark and Approach for Content-aware Visual-Textual Presentation Layout
Mar 28, 2023



Abstract:Content-aware visual-textual presentation layout aims at arranging spatial space on the given canvas for pre-defined elements, including text, logo, and underlay, which is a key to automatic template-free creative graphic design. In practical applications, e.g., poster designs, the canvas is originally non-empty, and both inter-element relationships as well as inter-layer relationships should be concerned when generating a proper layout. A few recent works deal with them simultaneously, but they still suffer from poor graphic performance, such as a lack of layout variety or spatial non-alignment. Since content-aware visual-textual presentation layout is a novel task, we first construct a new dataset named PosterLayout, which consists of 9,974 poster-layout pairs and 905 images, i.e., non-empty canvases. It is more challenging and useful for greater layout variety, domain diversity, and content diversity. Then, we propose design sequence formation (DSF) that reorganizes elements in layouts to imitate the design processes of human designers, and a novel CNN-LSTM-based conditional generative adversarial network (GAN) is presented to generate proper layouts. Specifically, the discriminator is design-sequence-aware and will supervise the "design" process of the generator. Experimental results verify the usefulness of the new benchmark and the effectiveness of the proposed approach, which achieves the best performance by generating suitable layouts for diverse canvases.
Scanning Only Once: An End-to-end Framework for Fast Temporal Grounding in Long Videos
Mar 22, 2023



Abstract:Video temporal grounding aims to pinpoint a video segment that matches the query description. Despite the recent advance in short-form videos (\textit{e.g.}, in minutes), temporal grounding in long videos (\textit{e.g.}, in hours) is still at its early stage. To address this challenge, a common practice is to employ a sliding window, yet can be inefficient and inflexible due to the limited number of frames within the window. In this work, we propose an end-to-end framework for fast temporal grounding, which is able to model an hours-long video with \textbf{one-time} network execution. Our pipeline is formulated in a coarse-to-fine manner, where we first extract context knowledge from non-overlapped video clips (\textit{i.e.}, anchors), and then supplement the anchors that highly response to the query with detailed content knowledge. Besides the remarkably high pipeline efficiency, another advantage of our approach is the capability of capturing long-range temporal correlation, thanks to modeling the entire video as a whole, and hence facilitates more accurate grounding. Experimental results suggest that, on the long-form video datasets MAD and Ego4d, our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-arts, and achieves \textbf{14.6$\times$} / \textbf{102.8$\times$} higher efficiency respectively. Project can be found at \url{https://github.com/afcedf/SOONet.git}.
Enhancing Unsupervised Audio Representation Learning via Adversarial Sample Generation
Mar 15, 2023Abstract:Existing audio analysis methods generally first transform the audio stream to spectrogram, and then feed it into CNN for further analysis. A standard CNN recognizes specific visual patterns over feature map, then pools for high-level representation, which overlooks the positional information of recognized patterns. However, unlike natural image, the semantic of an audio spectrogram is sensitive to positional change, as its vertical and horizontal axes indicate the frequency and temporal information of the audio, instead of naive rectangular coordinates. Thus, the insensitivity of CNN to positional change plays a negative role on audio spectrogram encoding. To address this issue, this paper proposes a new self-supervised learning mechanism, which enhances the audio representation by first generating adversarial samples (\textit{i.e.}, negative samples), then driving CNN to distinguish the embeddings of negative pairs in the latent space. Extensive experiments show that the proposed approach achieves best or competitive results on 9 downstream datasets compared with previous methods, which verifies its effectiveness on audio representation learning.
SIM-Trans: Structure Information Modeling Transformer for Fine-grained Visual Categorization
Aug 31, 2022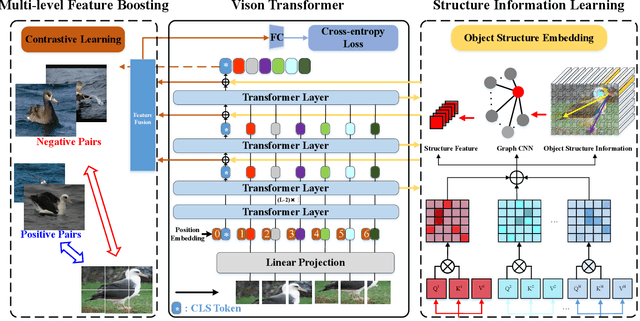

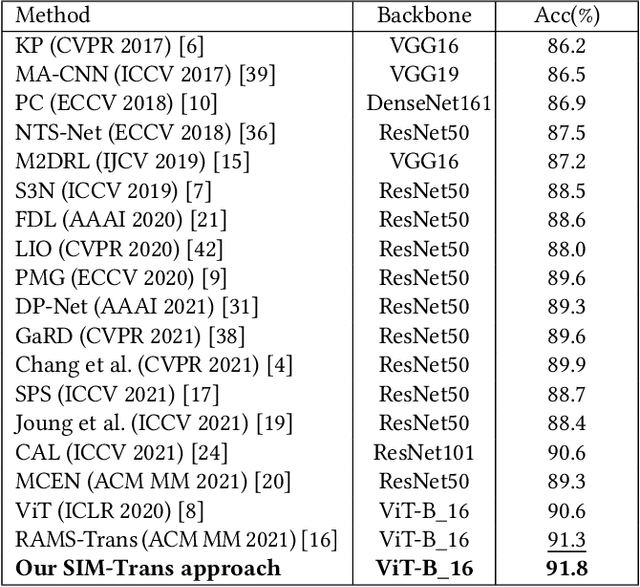
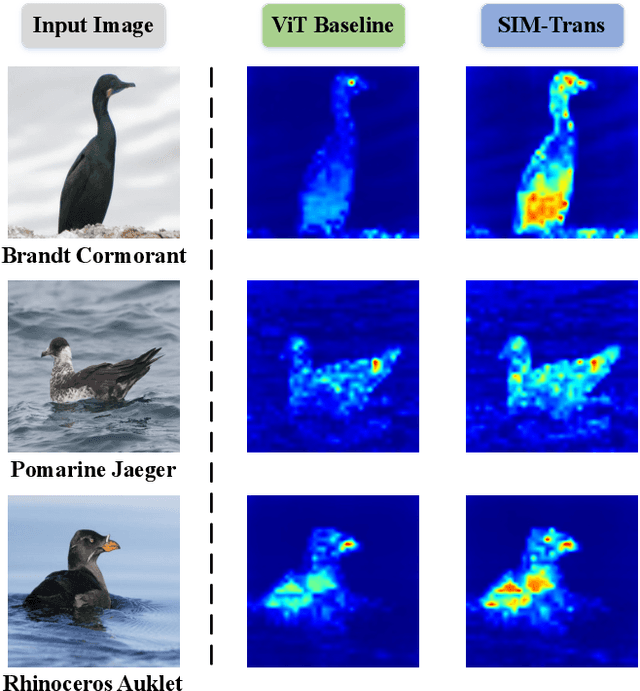
Abstract:Fine-grained visual categorization (FGVC) aims at recognizing objects from similar subordinate categories, which is challenging and practical for human's accurate automatic recognition needs. Most FGVC approaches focus on the attention mechanism research for discriminative regions mining while neglecting their interdependencies and composed holistic object structure, which are essential for model's discriminative information localization and understanding ability. To address the above limitations, we propose the Structure Information Modeling Transformer (SIM-Trans) to incorporate object structure information into transformer for enhancing discriminative representation learning to contain both the appearance information and structure information. Specifically, we encode the image into a sequence of patch tokens and build a strong vision transformer framework with two well-designed modules: (i) the structure information learning (SIL) module is proposed to mine the spatial context relation of significant patches within the object extent with the help of the transformer's self-attention weights, which is further injected into the model for importing structure information; (ii) the multi-level feature boosting (MFB) module is introduced to exploit the complementary of multi-level features and contrastive learning among classes to enhance feature robustness for accurate recognition. The proposed two modules are light-weighted and can be plugged into any transformer network and trained end-to-end easily, which only depends on the attention weights that come with the vision transformer itself. Extensive experiments and analyses demonstrate that the proposed SIM-Trans achieves state-of-the-art performance on fine-grained visual categorization benchmarks. The code is available at https://github.com/PKU-ICST-MIPL/SIM-Trans_ACMMM2022.
Video Similarity and Alignment Learning on Partial Video Copy Detection
Aug 04, 2021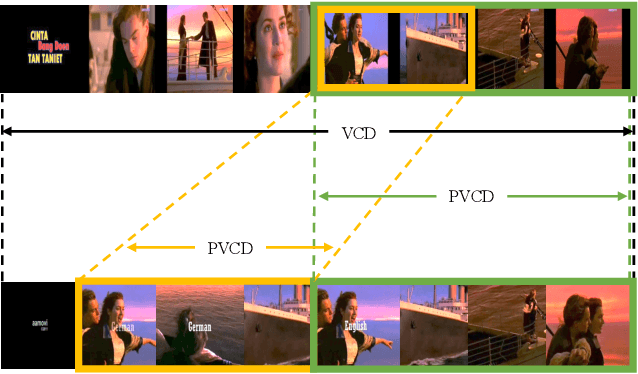



Abstract:Existing video copy detection methods generally measure video similarity based on spatial similarities between key frames, neglecting the latent similarity in temporal dimension, so that the video similarity is biased towards spatial information. There are methods modeling unified video similarity in an end-to-end way, but losing detailed partial alignment information, which causes the incapability of copy segments localization. To address the above issues, we propose the Video Similarity and Alignment Learning (VSAL) approach, which jointly models spatial similarity, temporal similarity and partial alignment. To mitigate the spatial similarity bias, we model the temporal similarity as the mask map predicted from frame-level spatial similarity, where each element indicates the probability of frame pair lying right on the partial alignments. To further localize partial copies, the step map is learned from the spatial similarity where the elements indicate extending directions of the current partial alignments on the spatial-temporal similarity map. Obtained from the mask map, the start points extend out into partial optimal alignments following instructions of the step map. With the similarity and alignment learning strategy, VSAL achieves the state-of-the-art F1-score on VCDB core dataset. Furthermore, we construct a new benchmark of partial video copy detection and localization by adding new segment-level annotations for FIVR-200k dataset, where VSAL also achieves the best performance, verifying its effectiveness in more challenging situations. Our project is publicly available at https://pvcd-vsal.github.io/vsal/.
HANet: Hierarchical Alignment Networks for Video-Text Retrieval
Jul 30, 2021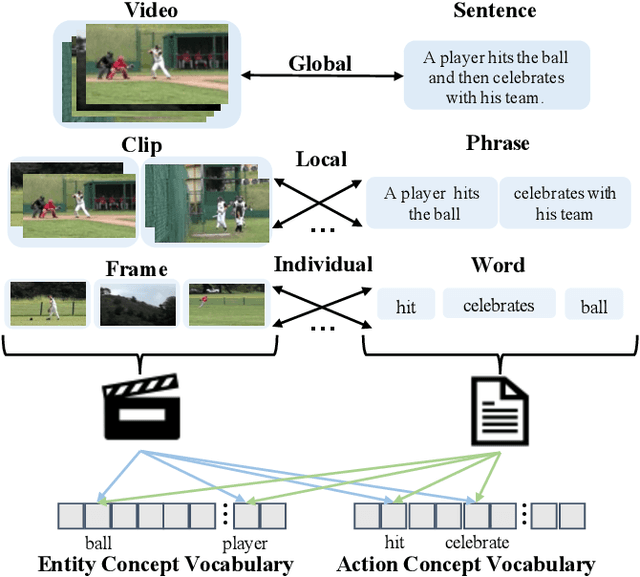
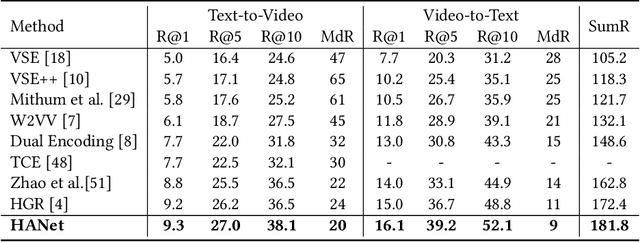
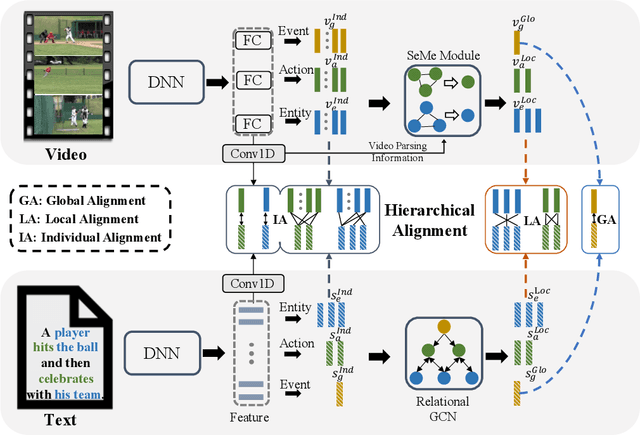

Abstract:Video-text retrieval is an important yet challenging task in vision-language understanding, which aims to learn a joint embedding space where related video and text instances are close to each other. Most current works simply measure the video-text similarity based on video-level and text-level embeddings. However, the neglect of more fine-grained or local information causes the problem of insufficient representation. Some works exploit the local details by disentangling sentences, but overlook the corresponding videos, causing the asymmetry of video-text representation. To address the above limitations, we propose a Hierarchical Alignment Network (HANet) to align different level representations for video-text matching. Specifically, we first decompose video and text into three semantic levels, namely event (video and text), action (motion and verb), and entity (appearance and noun). Based on these, we naturally construct hierarchical representations in the individual-local-global manner, where the individual level focuses on the alignment between frame and word, local level focuses on the alignment between video clip and textual context, and global level focuses on the alignment between the whole video and text. Different level alignments capture fine-to-coarse correlations between video and text, as well as take the advantage of the complementary information among three semantic levels. Besides, our HANet is also richly interpretable by explicitly learning key semantic concepts. Extensive experiments on two public datasets, namely MSR-VTT and VATEX, show the proposed HANet outperforms other state-of-the-art methods, which demonstrates the effectiveness of hierarchical representation and alignment. Our code is publicly available.
Self-supervised Video Retrieval Transformer Network
Apr 16, 2021



Abstract:Content-based video retrieval aims to find videos from a large video database that are similar to or even near-duplicate of a given query video. Video representation and similarity search algorithms are crucial to any video retrieval system. To derive effective video representation, most video retrieval systems require a large amount of manually annotated data for training, making it costly inefficient. In addition, most retrieval systems are based on frame-level features for video similarity searching, making it expensive both storage wise and search wise. We propose a novel video retrieval system, termed SVRTN, that effectively addresses the above shortcomings. It first applies self-supervised training to effectively learn video representation from unlabeled data to avoid the expensive cost of manual annotation. Then, it exploits transformer structure to aggregate frame-level features into clip-level to reduce both storage space and search complexity. It can learn the complementary and discriminative information from the interactions among clip frames, as well as acquire the frame permutation and missing invariant ability to support more flexible retrieval manners. Comprehensive experiments on two challenging video retrieval datasets, namely FIVR-200K and SVD, verify the effectiveness of our proposed SVRTN method, which achieves the best performance of video retrieval on accuracy and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge