Keyu Yan
the Key Laboratory of Child Development and Learning Science of Ministry of Education, and the Department of Information Science and Engineering, Southeast University, China, the Key Laboratory of Child Development and Learning Science of Ministry of Education, Research Center for Learning Science, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
DenseGRPO: From Sparse to Dense Reward for Flow Matching Model Alignment
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Recent GRPO-based approaches built on flow matching models have shown remarkable improvements in human preference alignment for text-to-image generation. Nevertheless, they still suffer from the sparse reward problem: the terminal reward of the entire denoising trajectory is applied to all intermediate steps, resulting in a mismatch between the global feedback signals and the exact fine-grained contributions at intermediate denoising steps. To address this issue, we introduce \textbf{DenseGRPO}, a novel framework that aligns human preference with dense rewards, which evaluates the fine-grained contribution of each denoising step. Specifically, our approach includes two key components: (1) we propose to predict the step-wise reward gain as dense reward of each denoising step, which applies a reward model on the intermediate clean images via an ODE-based approach. This manner ensures an alignment between feedback signals and the contributions of individual steps, facilitating effective training; and (2) based on the estimated dense rewards, a mismatch drawback between the uniform exploration setting and the time-varying noise intensity in existing GRPO-based methods is revealed, leading to an inappropriate exploration space. Thus, we propose a reward-aware scheme to calibrate the exploration space by adaptively adjusting a timestep-specific stochasticity injection in the SDE sampler, ensuring a suitable exploration space at all timesteps. Extensive experiments on multiple standard benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed DenseGRPO and highlight the critical role of the valid dense rewards in flow matching model alignment.
Taming OOD Actions for Offline Reinforcement Learning: An Advantage-Based Approach
May 08, 2025Abstract:Offline reinforcement learning (RL) aims to learn decision-making policies from fixed datasets without online interactions, providing a practical solution where online data collection is expensive or risky. However, offline RL often suffers from distribution shift, resulting in inaccurate evaluation and substantial overestimation on out-of-distribution (OOD) actions. To address this, existing approaches incorporate conservatism by indiscriminately discouraging all OOD actions, thereby hindering the agent's ability to generalize and exploit beneficial ones. In this paper, we propose Advantage-based Diffusion Actor-Critic (ADAC), a novel method that systematically evaluates OOD actions using the batch-optimal value function. Based on this evaluation, ADAC defines an advantage function to modulate the Q-function update, enabling more precise assessment of OOD action quality. We design a custom PointMaze environment and collect datasets to visually reveal that advantage modulation can effectively identify and select superior OOD actions. Extensive experiments show that ADAC achieves state-of-the-art performance on almost all tasks in the D4RL benchmark, with particularly clear margins on the more challenging tasks.
VIPO: Value Function Inconsistency Penalized Offline Reinforcement Learning
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Offline reinforcement learning (RL) learns effective policies from pre-collected datasets, offering a practical solution for applications where online interactions are risky or costly. Model-based approaches are particularly advantageous for offline RL, owing to their data efficiency and generalizability. However, due to inherent model errors, model-based methods often artificially introduce conservatism guided by heuristic uncertainty estimation, which can be unreliable. In this paper, we introduce VIPO, a novel model-based offline RL algorithm that incorporates self-supervised feedback from value estimation to enhance model training. Specifically, the model is learned by additionally minimizing the inconsistency between the value learned directly from the offline data and the one estimated from the model. We perform comprehensive evaluations from multiple perspectives to show that VIPO can learn a highly accurate model efficiently and consistently outperform existing methods. It offers a general framework that can be readily integrated into existing model-based offline RL algorithms to systematically enhance model accuracy. As a result, VIPO achieves state-of-the-art performance on almost all tasks in both D4RL and NeoRL benchmarks.
Wan: Open and Advanced Large-Scale Video Generative Models
Mar 26, 2025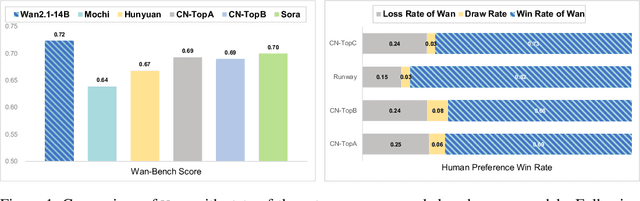



Abstract:This report presents Wan, a comprehensive and open suite of video foundation models designed to push the boundaries of video generation. Built upon the mainstream diffusion transformer paradigm, Wan achieves significant advancements in generative capabilities through a series of innovations, including our novel VAE, scalable pre-training strategies, large-scale data curation, and automated evaluation metrics. These contributions collectively enhance the model's performance and versatility. Specifically, Wan is characterized by four key features: Leading Performance: The 14B model of Wan, trained on a vast dataset comprising billions of images and videos, demonstrates the scaling laws of video generation with respect to both data and model size. It consistently outperforms the existing open-source models as well as state-of-the-art commercial solutions across multiple internal and external benchmarks, demonstrating a clear and significant performance superiority. Comprehensiveness: Wan offers two capable models, i.e., 1.3B and 14B parameters, for efficiency and effectiveness respectively. It also covers multiple downstream applications, including image-to-video, instruction-guided video editing, and personal video generation, encompassing up to eight tasks. Consumer-Grade Efficiency: The 1.3B model demonstrates exceptional resource efficiency, requiring only 8.19 GB VRAM, making it compatible with a wide range of consumer-grade GPUs. Openness: We open-source the entire series of Wan, including source code and all models, with the goal of fostering the growth of the video generation community. This openness seeks to significantly expand the creative possibilities of video production in the industry and provide academia with high-quality video foundation models. All the code and models are available at https://github.com/Wan-Video/Wan2.1.
Training-Free Large Model Priors for Multiple-in-One Image Restoration
Jul 18, 2024Abstract:Image restoration aims to reconstruct the latent clear images from their degraded versions. Despite the notable achievement, existing methods predominantly focus on handling specific degradation types and thus require specialized models, impeding real-world applications in dynamic degradation scenarios. To address this issue, we propose Large Model Driven Image Restoration framework (LMDIR), a novel multiple-in-one image restoration paradigm that leverages the generic priors from large multi-modal language models (MMLMs) and the pretrained diffusion models. In detail, LMDIR integrates three key prior knowledges: 1) global degradation knowledge from MMLMs, 2) scene-aware contextual descriptions generated by MMLMs, and 3) fine-grained high-quality reference images synthesized by diffusion models guided by MMLM descriptions. Standing on above priors, our architecture comprises a query-based prompt encoder, degradation-aware transformer block injecting global degradation knowledge, content-aware transformer block incorporating scene description, and reference-based transformer block incorporating fine-grained image priors. This design facilitates single-stage training paradigm to address various degradations while supporting both automatic and user-guided restoration. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our designed method outperforms state-of-the-art competitors on multiple evaluation benchmarks.
BACON: Supercharge Your VLM with Bag-of-Concept Graph to Mitigate Hallucinations
Jul 03, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents Bag-of-Concept Graph (BACON) to gift models with limited linguistic abilities to taste the privilege of Vision Language Models (VLMs) and boost downstream tasks such as detection, visual question answering (VQA), and image generation. Since the visual scenes in physical worlds are structured with complex relations between objects, BACON breaks down annotations into basic minimum elements and presents them in a graph structure. Element-wise style enables easy understanding, and structural composition liberates difficult locating. Careful prompt design births the BACON captions with the help of public-available VLMs and segmentation methods. In this way, we gather a dataset with 100K annotated images, which endow VLMs with remarkable capabilities, such as accurately generating BACON, transforming prompts into BACON format, envisioning scenarios in the style of BACONr, and dynamically modifying elements within BACON through interactive dialogue and more. Wide representative experiments, including detection, VQA, and image generation tasks, tell BACON as a lifeline to achieve previous out-of-reach tasks or excel in their current cutting-edge solutions.
ID-Animator: Zero-Shot Identity-Preserving Human Video Generation
Apr 23, 2024



Abstract:Generating high fidelity human video with specified identities has attracted significant attention in the content generation community. However, existing techniques struggle to strike a balance between training efficiency and identity preservation, either requiring tedious case-by-case finetuning or usually missing the identity details in video generation process. In this study, we present ID-Animator, a zero-shot human-video generation approach that can perform personalized video generation given single reference facial image without further training. ID-Animator inherits existing diffusion-based video generation backbones with a face adapter to encode the ID-relevant embeddings from learnable facial latent queries. To facilitate the extraction of identity information in video generation, we introduce an ID-oriented dataset construction pipeline, which incorporates decoupled human attribute and action captioning technique from a constructed facial image pool. Based on this pipeline, a random face reference training method is further devised to precisely capture the ID-relevant embeddings from reference images, thus improving the fidelity and generalization capacity of our model for ID-specific video generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of ID-Animator to generate personalized human videos over previous models. Moreover, our method is highly compatible with popular pre-trained T2V models like animatediff and various community backbone models, showing high extendability in real-world applications for video generation where identity preservation is highly desired. Our codes and checkpoints will be released at https://github.com/ID-Animator/ID-Animator.
Pan-Mamba: Effective pan-sharpening with State Space Model
Feb 19, 2024



Abstract:Pan-sharpening involves integrating information from lowresolution multi-spectral and high-resolution panchromatic images to generate high-resolution multi-spectral counterparts. While recent advancements in the state space model, particularly the efficient long-range dependency modeling achieved by Mamba, have revolutionized computer vision community, its untapped potential in pan-sharpening motivates our exploration. Our contribution, Pan-Mamba, represents a novel pansharpening network that leverages the efficiency of the Mamba model in global information modeling. In Pan-Mamba, we customize two core components: channel swapping Mamba and cross-modal Mamba, strategically designed for efficient cross-modal information exchange and fusion. The former initiates a lightweight cross-modal interaction through the exchange of partial panchromatic and multispectral channels, while the latter facilities the information representation capability by exploiting inherent cross-modal relationships. Through extensive experiments across diverse datasets, our proposed approach surpasses state-of-theart methods, showcasing superior fusion results in pan-sharpening. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first attempt in exploring the potential of the Mamba model and establishes a new frontier in the pan-sharpening techniques. The source code is available at https://github.com/alexhe101/Pan-Mamba .
Enhancing RAW-to-sRGB with Decoupled Style Structure in Fourier Domain
Jan 04, 2024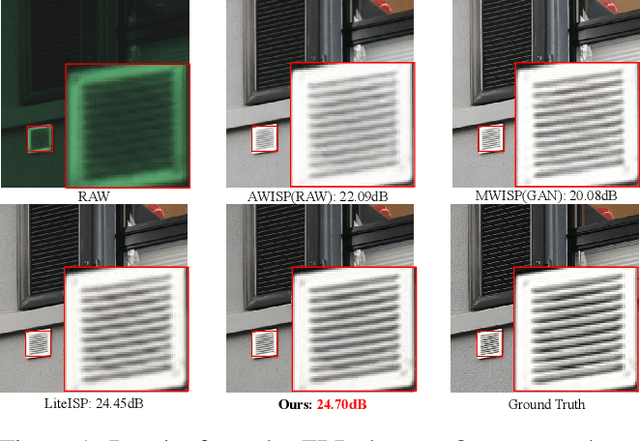
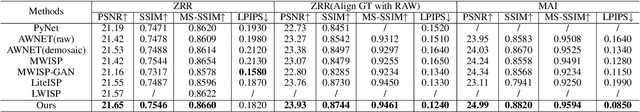
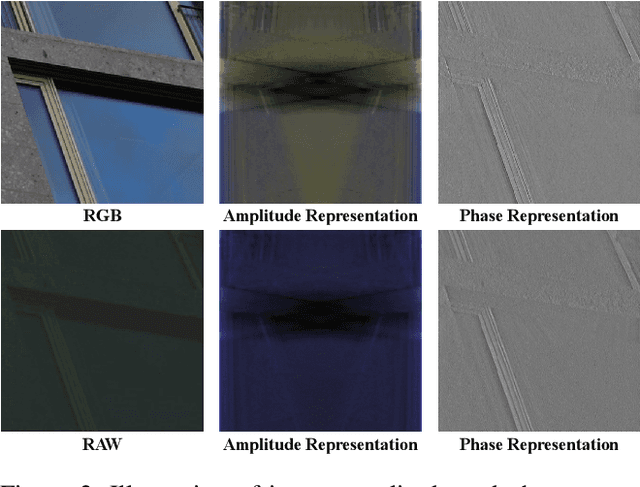
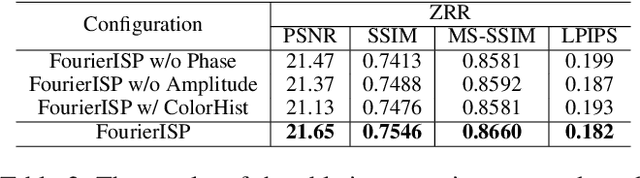
Abstract:RAW to sRGB mapping, which aims to convert RAW images from smartphones into RGB form equivalent to that of Digital Single-Lens Reflex (DSLR) cameras, has become an important area of research. However, current methods often ignore the difference between cell phone RAW images and DSLR camera RGB images, a difference that goes beyond the color matrix and extends to spatial structure due to resolution variations. Recent methods directly rebuild color mapping and spatial structure via shared deep representation, limiting optimal performance. Inspired by Image Signal Processing (ISP) pipeline, which distinguishes image restoration and enhancement, we present a novel Neural ISP framework, named FourierISP. This approach breaks the image down into style and structure within the frequency domain, allowing for independent optimization. FourierISP is comprised of three subnetworks: Phase Enhance Subnet for structural refinement, Amplitude Refine Subnet for color learning, and Color Adaptation Subnet for blending them in a smooth manner. This approach sharpens both color and structure, and extensive evaluations across varied datasets confirm that our approach realizes state-of-the-art results. Code will be available at ~\url{https://github.com/alexhe101/FourierISP}.
Frequency-Adaptive Pan-Sharpening with Mixture of Experts
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Pan-sharpening involves reconstructing missing high-frequency information in multi-spectral images with low spatial resolution, using a higher-resolution panchromatic image as guidance. Although the inborn connection with frequency domain, existing pan-sharpening research has not almost investigated the potential solution upon frequency domain. To this end, we propose a novel Frequency Adaptive Mixture of Experts (FAME) learning framework for pan-sharpening, which consists of three key components: the Adaptive Frequency Separation Prediction Module, the Sub-Frequency Learning Expert Module, and the Expert Mixture Module. In detail, the first leverages the discrete cosine transform to perform frequency separation by predicting the frequency mask. On the basis of generated mask, the second with low-frequency MOE and high-frequency MOE takes account for enabling the effective low-frequency and high-frequency information reconstruction. Followed by, the final fusion module dynamically weights high-frequency and low-frequency MOE knowledge to adapt to remote sensing images with significant content variations. Quantitative and qualitative experiments over multiple datasets demonstrate that our method performs the best against other state-of-the-art ones and comprises a strong generalization ability for real-world scenes. Code will be made publicly at \url{https://github.com/alexhe101/FAME-Net}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge