Hao Ding
TikArt: Aperture-Guided Observation for Fine-Grained Visual Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:We address fine-grained visual reasoning in multimodal large language models (MLLMs), where key evidence may reside in tiny objects, cluttered regions, or subtle markings that are lost under a single global image encoding. We introduce TikArt (Thinking Aperture), an aperture-guided agent that casts multi-step vision-language reasoning as a decision process over regions of interest. TikArt follows a Think-Aperture-Observe loop, alternating between language generation and two aperture actions: Zoom extracts rectangular crops, while Segment invokes SAM2 to obtain mask-based crops for irregular targets. After every action, the model must produce an explicit observation, turning local visual cues into persistent linguistic memory. Built on Qwen3-VL-8B, TikArt optimizes its reasoning policy with AGRPO, a GRPO-style reinforcement learning algorithm with a two-stage curriculum: it warms up segmentation actions and then jointly optimizes visual math, fine-grained VQA, and segmentation, using rewards that couple task success with purposeful aperture use. Experiments on V*, HR-Bench-4K/8K, MME-RealWorld-Lite, MMStar, RefCOCO, and ReasonSeg show consistent gains over the backbone and yield interpretable aperture trajectories for high-resolution reasoning.
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
BronchOpt : Vision-Based Pose Optimization with Fine-Tuned Foundation Models for Accurate Bronchoscopy Navigation
Nov 12, 2025



Abstract:Accurate intra-operative localization of the bronchoscope tip relative to patient anatomy remains challenging due to respiratory motion, anatomical variability, and CT-to-body divergence that cause deformation and misalignment between intra-operative views and pre-operative CT. Existing vision-based methods often fail to generalize across domains and patients, leading to residual alignment errors. This work establishes a generalizable foundation for bronchoscopy navigation through a robust vision-based framework and a new synthetic benchmark dataset that enables standardized and reproducible evaluation. We propose a vision-based pose optimization framework for frame-wise 2D-3D registration between intra-operative endoscopic views and pre-operative CT anatomy. A fine-tuned modality- and domain-invariant encoder enables direct similarity computation between real endoscopic RGB frames and CT-rendered depth maps, while a differentiable rendering module iteratively refines camera poses through depth consistency. To enhance reproducibility, we introduce the first public synthetic benchmark dataset for bronchoscopy navigation, addressing the lack of paired CT-endoscopy data. Trained exclusively on synthetic data distinct from the benchmark, our model achieves an average translational error of 2.65 mm and a rotational error of 0.19 rad, demonstrating accurate and stable localization. Qualitative results on real patient data further confirm strong cross-domain generalization, achieving consistent frame-wise 2D-3D alignment without domain-specific adaptation. Overall, the proposed framework achieves robust, domain-invariant localization through iterative vision-based optimization, while the new benchmark provides a foundation for standardized progress in vision-based bronchoscopy navigation.
TwinOR: Photorealistic Digital Twins of Dynamic Operating Rooms for Embodied AI Research
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Developing embodied AI for intelligent surgical systems requires safe, controllable environments for continual learning and evaluation. However, safety regulations and operational constraints in operating rooms (ORs) limit embodied agents from freely perceiving and interacting in realistic settings. Digital twins provide high-fidelity, risk-free environments for exploration and training. How we may create photorealistic and dynamic digital representations of ORs that capture relevant spatial, visual, and behavioral complexity remains unclear. We introduce TwinOR, a framework for constructing photorealistic, dynamic digital twins of ORs for embodied AI research. The system reconstructs static geometry from pre-scan videos and continuously models human and equipment motion through multi-view perception of OR activities. The static and dynamic components are fused into an immersive 3D environment that supports controllable simulation and embodied exploration. The proposed framework reconstructs complete OR geometry with centimeter level accuracy while preserving dynamic interaction across surgical workflows, enabling realistic renderings and a virtual playground for embodied AI systems. In our experiments, TwinOR simulates stereo and monocular sensor streams for geometry understanding and visual localization tasks. Models such as FoundationStereo and ORB-SLAM3 on TwinOR-synthesized data achieve performance within their reported accuracy on real indoor datasets, demonstrating that TwinOR provides sensor-level realism sufficient for perception and localization challenges. By establishing a real-to-sim pipeline for constructing dynamic, photorealistic digital twins of OR environments, TwinOR enables the safe, scalable, and data-efficient development and benchmarking of embodied AI, ultimately accelerating the deployment of embodied AI from sim-to-real.
Did you just see that? Arbitrary view synthesis for egocentric replay of operating room workflows from ambient sensors
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Observing surgical practice has historically relied on fixed vantage points or recollections, leaving the egocentric visual perspectives that guide clinical decisions undocumented. Fixed-camera video can capture surgical workflows at the room-scale, but cannot reconstruct what each team member actually saw. Thus, these videos only provide limited insights into how decisions that affect surgical safety, training, and workflow optimization are made. Here we introduce EgoSurg, the first framework to reconstruct the dynamic, egocentric replays for any operating room (OR) staff directly from wall-mounted fixed-camera video, and thus, without intervention to clinical workflow. EgoSurg couples geometry-driven neural rendering with diffusion-based view enhancement, enabling high-visual fidelity synthesis of arbitrary and egocentric viewpoints at any moment. In evaluation across multi-site surgical cases and controlled studies, EgoSurg reconstructs person-specific visual fields and arbitrary viewpoints with high visual quality and fidelity. By transforming existing OR camera infrastructure into a navigable dynamic 3D record, EgoSurg establishes a new foundation for immersive surgical data science, enabling surgical practice to be visualized, experienced, and analyzed from every angle.
Kimi K2: Open Agentic Intelligence
Jul 28, 2025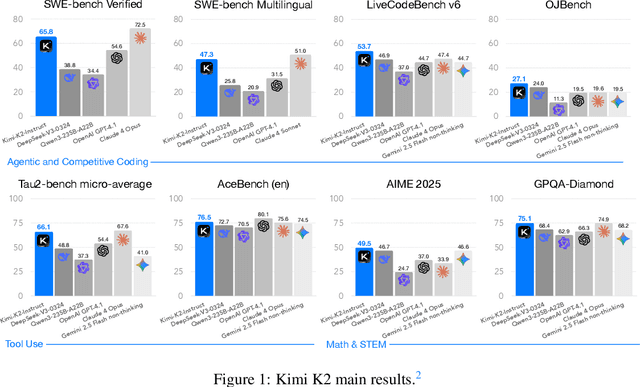
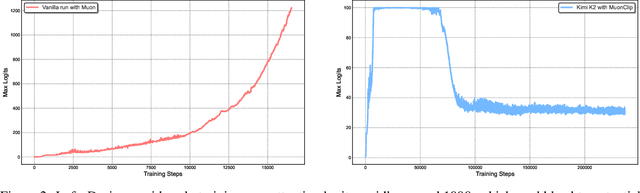
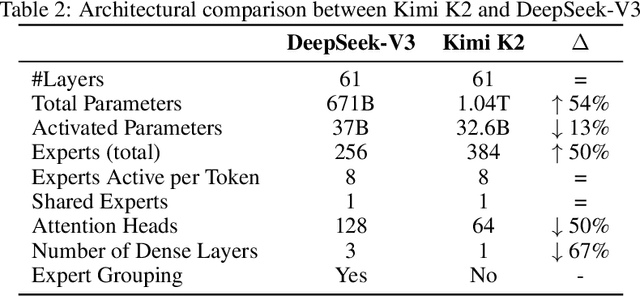
Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) large language model with 32 billion activated parameters and 1 trillion total parameters. We propose the MuonClip optimizer, which improves upon Muon with a novel QK-clip technique to address training instability while enjoying the advanced token efficiency of Muon. Based on MuonClip, K2 was pre-trained on 15.5 trillion tokens with zero loss spike. During post-training, K2 undergoes a multi-stage post-training process, highlighted by a large-scale agentic data synthesis pipeline and a joint reinforcement learning (RL) stage, where the model improves its capabilities through interactions with real and synthetic environments. Kimi K2 achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source non-thinking models, with strengths in agentic capabilities. Notably, K2 obtains 66.1 on Tau2-Bench, 76.5 on ACEBench (En), 65.8 on SWE-Bench Verified, and 47.3 on SWE-Bench Multilingual -- surpassing most open and closed-sourced baselines in non-thinking settings. It also exhibits strong capabilities in coding, mathematics, and reasoning tasks, with a score of 53.7 on LiveCodeBench v6, 49.5 on AIME 2025, 75.1 on GPQA-Diamond, and 27.1 on OJBench, all without extended thinking. These results position Kimi K2 as one of the most capable open-source large language models to date, particularly in software engineering and agentic tasks. We release our base and post-trained model checkpoints to facilitate future research and applications of agentic intelligence.
Position: Foundation Models Need Digital Twin Representations
May 01, 2025Abstract:Current foundation models (FMs) rely on token representations that directly fragment continuous real-world multimodal data into discrete tokens. They limit FMs to learning real-world knowledge and relationships purely through statistical correlation rather than leveraging explicit domain knowledge. Consequently, current FMs struggle with maintaining semantic coherence across modalities, capturing fine-grained spatial-temporal dynamics, and performing causal reasoning. These limitations cannot be overcome by simply scaling up model size or expanding datasets. This position paper argues that the machine learning community should consider digital twin (DT) representations, which are outcome-driven digital representations that serve as building blocks for creating virtual replicas of physical processes, as an alternative to the token representation for building FMs. Finally, we discuss how DT representations can address these challenges by providing physically grounded representations that explicitly encode domain knowledge and preserve the continuous nature of real-world processes.
DINOv2-powered Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation: A Unified Framework via Cross-Model Distillation and 4D Correlation Mining
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Few-shot semantic segmentation has gained increasing interest due to its generalization capability, i.e., segmenting pixels of novel classes requiring only a few annotated images. Prior work has focused on meta-learning for support-query matching, with extensive development in both prototype-based and aggregation-based methods. To address data scarcity, recent approaches have turned to foundation models to enhance representation transferability for novel class segmentation. Among them, a hybrid dual-modal framework including both DINOv2 and SAM has garnered attention due to their complementary capabilities. We wonder "can we build a unified model with knowledge from both foundation models?" To this end, we propose FS-DINO, with only DINOv2's encoder and a lightweight segmenter. The segmenter features a bottleneck adapter, a meta-visual prompt generator based on dense similarities and semantic embeddings, and a decoder. Through coarse-to-fine cross-model distillation, we effectively integrate SAM's knowledge into our lightweight segmenter, which can be further enhanced by 4D correlation mining on support-query pairs. Extensive experiments on COCO-20i, PASCAL-5i, and FSS-1000 demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method.
Kimi-VL Technical Report
Apr 10, 2025
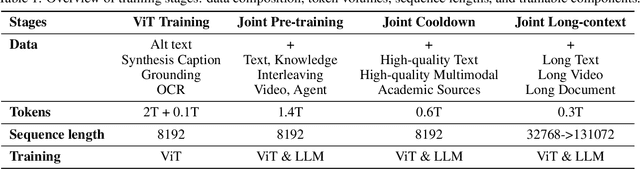
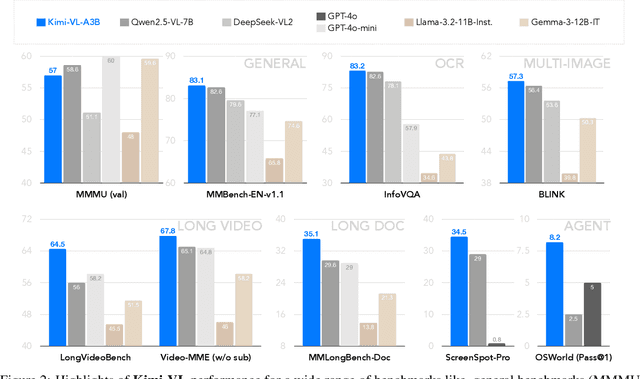
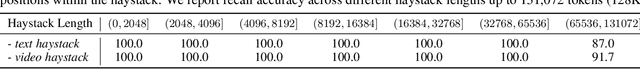
Abstract:We present Kimi-VL, an efficient open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) vision-language model (VLM) that offers advanced multimodal reasoning, long-context understanding, and strong agent capabilities - all while activating only 2.8B parameters in its language decoder (Kimi-VL-A3B). Kimi-VL demonstrates strong performance across challenging domains: as a general-purpose VLM, Kimi-VL excels in multi-turn agent tasks (e.g., OSWorld), matching flagship models. Furthermore, it exhibits remarkable capabilities across diverse challenging vision language tasks, including college-level image and video comprehension, OCR, mathematical reasoning, and multi-image understanding. In comparative evaluations, it effectively competes with cutting-edge efficient VLMs such as GPT-4o-mini, Qwen2.5-VL-7B, and Gemma-3-12B-IT, while surpassing GPT-4o in several key domains. Kimi-VL also advances in processing long contexts and perceiving clearly. With a 128K extended context window, Kimi-VL can process diverse long inputs, achieving impressive scores of 64.5 on LongVideoBench and 35.1 on MMLongBench-Doc. Its native-resolution vision encoder, MoonViT, further allows it to see and understand ultra-high-resolution visual inputs, achieving 83.2 on InfoVQA and 34.5 on ScreenSpot-Pro, while maintaining lower computational cost for common tasks. Building upon Kimi-VL, we introduce an advanced long-thinking variant: Kimi-VL-Thinking. Developed through long chain-of-thought (CoT) supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL), this model exhibits strong long-horizon reasoning capabilities. It achieves scores of 61.7 on MMMU, 36.8 on MathVision, and 71.3 on MathVista while maintaining the compact 2.8B activated LLM parameters, setting a new standard for efficient multimodal thinking models. Code and models are publicly accessible at https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-VL.
Endo3R: Unified Online Reconstruction from Dynamic Monocular Endoscopic Video
Apr 04, 2025



Abstract:Reconstructing 3D scenes from monocular surgical videos can enhance surgeon's perception and therefore plays a vital role in various computer-assisted surgery tasks. However, achieving scale-consistent reconstruction remains an open challenge due to inherent issues in endoscopic videos, such as dynamic deformations and textureless surfaces. Despite recent advances, current methods either rely on calibration or instrument priors to estimate scale, or employ SfM-like multi-stage pipelines, leading to error accumulation and requiring offline optimization. In this paper, we present Endo3R, a unified 3D foundation model for online scale-consistent reconstruction from monocular surgical video, without any priors or extra optimization. Our model unifies the tasks by predicting globally aligned pointmaps, scale-consistent video depths, and camera parameters without any offline optimization. The core contribution of our method is expanding the capability of the recent pairwise reconstruction model to long-term incremental dynamic reconstruction by an uncertainty-aware dual memory mechanism. The mechanism maintains history tokens of both short-term dynamics and long-term spatial consistency. Notably, to tackle the highly dynamic nature of surgical scenes, we measure the uncertainty of tokens via Sampson distance and filter out tokens with high uncertainty. Regarding the scarcity of endoscopic datasets with ground-truth depth and camera poses, we further devise a self-supervised mechanism with a novel dynamics-aware flow loss. Abundant experiments on SCARED and Hamlyn datasets demonstrate our superior performance in zero-shot surgical video depth prediction and camera pose estimation with online efficiency. Project page: https://wrld.github.io/Endo3R/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge