Yuchen Yuan
The RoboSense Challenge: Sense Anything, Navigate Anywhere, Adapt Across Platforms
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Autonomous systems are increasingly deployed in open and dynamic environments -- from city streets to aerial and indoor spaces -- where perception models must remain reliable under sensor noise, environmental variation, and platform shifts. However, even state-of-the-art methods often degrade under unseen conditions, highlighting the need for robust and generalizable robot sensing. The RoboSense 2025 Challenge is designed to advance robustness and adaptability in robot perception across diverse sensing scenarios. It unifies five complementary research tracks spanning language-grounded decision making, socially compliant navigation, sensor configuration generalization, cross-view and cross-modal correspondence, and cross-platform 3D perception. Together, these tasks form a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating real-world sensing reliability under domain shifts, sensor failures, and platform discrepancies. RoboSense 2025 provides standardized datasets, baseline models, and unified evaluation protocols, enabling large-scale and reproducible comparison of robust perception methods. The challenge attracted 143 teams from 85 institutions across 16 countries, reflecting broad community engagement. By consolidating insights from 23 winning solutions, this report highlights emerging methodological trends, shared design principles, and open challenges across all tracks, marking a step toward building robots that can sense reliably, act robustly, and adapt across platforms in real-world environments.
MEJO: MLLM-Engaged Surgical Triplet Recognition via Inter- and Intra-Task Joint Optimization
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Surgical triplet recognition, which involves identifying instrument, verb, target, and their combinations, is a complex surgical scene understanding challenge plagued by long-tailed data distribution. The mainstream multi-task learning paradigm benefiting from cross-task collaborative promotion has shown promising performance in identifying triples, but two key challenges remain: 1) inter-task optimization conflicts caused by entangling task-generic and task-specific representations; 2) intra-task optimization conflicts due to class-imbalanced training data. To overcome these difficulties, we propose the MLLM-Engaged Joint Optimization (MEJO) framework that empowers both inter- and intra-task optimization for surgical triplet recognition. For inter-task optimization, we introduce the Shared-Specific-Disentangled (S$^2$D) learning scheme that decomposes representations into task-shared and task-specific components. To enhance task-shared representations, we construct a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) powered probabilistic prompt pool to dynamically augment visual features with expert-level semantic cues. Additionally, comprehensive task-specific cues are modeled via distinct task prompts covering the temporal-spatial dimensions, effectively mitigating inter-task ambiguities. To tackle intra-task optimization conflicts, we develop a Coordinated Gradient Learning (CGL) strategy, which dissects and rebalances the positive-negative gradients originating from head and tail classes for more coordinated learning behaviors. Extensive experiments on the CholecT45 and CholecT50 datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed framework, validating its effectiveness in handling optimization conflicts.
Medical Large Vision Language Models with Multi-Image Visual Ability
May 25, 2025Abstract:Medical large vision-language models (LVLMs) have demonstrated promising performance across various single-image question answering (QA) benchmarks, yet their capability in processing multi-image clinical scenarios remains underexplored. Unlike single image based tasks, medical tasks involving multiple images often demand sophisticated visual understanding capabilities, such as temporal reasoning and cross-modal analysis, which are poorly supported by current medical LVLMs. To bridge this critical gap, we present the Med-MIM instruction dataset, comprising 83.2K medical multi-image QA pairs that span four types of multi-image visual abilities (temporal understanding, reasoning, comparison, co-reference). Using this dataset, we fine-tune Mantis and LLaVA-Med, resulting in two specialized medical VLMs: MIM-LLaVA-Med and Med-Mantis, both optimized for multi-image analysis. Additionally, we develop the Med-MIM benchmark to comprehensively evaluate the medical multi-image understanding capabilities of LVLMs. We assess eight popular LVLMs, including our two models, on the Med-MIM benchmark. Experimental results show that both Med-Mantis and MIM-LLaVA-Med achieve superior performance on the held-in and held-out subsets of the Med-MIM benchmark, demonstrating that the Med-MIM instruction dataset effectively enhances LVLMs' multi-image understanding capabilities in the medical domain.
MedHallTune: An Instruction-Tuning Benchmark for Mitigating Medical Hallucination in Vision-Language Models
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:The increasing use of vision-language models (VLMs) in healthcare applications presents great challenges related to hallucinations, in which the models may generate seemingly plausible results that are in fact incorrect. Such hallucinations can jeopardize clinical decision making, potentially harming the diagnosis and treatments. In this work, we propose MedHallTune, a large-scale benchmark designed specifically to evaluate and mitigate hallucinations in medical VLMs. Comprising over 100,000 images and 1,000,000 instruction pairs, MedHallTune includes both hallucination and non-hallucination samples, each with ground-truth annotations. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation of current medical and general VLMs using MedHallTune, assessing their performance across key metrics, including clinical accuracy, relevance, detail level, and risk level. The experimental results show that fine-tuning with MedHallTune successfully improves the ability of several existing models to manage hallucinations and boost their zero-shot performance on downstream visual-question-answering (VQA) tasks, making them more reliable for practical medical applications. Our work contributes to the development of more trustworthy VLMs. Codes and dataset will be available at \href{https://github.com/russellyq/MedHallTune}{MedHallTune}.
Multi-scale Spatio-temporal Transformer-based Imbalanced Longitudinal Learning for Glaucoma Forecasting from Irregular Time Series Images
Feb 21, 2024



Abstract:Glaucoma is one of the major eye diseases that leads to progressive optic nerve fiber damage and irreversible blindness, afflicting millions of individuals. Glaucoma forecast is a good solution to early screening and intervention of potential patients, which is helpful to prevent further deterioration of the disease. It leverages a series of historical fundus images of an eye and forecasts the likelihood of glaucoma occurrence in the future. However, the irregular sampling nature and the imbalanced class distribution are two challenges in the development of disease forecasting approaches. To this end, we introduce the Multi-scale Spatio-temporal Transformer Network (MST-former) based on the transformer architecture tailored for sequential image inputs, which can effectively learn representative semantic information from sequential images on both temporal and spatial dimensions. Specifically, we employ a multi-scale structure to extract features at various resolutions, which can largely exploit rich spatial information encoded in each image. Besides, we design a time distance matrix to scale time attention in a non-linear manner, which could effectively deal with the irregularly sampled data. Furthermore, we introduce a temperature-controlled Balanced Softmax Cross-entropy loss to address the class imbalance issue. Extensive experiments on the Sequential fundus Images for Glaucoma Forecast (SIGF) dataset demonstrate the superiority of the proposed MST-former method, achieving an AUC of 98.6% for glaucoma forecasting. Besides, our method shows excellent generalization capability on the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) MRI dataset, with an accuracy of 90.3% for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease prediction, outperforming the compared method by a large margin.
PointTrack++ for Effective Online Multi-Object Tracking and Segmentation
Jul 03, 2020
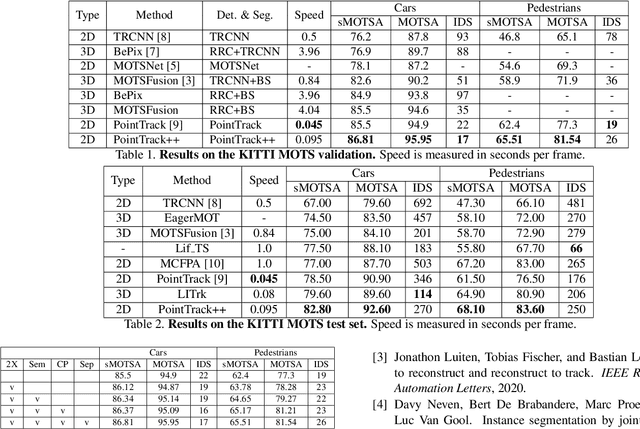

Abstract:Multiple-object tracking and segmentation (MOTS) is a novel computer vision task that aims to jointly perform multiple object tracking (MOT) and instance segmentation. In this work, we present PointTrack++, an effective on-line framework for MOTS, which remarkably extends our recently proposed PointTrack framework. To begin with, PointTrack adopts an efficient one-stage framework for instance segmentation, and learns instance embeddings by converting compact image representations to un-ordered 2D point cloud. Compared with PointTrack, our proposed PointTrack++ offers three major improvements. Firstly, in the instance segmentation stage, we adopt a semantic segmentation decoder trained with focal loss to improve the instance selection quality. Secondly, to further boost the segmentation performance, we propose a data augmentation strategy by copy-and-paste instances into training images. Finally, we introduce a better training strategy in the instance association stage to improve the distinguishability of learned instance embeddings. The resulting framework achieves the state-of-the-art performance on the 5th BMTT MOTChallenge.
Perspective-Guided Convolution Networks for Crowd Counting
Sep 16, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel perspective-guided convolution (PGC) for convolutional neural network (CNN) based crowd counting (i.e. PGCNet), which aims to overcome the dramatic intra-scene scale variations of people due to the perspective effect. While most state-of-the-arts adopt multi-scale or multi-column architectures to address such issue, they generally fail in modeling continuous scale variations since only discrete representative scales are considered. PGCNet, on the other hand, utilizes perspective information to guide the spatially variant smoothing of feature maps before feeding them to the successive convolutions. An effective perspective estimation branch is also introduced to PGCNet, which can be trained in either supervised setting or weakly-supervised setting when the branch has been pre-trained. Our PGCNet is single-column with moderate increase in computation, and extensive experimental results on four benchmark datasets show the improvements of our method against the state-of-the-arts. Additionally, we also introduce Crowd Surveillance, a large scale dataset for crowd counting that contains 13,000+ high-resolution images with challenging scenarios.
* Accepted by ICCV 2019
Recognizing Part Attributes with Insufficient Data
Aug 13, 2019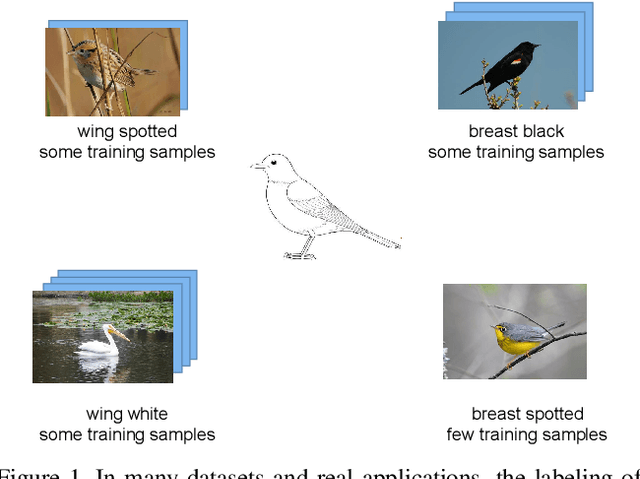

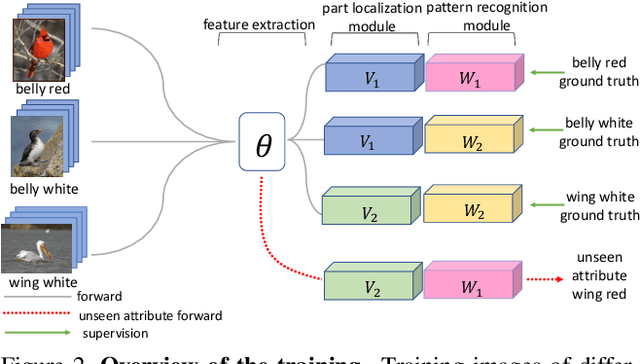

Abstract:Recognizing attributes of objects and their parts is important to many computer vision applications. Although great progress has been made to apply object-level recognition, recognizing the attributes of parts remains less applicable since the training data for part attributes recognition is usually scarce especially for internet-scale applications. Furthermore, most existing part attribute recognition methods rely on the part annotation which is more expensive to obtain. To solve the data insufficiency problem and get rid of dependence on the part annotation, we introduce a novel Concept Sharing Network (CSN) for part attribute recognition. A great advantage of CSN is its capability of recognizing the part attribute (a combination of part location and appearance pattern) that has insufficient or zero training data, by learning the part location and appearance pattern respectively from the training data that usually mix them in a single label. Extensive experiments on CUB-200-2011 [51], CelebA [35] and a newly proposed human attribute dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of CSN and its advantages over other methods, especially for the attributes with few training samples. Further experiments show that CSN can also perform zero-shot part attribute recognition. The code will be made available at https://github.com/Zhaoxiangyun/Concept-Sharing-Network.
Deep Density-aware Count Regressor
Aug 09, 2019
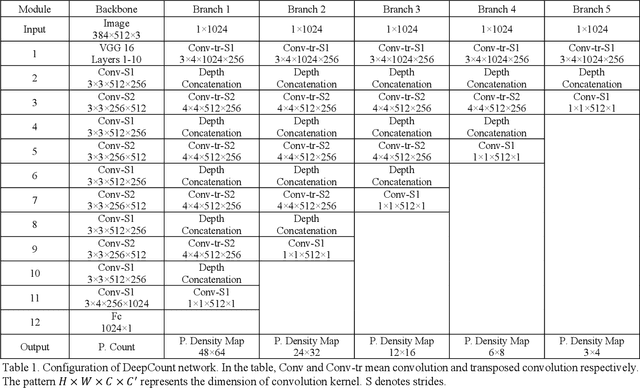
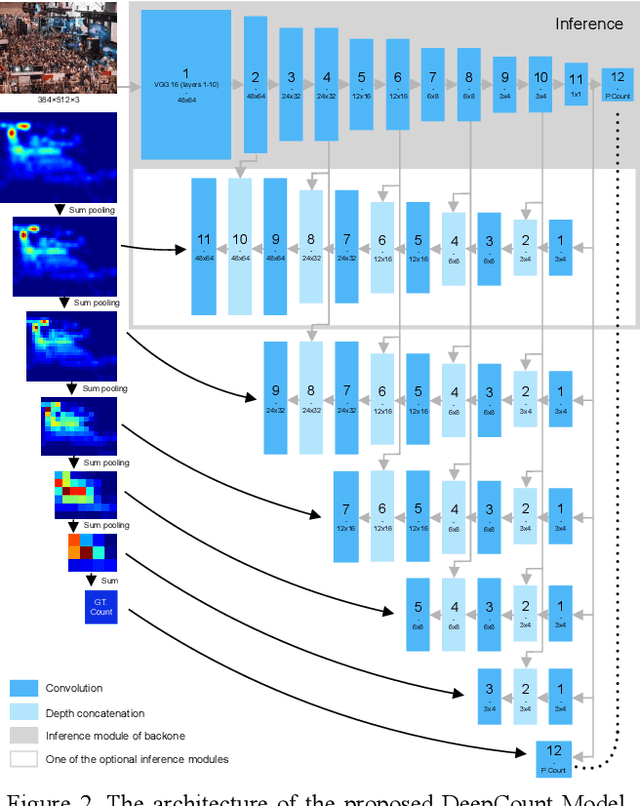
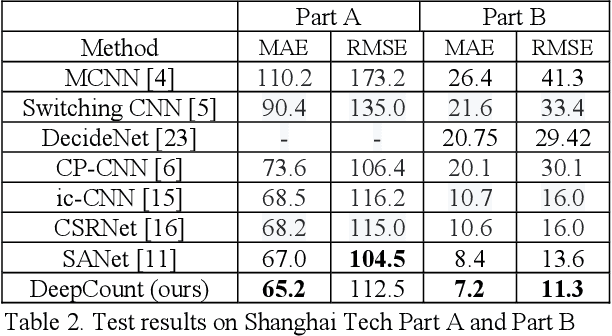
Abstract:We seek to improve crowd counting as we perceive limits of currently prevalent density map estimation approach on both prediction accuracy and time efficiency. We show that a CNN regressing a global count trained with density map supervision can make more accurate prediction. We introduce multilayer gradient fusion for training a densityaware global count regressor. More specifically, on training stage, a backbone network receives gradients from multiple branches to learn the density information, whereas those branches are to be detached to accelerate inference. By taking advantages of such method, our model improves benchmark results on public datasets and exhibits itself to be a new solution to crowd counting problem in practice.
Compact Generalized Non-local Network
Nov 01, 2018
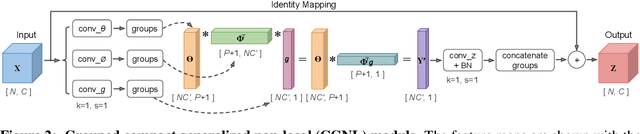
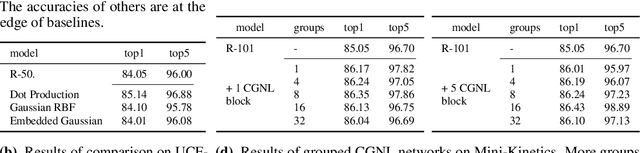

Abstract:The non-local module is designed for capturing long-range spatio-temporal dependencies in images and videos. Although having shown excellent performance, it lacks the mechanism to model the interactions between positions across channels, which are of vital importance in recognizing fine-grained objects and actions. To address this limitation, we generalize the non-local module and take the correlations between the positions of any two channels into account. This extension utilizes the compact representation for multiple kernel functions with Taylor expansion that makes the generalized non-local module in a fast and low-complexity computation flow. Moreover, we implement our generalized non-local method within channel groups to ease the optimization. Experimental results illustrate the clear-cut improvements and practical applicability of the generalized non-local module on both fine-grained object recognition and video classification. Code is available at: https://github.com/KaiyuYue/cgnl-network.pytorch.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge