Wenqi Ren
ODAR: Principled Adaptive Routing for LLM Reasoning via Active Inference
Feb 27, 2026Abstract:The paradigm of large language model (LLM) reasoning is shifting from parameter scaling to test-time compute scaling, yet many existing approaches still rely on uniform brute-force sampling (for example, fixed best-of-N or self-consistency) that is costly, hard to attribute, and can trigger overthinking with diminishing returns. We propose ODAR-Expert, an adaptive routing framework that optimizes the accuracy-efficiency trade-off via principled resource allocation. ODAR uses a difficulty estimator grounded in amortized active inference to dynamically route queries between a heuristic Fast Agent and a deliberative Slow Agent. We further introduce a free-energy-principled, risk-sensitive fusion mechanism that selects answers by minimizing a variational free energy objective, balancing log-likelihood with epistemic uncertainty (varentropy) as a principled alternative to ad hoc voting over heterogeneous candidates. Extensive evaluation across 23 benchmarks shows strong and consistent gains, including 98.2% accuracy on MATH and 54.8% on Humanity's Last Exam (HLE), while improving the compute-accuracy frontier under compute-matched settings. We also validate reproducibility on a fully open-source stack (Llama 4 + DeepSeek), where ODAR surpasses homogeneous sampling strategies while reducing computational costs by 82%. Overall, our results suggest that thinking-optimal scaling requires adaptive resource allocation with free-energy-based decision-making rather than simply increasing test-time compute.
SkillJect: Automating Stealthy Skill-Based Prompt Injection for Coding Agents with Trace-Driven Closed-Loop Refinement
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:Agent skills are becoming a core abstraction in coding agents, packaging long-form instructions and auxiliary scripts to extend tool-augmented behaviors. This abstraction introduces an under-measured attack surface: skill-based prompt injection, where poisoned skills can steer agents away from user intent and safety policies. In practice, naive injections often fail because the malicious intent is too explicit or drifts too far from the original skill, leading agents to ignore or refuse them; existing attacks are also largely hand-crafted. We propose the first automated framework for stealthy prompt injection tailored to agent skills. The framework forms a closed loop with three agents: an Attack Agent that synthesizes injection skills under explicit stealth constraints, a Code Agent that executes tasks using the injected skills in a realistic tool environment, and an Evaluate Agent that logs action traces (e.g., tool calls and file operations) and verifies whether targeted malicious behaviors occurred. We also propose a malicious payload hiding strategy that conceals adversarial operations in auxiliary scripts while injecting optimized inducement prompts to trigger tool execution. Extensive experiments across diverse coding-agent settings and real-world software engineering tasks show that our method consistently achieves high attack success rates under realistic settings.
Reason-IAD: Knowledge-Guided Dynamic Latent Reasoning for Explainable Industrial Anomaly Detection
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:Industrial anomaly detection demands precise reasoning over fine-grained defect patterns. However, existing multimodal large language models (MLLMs), pretrained on general-domain data, often struggle to capture category-specific anomalies, thereby limiting both detection accuracy and interpretability. To address these limitations, we propose Reason-IAD, a knowledge-guided dynamic latent reasoning framework for explainable industrial anomaly detection. Reason-IAD comprises two core components. First, a retrieval-augmented knowledge module incorporates category-specific textual descriptions into the model input, enabling context-aware reasoning over domain-specific defects. Second, an entropy-driven latent reasoning mechanism conducts iterative exploration within a compact latent space using optimizable latent think tokens, guided by an entropy-based reward that encourages confident and stable predictions. Furthermore, a dynamic visual injection strategy selectively incorporates the most informative image patches into the latent sequence, directing the reasoning process toward regions critical for anomaly detection. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that Reason-IAD consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods. The code will be publicly available at https://github.com/chenpeng052/Reason-IAD.
Advances and Innovations in the Multi-Agent Robotic System (MARS) Challenge
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in multimodal large language models and vision-languageaction models have significantly driven progress in Embodied AI. As the field transitions toward more complex task scenarios, multi-agent system frameworks are becoming essential for achieving scalable, efficient, and collaborative solutions. This shift is fueled by three primary factors: increasing agent capabilities, enhancing system efficiency through task delegation, and enabling advanced human-agent interactions. To address the challenges posed by multi-agent collaboration, we propose the Multi-Agent Robotic System (MARS) Challenge, held at the NeurIPS 2025 Workshop on SpaVLE. The competition focuses on two critical areas: planning and control, where participants explore multi-agent embodied planning using vision-language models (VLMs) to coordinate tasks and policy execution to perform robotic manipulation in dynamic environments. By evaluating solutions submitted by participants, the challenge provides valuable insights into the design and coordination of embodied multi-agent systems, contributing to the future development of advanced collaborative AI systems.
Advancing Adaptive Multi-Stage Video Anomaly Reasoning: A Benchmark Dataset and Method
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Recent progress in reasoning capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models(MLLMs) has highlighted their potential for performing complex video understanding tasks. However, in the domain of Video Anomaly Detection and Understanding (VAD&U), existing MLLM-based methods are largely limited to anomaly localization or post-hoc description, lacking explicit reasoning processes, risk awareness, and decision-oriented interpretation. To address this gap, we define a new task termed Video Anomaly Reasoning (VAR), which elevates video anomaly analysis from descriptive understanding to structured, multi-stage reasoning. VAR explicitly requires models to perform progressive reasoning over anomalous events before answering anomaly-related questions, encompassing visual perception, causal interpretation, and risk-aware decision making. To support this task, we present a new dataset with 8,641 videos, where each video is annotated with diverse question types corresponding to different reasoning depths, totaling more than 50,000 samples, making it one of the largest datasets for video anomaly. The annotations are based on a structured Perception-Cognition-Action Chain-of-Thought (PerCoAct-CoT), which formalizes domain-specific reasoning priors for video anomaly understanding. This design enables systematic evaluation of multi-stage and adaptive anomaly reasoning. In addition, we propose Anomaly-Aware Group Relative Policy Optimization to further enhance reasoning reliability under weak supervision. Building upon the proposed task and dataset, we develop an end-to-end MLLM-based VAR model termed Vad-R1-Plus, which supports adaptive hierarchical reasoning and risk-aware decision making. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed benchmark and method effectively advance the reasoning capabilities of MLLMs on VAR tasks, outperforming both open-source and proprietary baselines.
In defense of the two-stage framework for open-set domain adaptive semantic segmentation
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Open-Set Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation (OSDA-SS) presents a significant challenge, as it requires both domain adaptation for known classes and the distinction of unknowns. Existing methods attempt to address both tasks within a single unified stage. We question this design, as the annotation imbalance between known and unknown classes often leads to negative transfer of known classes and underfitting for unknowns. To overcome these issues, we propose SATS, a Separating-then-Adapting Training Strategy, which addresses OSDA-SS through two sequential steps: known/unknown separation and unknown-aware domain adaptation. By providing the model with more accurate and well-aligned unknown classes, our method ensures a balanced learning of discriminative features for both known and unknown classes, steering the model toward discovering truly unknown objects. Additionally, we present hard unknown exploration, an innovative data augmentation method that exposes the model to more challenging unknowns, strengthening its ability to capture more comprehensive understanding of target unknowns. We evaluate our method on public OSDA-SS benchmarks. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves a substantial advancement, with a +3.85% H-Score improvement for GTA5-to-Cityscapes and +18.64% for SYNTHIA-to-Cityscapes, outperforming previous state-of-the-art methods.
UAGLNet: Uncertainty-Aggregated Global-Local Fusion Network with Cooperative CNN-Transformer for Building Extraction
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Building extraction from remote sensing images is a challenging task due to the complex structure variations of the buildings. Existing methods employ convolutional or self-attention blocks to capture the multi-scale features in the segmentation models, while the inherent gap of the feature pyramids and insufficient global-local feature integration leads to inaccurate, ambiguous extraction results. To address this issue, in this paper, we present an Uncertainty-Aggregated Global-Local Fusion Network (UAGLNet), which is capable to exploit high-quality global-local visual semantics under the guidance of uncertainty modeling. Specifically, we propose a novel cooperative encoder, which adopts hybrid CNN and transformer layers at different stages to capture the local and global visual semantics, respectively. An intermediate cooperative interaction block (CIB) is designed to narrow the gap between the local and global features when the network becomes deeper. Afterwards, we propose a Global-Local Fusion (GLF) module to complementarily fuse the global and local representations. Moreover, to mitigate the segmentation ambiguity in uncertain regions, we propose an Uncertainty-Aggregated Decoder (UAD) to explicitly estimate the pixel-wise uncertainty to enhance the segmentation accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance to other state-of-the-art methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/Dstate/UAGLNet
SFP: Real-World Scene Recovery Using Spatial and Frequency Priors
Dec 09, 2025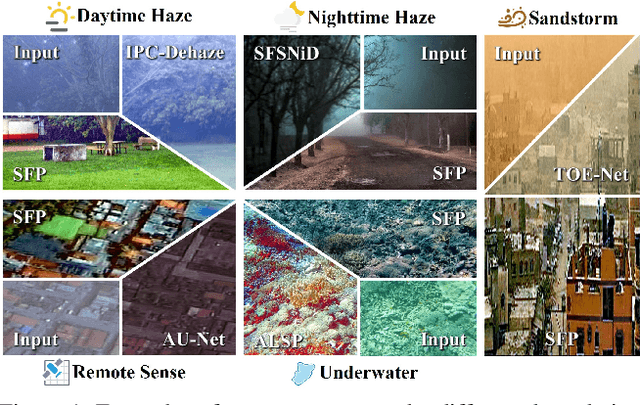
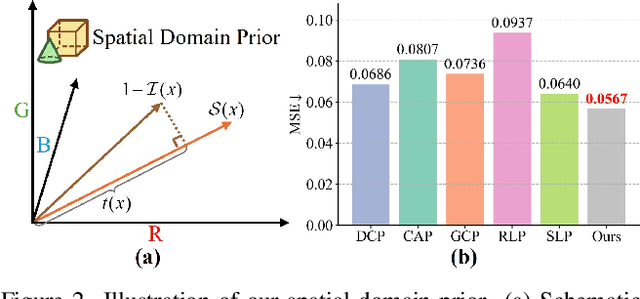
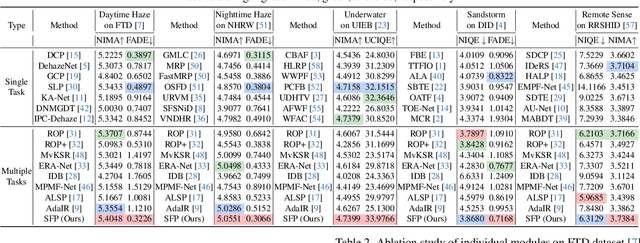
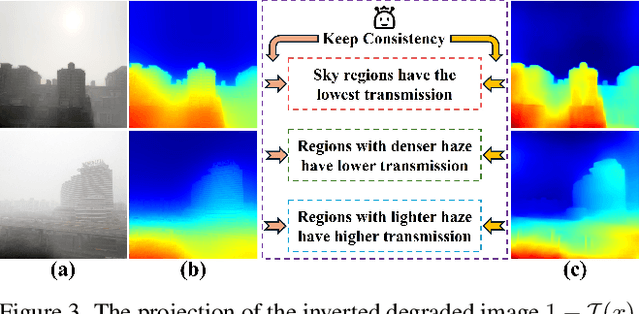
Abstract:Scene recovery serves as a critical task for various computer vision applications. Existing methods typically rely on a single prior, which is inherently insufficient to handle multiple degradations, or employ complex network architectures trained on synthetic data, which suffer from poor generalization for diverse real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose Spatial and Frequency Priors (SFP) for real-world scene recovery. In the spatial domain, we observe that the inverse of the degraded image exhibits a projection along its spectral direction that resembles the scene transmission. Leveraging this spatial prior, the transmission map is estimated to recover the scene from scattering degradation. In the frequency domain, a mask is constructed for adaptive frequency enhancement, with two parameters estimated using our proposed novel priors. Specifically, one prior assumes that the mean intensity of the degraded image's direct current (DC) components across three channels in the frequency domain closely approximates that of each channel in the clear image. The second prior is based on the observation that, for clear images, the magnitude of low radial frequencies below 0.001 constitutes approximately 1% of the total spectrum. Finally, we design a weighted fusion strategy to integrate spatial-domain restoration, frequency-domain enhancement, and salient features from the input image, yielding the final recovered result. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed SFP for scene recovery under various degradation conditions.
4KDehazeFlow: Ultra-High-Definition Image Dehazing via Flow Matching
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Ultra-High-Definition (UHD) image dehazing faces challenges such as limited scene adaptability in prior-based methods and high computational complexity with color distortion in deep learning approaches. To address these issues, we propose 4KDehazeFlow, a novel method based on Flow Matching and the Haze-Aware vector field. This method models the dehazing process as a progressive optimization of continuous vector field flow, providing efficient data-driven adaptive nonlinear color transformation for high-quality dehazing. Specifically, our method has the following advantages: 1) 4KDehazeFlow is a general method compatible with various deep learning networks, without relying on any specific network architecture. 2) We propose a learnable 3D lookup table (LUT) that encodes haze transformation parameters into a compact 3D mapping matrix, enabling efficient inference through precomputed mappings. 3) We utilize a fourth-order Runge-Kutta (RK4) ordinary differential equation (ODE) solver to stably solve the dehazing flow field through an accurate step-by-step iterative method, effectively suppressing artifacts. Extensive experiments show that 4KDehazeFlow exceeds seven state-of-the-art methods. It delivers a 2dB PSNR increase and better performance in dense haze and color fidelity.
DidSee: Diffusion-Based Depth Completion for Material-Agnostic Robotic Perception and Manipulation
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:Commercial RGB-D cameras often produce noisy, incomplete depth maps for non-Lambertian objects. Traditional depth completion methods struggle to generalize due to the limited diversity and scale of training data. Recent advances exploit visual priors from pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models to enhance generalization in dense prediction tasks. However, we find that biases arising from training-inference mismatches in the vanilla diffusion framework significantly impair depth completion performance. Additionally, the lack of distinct visual features in non-Lambertian regions further hinders precise prediction. To address these issues, we propose \textbf{DidSee}, a diffusion-based framework for depth completion on non-Lambertian objects. First, we integrate a rescaled noise scheduler enforcing a zero terminal signal-to-noise ratio to eliminate signal leakage bias. Second, we devise a noise-agnostic single-step training formulation to alleviate error accumulation caused by exposure bias and optimize the model with a task-specific loss. Finally, we incorporate a semantic enhancer that enables joint depth completion and semantic segmentation, distinguishing objects from backgrounds and yielding precise, fine-grained depth maps. DidSee achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks, demonstrates robust real-world generalization, and effectively improves downstream tasks such as category-level pose estimation and robotic grasping.Project page: https://wenzhoulyu.github.io/DidSee/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge