Qi Dou
for the ALFA study
Real-time Monocular 2D and 3D Perception of Endoluminal Scenes for Controlling Flexible Robotic Endoscopic Instruments
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Endoluminal surgery offers a minimally invasive option for early-stage gastrointestinal and urinary tract cancers but is limited by surgical tools and a steep learning curve. Robotic systems, particularly continuum robots, provide flexible instruments that enable precise tissue resection, potentially improving outcomes. This paper presents a visual perception platform for a continuum robotic system in endoluminal surgery. Our goal is to utilize monocular endoscopic image-based perception algorithms to identify position and orientation of flexible instruments and measure their distances from tissues. We introduce 2D and 3D learning-based perception algorithms and develop a physically-realistic simulator that models flexible instruments dynamics. This simulator generates realistic endoluminal scenes, enabling control of flexible robots and substantial data collection. Using a continuum robot prototype, we conducted module and system-level evaluations. Results show that our algorithms improve control of flexible instruments, reducing manipulation time by over 70% for trajectory-following tasks and enhancing understanding of surgical scenarios, leading to robust endoluminal surgeries.
ARport: An Augmented Reality System for Markerless Image-Guided Port Placement in Robotic Surgery
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:Purpose: Precise port placement is a critical step in robot-assisted surgery, where port configuration influences both visual access to the operative field and instrument maneuverability. To bridge the gap between preoperative planning and intraoperative execution, we present ARport, an augmented reality (AR) system that automatically maps pre-planned trocar layouts onto the patient's body surface, providing intuitive spatial guidance during surgical preparation. Methods: ARport, implemented on an optical see-through head-mounted display (OST-HMD), operates without any external sensors or markers, simplifying setup and enhancing workflow integration. It reconstructs the operative scene from RGB, depth, and pose data captured by the OST-HMD, extracts the patient's body surface using a foundation model, and performs surface-based markerless registration to align preoperative anatomical models to the extracted patient's body surface, enabling in-situ visualization of planned trocar layouts. A demonstration video illustrating the overall workflow is available online. Results: In full-scale human-phantom experiments, ARport accurately overlaid pre-planned trocar sites onto the physical phantom, achieving consistent spatial correspondence between virtual plans and real anatomy. Conclusion: ARport provides a fully marker-free and hardware-minimal solution for visualizing preoperative trocar plans directly on the patient's body surface. The system facilitates efficient intraoperative setup and demonstrates potential for seamless integration into routine clinical workflows.
Concepts from Representations: Post-hoc Concept Bottleneck Models via Sparse Decomposition of Visual Representations
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Deep learning has achieved remarkable success in image recognition, yet their inherent opacity poses challenges for deployment in critical domains. Concept-based interpretations aim to address this by explaining model reasoning through human-understandable concepts. However, existing post-hoc methods and ante-hoc concept bottleneck models (CBMs), suffer from limitations such as unreliable concept relevance, non-visual or labor-intensive concept definitions, and model or data-agnostic assumptions. This paper introduces Post-hoc Concept Bottleneck Model via Representation Decomposition (PCBM-ReD), a novel pipeline that retrofits interpretability onto pretrained opaque models. PCBM-ReD automatically extracts visual concepts from a pre-trained encoder, employs multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to label and filter concepts based on visual identifiability and task relevance, and selects an independent subset via reconstruction-guided optimization. Leveraging CLIP's visual-text alignment, it decomposes image representations into linear combination of concept embeddings to fit into the CBMs abstraction. Extensive experiments across 11 image classification tasks show PCBM-ReD achieves state-of-the-art accuracy, narrows the performance gap with end-to-end models, and exhibits better interpretability.
DSTED: Decoupling Temporal Stabilization and Discriminative Enhancement for Surgical Workflow Recognition
Dec 22, 2025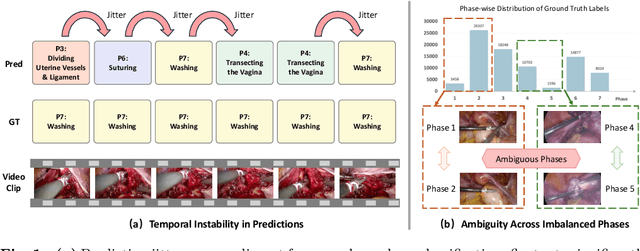
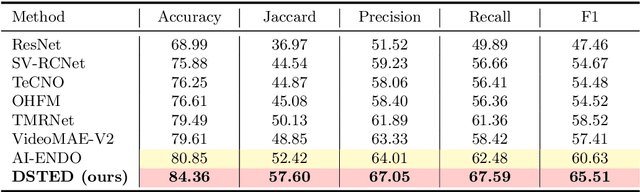
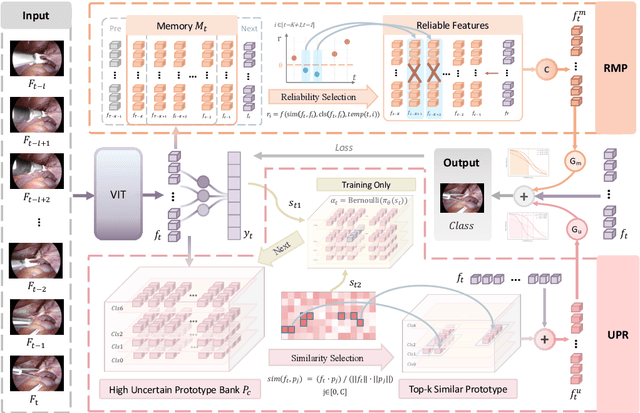
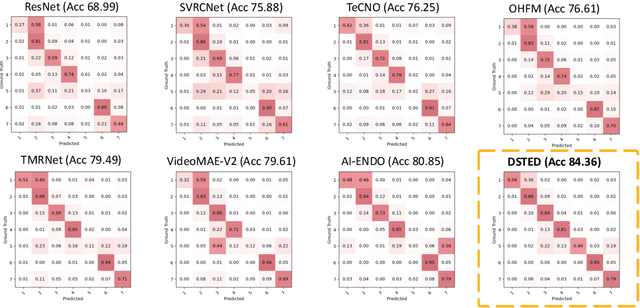
Abstract:Purpose: Surgical workflow recognition enables context-aware assistance and skill assessment in computer-assisted interventions. Despite recent advances, current methods suffer from two critical challenges: prediction jitter across consecutive frames and poor discrimination of ambiguous phases. This paper aims to develop a stable framework by selectively propagating reliable historical information and explicitly modeling uncertainty for hard sample enhancement. Methods: We propose a dual-pathway framework DSTED with Reliable Memory Propagation (RMP) and Uncertainty-Aware Prototype Retrieval (UPR). RMP maintains temporal coherence by filtering and fusing high-confidence historical features through multi-criteria reliability assessment. UPR constructs learnable class-specific prototypes from high-uncertainty samples and performs adaptive prototype matching to refine ambiguous frame representations. Finally, a confidence-driven gate dynamically balances both pathways based on prediction certainty. Results: Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on AutoLaparo-hysterectomy with 84.36% accuracy and 65.51% F1-score, surpassing the second-best method by 3.51% and 4.88% respectively. Ablations reveal complementary gains from RMP (2.19%) and UPR (1.93%), with synergistic effects when combined. Extensive analysis confirms substantial reduction in temporal jitter and marked improvement on challenging phase transitions. Conclusion: Our dual-pathway design introduces a novel paradigm for stable workflow recognition, demonstrating that decoupling the modeling of temporal consistency and phase ambiguity yields superior performance and clinical applicability.
CP-Env: Evaluating Large Language Models on Clinical Pathways in a Controllable Hospital Environment
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Medical care follows complex clinical pathways that extend beyond isolated physician-patient encounters, emphasizing decision-making and transitions between different stages. Current benchmarks focusing on static exams or isolated dialogues inadequately evaluate large language models (LLMs) in dynamic clinical scenarios. We introduce CP-Env, a controllable agentic hospital environment designed to evaluate LLMs across end-to-end clinical pathways. CP-Env simulates a hospital ecosystem with patient and physician agents, constructing scenarios ranging from triage and specialist consultation to diagnostic testing and multidisciplinary team meetings for agent interaction. Following real hospital adaptive flow of healthcare, it enables branching, long-horizon task execution. We propose a three-tiered evaluation framework encompassing Clinical Efficacy, Process Competency, and Professional Ethics. Results reveal that most models struggle with pathway complexity, exhibiting hallucinations and losing critical diagnostic details. Interestingly, excessive reasoning steps can sometimes prove counterproductive, while top models tend to exhibit reduced tool dependency through internalized knowledge. CP-Env advances medical AI agents development through comprehensive end-to-end clinical evaluation. We provide the benchmark and evaluation tools for further research and development at https://github.com/SPIRAL-MED/CP_ENV.
Vulnerable Agent Identification in Large-Scale Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Partial agent failure becomes inevitable when systems scale up, making it crucial to identify the subset of agents whose compromise would most severely degrade overall performance. In this paper, we study this Vulnerable Agent Identification (VAI) problem in large-scale multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). We frame VAI as a Hierarchical Adversarial Decentralized Mean Field Control (HAD-MFC), where the upper level involves an NP-hard combinatorial task of selecting the most vulnerable agents, and the lower level learns worst-case adversarial policies for these agents using mean-field MARL. The two problems are coupled together, making HAD-MFC difficult to solve. To solve this, we first decouple the hierarchical process by Fenchel-Rockafellar transform, resulting a regularized mean-field Bellman operator for upper level that enables independent learning at each level, thus reducing computational complexity. We then reformulate the upper-level combinatorial problem as a MDP with dense rewards from our regularized mean-field Bellman operator, enabling us to sequentially identify the most vulnerable agents by greedy and RL algorithms. This decomposition provably preserves the optimal solution of the original HAD-MFC. Experiments show our method effectively identifies more vulnerable agents in large-scale MARL and the rule-based system, fooling system into worse failures, and learns a value function that reveals the vulnerability of each agent.
Toward Robust Medical Fairness: Debiased Dual-Modal Alignment via Text-Guided Attribute-Disentangled Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Models
Aug 26, 2025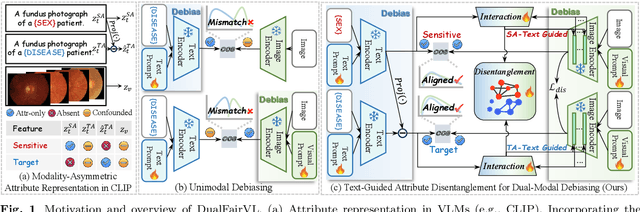
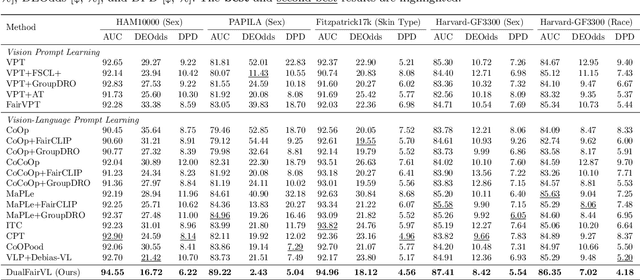
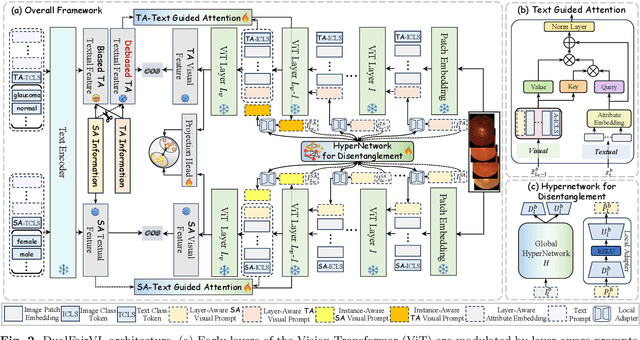
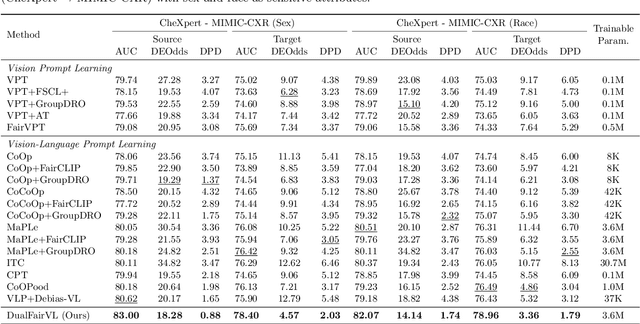
Abstract:Ensuring fairness across demographic groups in medical diagnosis is essential for equitable healthcare, particularly under distribution shifts caused by variations in imaging equipment and clinical practice. Vision-language models (VLMs) exhibit strong generalization, and text prompts encode identity attributes, enabling explicit identification and removal of sensitive directions. However, existing debiasing approaches typically address vision and text modalities independently, leaving residual cross-modal misalignment and fairness gaps. To address this challenge, we propose DualFairVL, a multimodal prompt-learning framework that jointly debiases and aligns cross-modal representations. DualFairVL employs a parallel dual-branch architecture that separates sensitive and target attributes, enabling disentangled yet aligned representations across modalities. Approximately orthogonal text anchors are constructed via linear projections, guiding cross-attention mechanisms to produce fused features. A hypernetwork further disentangles attribute-related information and generates instance-aware visual prompts, which encode dual-modal cues for fairness and robustness. Prototype-based regularization is applied in the visual branch to enforce separation of sensitive features and strengthen alignment with textual anchors. Extensive experiments on eight medical imaging datasets across four modalities show that DualFairVL achieves state-of-the-art fairness and accuracy under both in- and out-of-distribution settings, outperforming full fine-tuning and parameter-efficient baselines with only 3.6M trainable parameters. Code will be released upon publication.
ToonComposer: Streamlining Cartoon Production with Generative Post-Keyframing
Aug 14, 2025
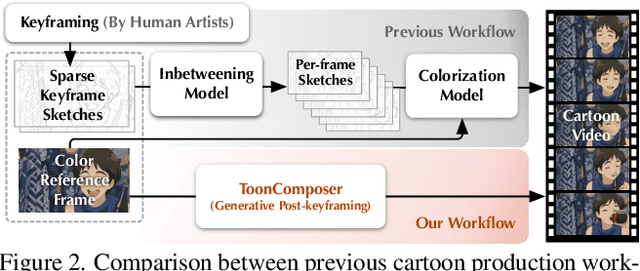
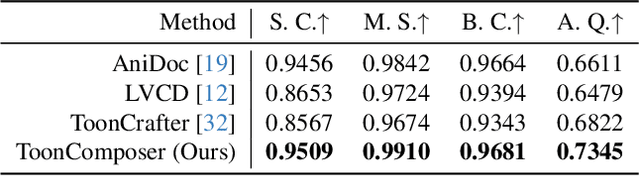
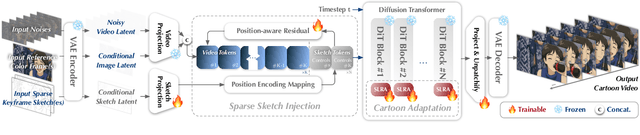
Abstract:Traditional cartoon and anime production involves keyframing, inbetweening, and colorization stages, which require intensive manual effort. Despite recent advances in AI, existing methods often handle these stages separately, leading to error accumulation and artifacts. For instance, inbetweening approaches struggle with large motions, while colorization methods require dense per-frame sketches. To address this, we introduce ToonComposer, a generative model that unifies inbetweening and colorization into a single post-keyframing stage. ToonComposer employs a sparse sketch injection mechanism to provide precise control using keyframe sketches. Additionally, it uses a cartoon adaptation method with the spatial low-rank adapter to tailor a modern video foundation model to the cartoon domain while keeping its temporal prior intact. Requiring as few as a single sketch and a colored reference frame, ToonComposer excels with sparse inputs, while also supporting multiple sketches at any temporal location for more precise motion control. This dual capability reduces manual workload and improves flexibility, empowering artists in real-world scenarios. To evaluate our model, we further created PKBench, a benchmark featuring human-drawn sketches that simulate real-world use cases. Our evaluation demonstrates that ToonComposer outperforms existing methods in visual quality, motion consistency, and production efficiency, offering a superior and more flexible solution for AI-assisted cartoon production.
ClipGS: Clippable Gaussian Splatting for Interactive Cinematic Visualization of Volumetric Medical Data
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:The visualization of volumetric medical data is crucial for enhancing diagnostic accuracy and improving surgical planning and education. Cinematic rendering techniques significantly enrich this process by providing high-quality visualizations that convey intricate anatomical details, thereby facilitating better understanding and decision-making in medical contexts. However, the high computing cost and low rendering speed limit the requirement of interactive visualization in practical applications. In this paper, we introduce ClipGS, an innovative Gaussian splatting framework with the clipping plane supported, for interactive cinematic visualization of volumetric medical data. To address the challenges posed by dynamic interactions, we propose a learnable truncation scheme that automatically adjusts the visibility of Gaussian primitives in response to the clipping plane. Besides, we also design an adaptive adjustment model to dynamically adjust the deformation of Gaussians and refine the rendering performance. We validate our method on five volumetric medical data (including CT and anatomical slice data), and reach an average 36.635 PSNR rendering quality with 156 FPS and 16.1 MB model size, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in rendering quality and efficiency.
Toward Reliable AR-Guided Surgical Navigation: Interactive Deformation Modeling with Data-Driven Biomechanics and Prompts
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:In augmented reality (AR)-guided surgical navigation, preoperative organ models are superimposed onto the patient's intraoperative anatomy to visualize critical structures such as vessels and tumors. Accurate deformation modeling is essential to maintain the reliability of AR overlays by ensuring alignment between preoperative models and the dynamically changing anatomy. Although the finite element method (FEM) offers physically plausible modeling, its high computational cost limits intraoperative applicability. Moreover, existing algorithms often fail to handle large anatomical changes, such as those induced by pneumoperitoneum or ligament dissection, leading to inaccurate anatomical correspondences and compromised AR guidance. To address these challenges, we propose a data-driven biomechanics algorithm that preserves FEM-level accuracy while improving computational efficiency. In addition, we introduce a novel human-in-the-loop mechanism into the deformation modeling process. This enables surgeons to interactively provide prompts to correct anatomical misalignments, thereby incorporating clinical expertise and allowing the model to adapt dynamically to complex surgical scenarios. Experiments on a publicly available dataset demonstrate that our algorithm achieves a mean target registration error of 3.42 mm. Incorporating surgeon prompts through the interactive framework further reduces the error to 2.78 mm, surpassing state-of-the-art methods in volumetric accuracy. These results highlight the ability of our framework to deliver efficient and accurate deformation modeling while enhancing surgeon-algorithm collaboration, paving the way for safer and more reliable computer-assisted surgeries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge