Linlin Shen
Vision KAN: Towards an Attention-Free Backbone for Vision with Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Attention mechanisms have become a key module in modern vision backbones due to their ability to model long-range dependencies. However, their quadratic complexity in sequence length and the difficulty of interpreting attention weights limit both scalability and clarity. Recent attention-free architectures demonstrate that strong performance can be achieved without pairwise attention, motivating the search for alternatives. In this work, we introduce Vision KAN (ViK), an attention-free backbone inspired by the Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks. At its core lies MultiPatch-RBFKAN, a unified token mixer that combines (a) patch-wise nonlinear transform with Radial Basis Function-based KANs, (b) axis-wise separable mixing for efficient local propagation, and (c) low-rank global mapping for long-range interaction. Employing as a drop-in replacement for attention modules, this formulation tackles the prohibitive cost of full KANs on high-resolution features by adopting a patch-wise grouping strategy with lightweight operators to restore cross-patch dependencies. Experiments on ImageNet-1K show that ViK achieves competitive accuracy with linear complexity, demonstrating the potential of KAN-based token mixing as an efficient and theoretically grounded alternative to attention.
YOLO-DS: Fine-Grained Feature Decoupling via Dual-Statistic Synergy Operator for Object Detection
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:One-stage object detection, particularly the YOLO series, strikes a favorable balance between accuracy and efficiency. However, existing YOLO detectors lack explicit modeling of heterogeneous object responses within shared feature channels, which limits further performance gains. To address this, we propose YOLO-DS, a framework built around a novel Dual-Statistic Synergy Operator (DSO). The DSO decouples object features by jointly modeling the channel-wise mean and the peak-to-mean difference. Building upon the DSO, we design two lightweight gating modules: the Dual-Statistic Synergy Gating (DSG) module for adaptive channel-wise feature selection, and the Multi-Path Segmented Gating (MSG) module for depth-wise feature weighting. On the MS-COCO benchmark, YOLO-DS consistently outperforms YOLOv8 across five model scales (N, S, M, L, X), achieving AP gains of 1.1% to 1.7% with only a minimal increase in inference latency. Extensive visualization, ablation, and comparative studies validate the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating its superior capability in discriminating heterogeneous objects with high efficiency.
RegFreeNet: A Registration-Free Network for CBCT-based 3D Dental Implant Planning
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:As the commercial surgical guide design software usually does not support the export of implant position for pre-implantation data, existing methods have to scan the post-implantation data and map the implant to pre-implantation space to get the label of implant position for training. Such a process is time-consuming and heavily relies on the accuracy of registration algorithm. Moreover, not all hospitals have paired CBCT data, limitting the construction of multi-center dataset. Inspired by the way dentists determine the implant position based on the neighboring tooth texture, we found that even if the implant area is masked, it will not affect the determination of the implant position. Therefore, we propose to mask the implants in the post-implantation data so that any CBCT containing the implants can be used as training data. This paradigm enables us to discard the registration process and makes it possible to construct a large-scale multi-center implant dataset. On this basis, we proposes ImplantFairy, a comprehensive, publicly accessible dental implant dataset with voxel-level 3D annotations of 1622 CBCT data. Furthermore, according to the area variation characteristics of the tooth's spatial structure and the slope information of the implant, we designed a slope-aware implant position prediction network. Specifically, a neighboring distance perception (NDP) module is designed to adaptively extract tooth area variation features, and an implant slope prediction branch assists the network in learning more robust features through additional implant supervision information. Extensive experiments conducted on ImplantFairy and two public dataset demonstrate that the proposed RegFreeNet achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
MMedExpert-R1: Strengthening Multimodal Medical Reasoning via Domain-Specific Adaptation and Clinical Guideline Reinforcement
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Medical Vision-Language Models (MedVLMs) excel at perception tasks but struggle with complex clinical reasoning required in real-world scenarios. While reinforcement learning (RL) has been explored to enhance reasoning capabilities, existing approaches face critical mismatches: the scarcity of deep reasoning data, cold-start limits multi-specialty alignment, and standard RL algorithms fail to model clinical reasoning diversity. We propose MMedExpert-R1, a novel reasoning MedVLM that addresses these challenges through domain-specific adaptation and clinical guideline reinforcement. We construct MMedExpert, a high-quality dataset of 10K samples across four specialties with step-by-step reasoning traces. Our Domain-Specific Adaptation (DSA) creates specialty-specific LoRA modules to provide diverse initialization, while Guideline-Based Advantages (GBA) explicitly models different clinical reasoning perspectives to align with real-world diagnostic strategies. Conflict-Aware Capability Integration then merges these specialized experts into a unified agent, ensuring robust multi-specialty alignment. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance, with our 7B model achieving 27.50 on MedXpert-MM and 83.03 on OmniMedVQA, establishing a robust foundation for reliable multimodal medical reasoning systems.
Benchmarking Egocentric Clinical Intent Understanding Capability for Medical Multimodal Large Language Models
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Medical Multimodal Large Language Models (Med-MLLMs) require egocentric clinical intent understanding for real-world deployment, yet existing benchmarks fail to evaluate this critical capability. To address these challenges, we introduce MedGaze-Bench, the first benchmark leveraging clinician gaze as a Cognitive Cursor to assess intent understanding across surgery, emergency simulation, and diagnostic interpretation. Our benchmark addresses three fundamental challenges: visual homogeneity of anatomical structures, strict temporal-causal dependencies in clinical workflows, and implicit adherence to safety protocols. We propose a Three-Dimensional Clinical Intent Framework evaluating: (1) Spatial Intent: discriminating precise targets amid visual noise, (2) Temporal Intent: inferring causal rationale through retrospective and prospective reasoning, and (3) Standard Intent: verifying protocol compliance through safety checks. Beyond accuracy metrics, we introduce Trap QA mechanisms to stress-test clinical reliability by penalizing hallucinations and cognitive sycophancy. Experiments reveal current MLLMs struggle with egocentric intent due to over-reliance on global features, leading to fabricated observations and uncritical acceptance of invalid instructions.
X-ray Insights Unleashed: Pioneering the Enhancement of Multi-Label Long-Tail Data
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Long-tailed pulmonary anomalies in chest radiography present formidable diagnostic challenges. Despite the recent strides in diffusion-based methods for enhancing the representation of tailed lesions, the paucity of rare lesion exemplars curtails the generative capabilities of these approaches, thereby leaving the diagnostic precision less than optimal. In this paper, we propose a novel data synthesis pipeline designed to augment tail lesions utilizing a copious supply of conventional normal X-rays. Specifically, a sufficient quantity of normal samples is amassed to train a diffusion model capable of generating normal X-ray images. This pre-trained diffusion model is subsequently utilized to inpaint the head lesions present in the diseased X-rays, thereby preserving the tail classes as augmented training data. Additionally, we propose the integration of a Large Language Model Knowledge Guidance (LKG) module alongside a Progressive Incremental Learning (PIL) strategy to stabilize the inpainting fine-tuning process. Comprehensive evaluations conducted on the public lung datasets MIMIC and CheXpert demonstrate that the proposed method sets a new benchmark in performance.
SSA3D: Text-Conditioned Assisted Self-Supervised Framework for Automatic Dental Abutment Design
Dec 12, 2025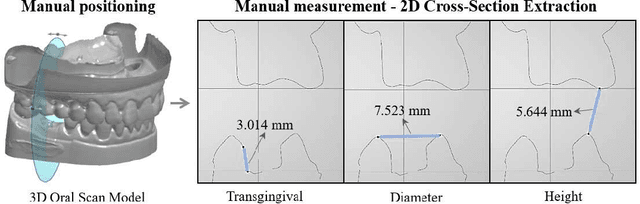
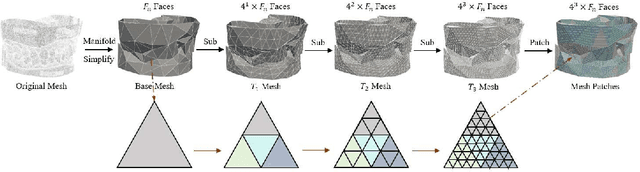
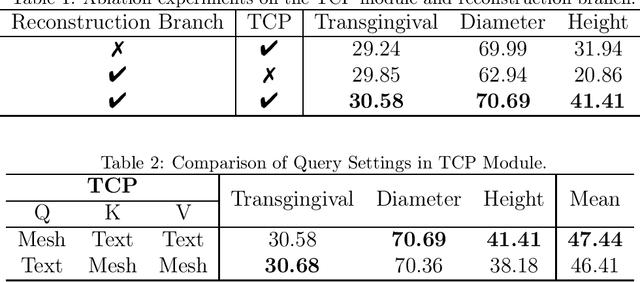
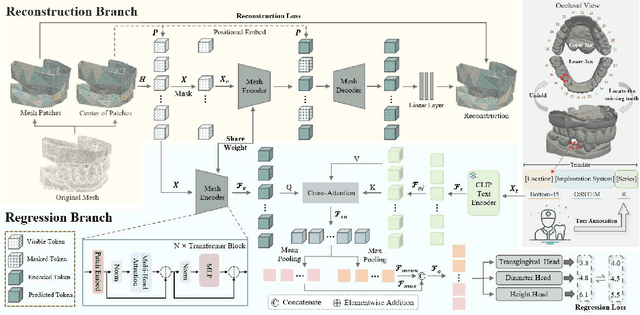
Abstract:Abutment design is a critical step in dental implant restoration. However, manual design involves tedious measurement and fitting, and research on automating this process with AI is limited, due to the unavailability of large annotated datasets. Although self-supervised learning (SSL) can alleviate data scarcity, its need for pre-training and fine-tuning results in high computational costs and long training times. In this paper, we propose a Self-supervised assisted automatic abutment design framework (SS$A^3$D), which employs a dual-branch architecture with a reconstruction branch and a regression branch. The reconstruction branch learns to restore masked intraoral scan data and transfers the learned structural information to the regression branch. The regression branch then predicts the abutment parameters under supervised learning, which eliminates the separate pre-training and fine-tuning process. We also design a Text-Conditioned Prompt (TCP) module to incorporate clinical information (such as implant location, system, and series) into SS$A^3$D. This guides the network to focus on relevant regions and constrains the parameter predictions. Extensive experiments on a collected dataset show that SS$A^3$D saves half of the training time and achieves higher accuracy than traditional SSL methods. It also achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to other methods, significantly improving the accuracy and efficiency of automated abutment design.
A Lightweight 3D Anomaly Detection Method with Rotationally Invariant Features
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:3D anomaly detection (AD) is a crucial task in computer vision, aiming to identify anomalous points or regions from point cloud data. However, existing methods may encounter challenges when handling point clouds with changes in orientation and position because the resulting features may vary significantly. To address this problem, we propose a novel Rotationally Invariant Features (RIF) framework for 3D AD. Firstly, to remove the adverse effect of variations on point cloud data, we develop a Point Coordinate Mapping (PCM) technique, which maps each point into a rotationally invariant space to maintain consistency of representation. Then, to learn robust and discriminative features, we design a lightweight Convolutional Transform Feature Network (CTF-Net) to extract rotationally invariant features for the memory bank. To improve the ability of the feature extractor, we introduce the idea of transfer learning to pre-train the feature extractor with 3D data augmentation. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves the advanced performance on the Anomaly-ShapeNet dataset, with an average P-AUROC improvement of 17.7\%, and also gains the best performance on the Real3D-AD dataset, with an average P-AUROC improvement of 1.6\%. The strong generalization ability of RIF has been verified by combining it with traditional feature extraction methods on anomaly detection tasks, demonstrating great potential for industrial applications.
Context-Gated Cross-Modal Perception with Visual Mamba for PET-CT Lung Tumor Segmentation
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Accurate lung tumor segmentation is vital for improving diagnosis and treatment planning, and effectively combining anatomical and functional information from PET and CT remains a major challenge. In this study, we propose vMambaX, a lightweight multimodal framework integrating PET and CT scan images through a Context-Gated Cross-Modal Perception Module (CGM). Built on the Visual Mamba architecture, vMambaX adaptively enhances inter-modality feature interaction, emphasizing informative regions while suppressing noise. Evaluated on the PCLT20K dataset, the model outperforms baseline models while maintaining lower computational complexity. These results highlight the effectiveness of adaptive cross-modal gating for multimodal tumor segmentation and demonstrate the potential of vMambaX as an efficient and scalable framework for advanced lung cancer analysis. The code is available at https://github.com/arco-group/vMambaX.
DAP-MAE: Domain-Adaptive Point Cloud Masked Autoencoder for Effective Cross-Domain Learning
Oct 24, 2025Abstract:Compared to 2D data, the scale of point cloud data in different domains available for training, is quite limited. Researchers have been trying to combine these data of different domains for masked autoencoder (MAE) pre-training to leverage such a data scarcity issue. However, the prior knowledge learned from mixed domains may not align well with the downstream 3D point cloud analysis tasks, leading to degraded performance. To address such an issue, we propose the Domain-Adaptive Point Cloud Masked Autoencoder (DAP-MAE), an MAE pre-training method, to adaptively integrate the knowledge of cross-domain datasets for general point cloud analysis. In DAP-MAE, we design a heterogeneous domain adapter that utilizes an adaptation mode during pre-training, enabling the model to comprehensively learn information from point clouds across different domains, while employing a fusion mode in the fine-tuning to enhance point cloud features. Meanwhile, DAP-MAE incorporates a domain feature generator to guide the adaptation of point cloud features to various downstream tasks. With only one pre-training, DAP-MAE achieves excellent performance across four different point cloud analysis tasks, reaching 95.18% in object classification on ScanObjectNN and 88.45% in facial expression recognition on Bosphorus.
* 14 pages, 7 figures, conference
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge