Terrence Chen
S$^3$POT: Contrast-Driven Face Occlusion Segmentation via Self-Supervised Prompt Learning
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Existing face parsing methods usually misclassify occlusions as facial components. This is because occlusion is a high-level concept, it does not refer to a concrete category of object. Thus, constructing a real-world face dataset covering all categories of occlusion object is almost impossible and accurate mask annotation is labor-intensive. To deal with the problems, we present S$^3$POT, a contrast-driven framework synergizing face generation with self-supervised spatial prompting, to achieve occlusion segmentation. The framework is inspired by the insights: 1) Modern face generators' ability to realistically reconstruct occluded regions, creating an image that preserve facial geometry while eliminating occlusion, and 2) Foundation segmentation models' (e.g., SAM) capacity to extract precise mask when provided with appropriate prompts. In particular, S$^3$POT consists of three modules: Reference Generation (RF), Feature enhancement (FE), and Prompt Selection (PS). First, a reference image is produced by RF using structural guidance from parsed mask. Second, FE performs contrast of tokens between raw and reference images to obtain an initial prompt, then modifies image features with the prompt by cross-attention. Third, based on the enhanced features, PS constructs a set of positive and negative prompts and screens them with a self-attention network for a mask decoder. The network is learned under the guidance of three novel and complementary objective functions without occlusion ground truth mask involved. Extensive experiments on a dedicatedly collected dataset demonstrate S$^3$POT's superior performance and the effectiveness of each module.
Consistent Instance Field for Dynamic Scene Understanding
Dec 16, 2025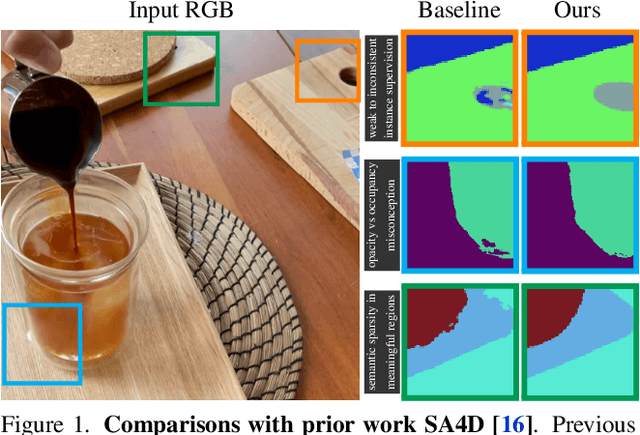
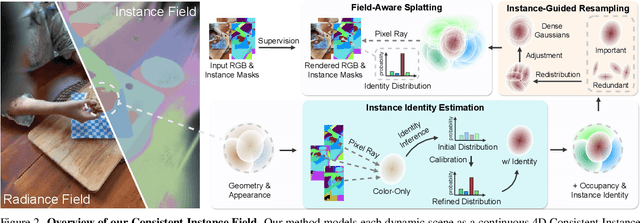
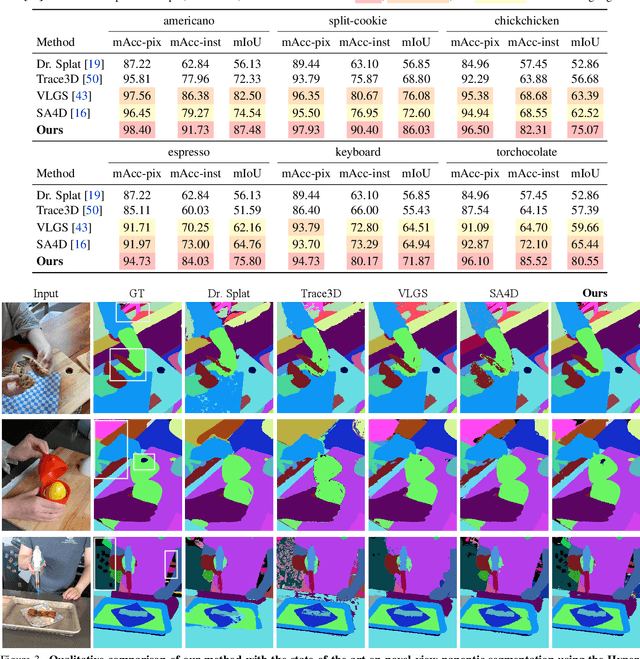
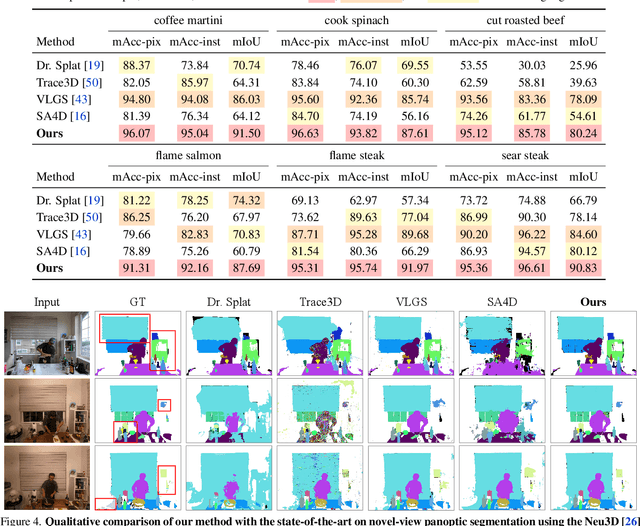
Abstract:We introduce Consistent Instance Field, a continuous and probabilistic spatio-temporal representation for dynamic scene understanding. Unlike prior methods that rely on discrete tracking or view-dependent features, our approach disentangles visibility from persistent object identity by modeling each space-time point with an occupancy probability and a conditional instance distribution. To realize this, we introduce a novel instance-embedded representation based on deformable 3D Gaussians, which jointly encode radiance and semantic information and are learned directly from input RGB images and instance masks through differentiable rasterization. Furthermore, we introduce new mechanisms to calibrate per-Gaussian identities and resample Gaussians toward semantically active regions, ensuring consistent instance representations across space and time. Experiments on HyperNeRF and Neu3D datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on novel-view panoptic segmentation and open-vocabulary 4D querying tasks.
From Particles to Fields: Reframing Photon Mapping with Continuous Gaussian Photon Fields
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Accurately modeling light transport is essential for realistic image synthesis. Photon mapping provides physically grounded estimates of complex global illumination effects such as caustics and specular-diffuse interactions, yet its per-view radiance estimation remains computationally inefficient when rendering multiple views of the same scene. The inefficiency arises from independent photon tracing and stochastic kernel estimation at each viewpoint, leading to inevitable redundant computation. To accelerate multi-view rendering, we reformulate photon mapping as a continuous and reusable radiance function. Specifically, we introduce the Gaussian Photon Field (GPF), a learnable representation that encodes photon distributions as anisotropic 3D Gaussian primitives parameterized by position, rotation, scale, and spectrum. GPF is initialized from physically traced photons in the first SPPM iteration and optimized using multi-view supervision of final radiance, distilling photon-based light transport into a continuous field. Once trained, the field enables differentiable radiance evaluation along camera rays without repeated photon tracing or iterative refinement. Extensive experiments on scenes with complex light transport, such as caustics and specular-diffuse interactions, demonstrate that GPF attains photon-level accuracy while reducing computation by orders of magnitude, unifying the physical rigor of photon-based rendering with the efficiency of neural scene representations.
RAU: Reference-based Anatomical Understanding with Vision Language Models
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Anatomical understanding through deep learning is critical for automatic report generation, intra-operative navigation, and organ localization in medical imaging; however, its progress is constrained by the scarcity of expert-labeled data. A promising remedy is to leverage an annotated reference image to guide the interpretation of an unlabeled target. Although recent vision-language models (VLMs) exhibit non-trivial visual reasoning, their reference-based understanding and fine-grained localization remain limited. We introduce RAU, a framework for reference-based anatomical understanding with VLMs. We first show that a VLM learns to identify anatomical regions through relative spatial reasoning between reference and target images, trained on a moderately sized dataset. We validate this capability through visual question answering (VQA) and bounding box prediction. Next, we demonstrate that the VLM-derived spatial cues can be seamlessly integrated with the fine-grained segmentation capability of SAM2, enabling localization and pixel-level segmentation of small anatomical regions, such as vessel segments. Across two in-distribution and two out-of-distribution datasets, RAU consistently outperforms a SAM2 fine-tuning baseline using the same memory setup, yielding more accurate segmentations and more reliable localization. More importantly, its strong generalization ability makes it scalable to out-of-distribution datasets, a property crucial for medical image applications. To the best of our knowledge, RAU is the first to explore the capability of VLMs for reference-based identification, localization, and segmentation of anatomical structures in medical images. Its promising performance highlights the potential of VLM-driven approaches for anatomical understanding in automated clinical workflows.
Render-FM: A Foundation Model for Real-time Photorealistic Volumetric Rendering
May 22, 2025Abstract:Volumetric rendering of Computed Tomography (CT) scans is crucial for visualizing complex 3D anatomical structures in medical imaging. Current high-fidelity approaches, especially neural rendering techniques, require time-consuming per-scene optimization, limiting clinical applicability due to computational demands and poor generalizability. We propose Render-FM, a novel foundation model for direct, real-time volumetric rendering of CT scans. Render-FM employs an encoder-decoder architecture that directly regresses 6D Gaussian Splatting (6DGS) parameters from CT volumes, eliminating per-scan optimization through large-scale pre-training on diverse medical data. By integrating robust feature extraction with the expressive power of 6DGS, our approach efficiently generates high-quality, real-time interactive 3D visualizations across diverse clinical CT data. Experiments demonstrate that Render-FM achieves visual fidelity comparable or superior to specialized per-scan methods while drastically reducing preparation time from nearly an hour to seconds for a single inference step. This advancement enables seamless integration into real-time surgical planning and diagnostic workflows. The project page is: https://gaozhongpai.github.io/renderfm/.
Leveraging Diffusion Model and Image Foundation Model for Improved Correspondence Matching in Coronary Angiography
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Accurate correspondence matching in coronary angiography images is crucial for reconstructing 3D coronary artery structures, which is essential for precise diagnosis and treatment planning of coronary artery disease (CAD). Traditional matching methods for natural images often fail to generalize to X-ray images due to inherent differences such as lack of texture, lower contrast, and overlapping structures, compounded by insufficient training data. To address these challenges, we propose a novel pipeline that generates realistic paired coronary angiography images using a diffusion model conditioned on 2D projections of 3D reconstructed meshes from Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA), providing high-quality synthetic data for training. Additionally, we employ large-scale image foundation models to guide feature aggregation, enhancing correspondence matching accuracy by focusing on semantically relevant regions and keypoints. Our approach demonstrates superior matching performance on synthetic datasets and effectively generalizes to real-world datasets, offering a practical solution for this task. Furthermore, our work investigates the efficacy of different foundation models in correspondence matching, providing novel insights into leveraging advanced image foundation models for medical imaging applications.
DiffDenoise: Self-Supervised Medical Image Denoising with Conditional Diffusion Models
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Many self-supervised denoising approaches have been proposed in recent years. However, these methods tend to overly smooth images, resulting in the loss of fine structures that are essential for medical applications. In this paper, we propose DiffDenoise, a powerful self-supervised denoising approach tailored for medical images, designed to preserve high-frequency details. Our approach comprises three stages. First, we train a diffusion model on noisy images, using the outputs of a pretrained Blind-Spot Network as conditioning inputs. Next, we introduce a novel stabilized reverse sampling technique, which generates clean images by averaging diffusion sampling outputs initialized with a pair of symmetric noises. Finally, we train a supervised denoising network using noisy images paired with the denoised outputs generated by the diffusion model. Our results demonstrate that DiffDenoise outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in both synthetic and real-world medical image denoising tasks. We provide both a theoretical foundation and practical insights, demonstrating the method's effectiveness across various medical imaging modalities and anatomical structures.
PolypSegTrack: Unified Foundation Model for Colonoscopy Video Analysis
Mar 31, 2025



Abstract:Early detection, accurate segmentation, classification and tracking of polyps during colonoscopy are critical for preventing colorectal cancer. Many existing deep-learning-based methods for analyzing colonoscopic videos either require task-specific fine-tuning, lack tracking capabilities, or rely on domain-specific pre-training. In this paper, we introduce \textit{PolypSegTrack}, a novel foundation model that jointly addresses polyp detection, segmentation, classification and unsupervised tracking in colonoscopic videos. Our approach leverages a novel conditional mask loss, enabling flexible training across datasets with either pixel-level segmentation masks or bounding box annotations, allowing us to bypass task-specific fine-tuning. Our unsupervised tracking module reliably associates polyp instances across frames using object queries, without relying on any heuristics. We leverage a robust vision foundation model backbone that is pre-trained unsupervisedly on natural images, thereby removing the need for domain-specific pre-training. Extensive experiments on multiple polyp benchmarks demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches in detection, segmentation, classification, and tracking.
Adapting Vision Foundation Models for Real-time Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel approach that adapts hierarchical vision foundation models for real-time ultrasound image segmentation. Existing ultrasound segmentation methods often struggle with adaptability to new tasks, relying on costly manual annotations, while real-time approaches generally fail to match state-of-the-art performance. To overcome these limitations, we introduce an adaptive framework that leverages the vision foundation model Hiera to extract multi-scale features, interleaved with DINOv2 representations to enhance visual expressiveness. These enriched features are then decoded to produce precise and robust segmentation. We conduct extensive evaluations on six public datasets and one in-house dataset, covering both cardiac and thyroid ultrasound segmentation. Experiments show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods across multiple datasets and excels with limited supervision, surpassing nnUNet by over 20\% on average in the 1\% and 10\% data settings. Our method achieves $\sim$77 FPS inference speed with TensorRT on a single GPU, enabling real-time clinical applications.
CHROME: Clothed Human Reconstruction with Occlusion-Resilience and Multiview-Consistency from a Single Image
Mar 19, 2025



Abstract:Reconstructing clothed humans from a single image is a fundamental task in computer vision with wide-ranging applications. Although existing monocular clothed human reconstruction solutions have shown promising results, they often rely on the assumption that the human subject is in an occlusion-free environment. Thus, when encountering in-the-wild occluded images, these algorithms produce multiview inconsistent and fragmented reconstructions. Additionally, most algorithms for monocular 3D human reconstruction leverage geometric priors such as SMPL annotations for training and inference, which are extremely challenging to acquire in real-world applications. To address these limitations, we propose CHROME: Clothed Human Reconstruction with Occlusion-Resilience and Multiview-ConsistEncy from a Single Image, a novel pipeline designed to reconstruct occlusion-resilient 3D humans with multiview consistency from a single occluded image, without requiring either ground-truth geometric prior annotations or 3D supervision. Specifically, CHROME leverages a multiview diffusion model to first synthesize occlusion-free human images from the occluded input, compatible with off-the-shelf pose control to explicitly enforce cross-view consistency during synthesis. A 3D reconstruction model is then trained to predict a set of 3D Gaussians conditioned on both the occluded input and synthesized views, aligning cross-view details to produce a cohesive and accurate 3D representation. CHROME achieves significant improvements in terms of both novel view synthesis (upto 3 db PSNR) and geometric reconstruction under challenging conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge