Zhao Wang
ProRAG: Process-Supervised Reinforcement Learning for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has become a promising paradigm for optimizing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) in complex reasoning tasks. However, traditional outcome-based RL approaches often suffer from reward sparsity and inefficient credit assignment, as coarse-grained scalar rewards fail to identify specific erroneous steps within long-horizon trajectories. This ambiguity frequently leads to "process hallucinations", where models reach correct answers through flawed logic or redundant retrieval steps. Although recent process-aware approaches attempt to mitigate this via static preference learning or heuristic reward shaping, they often lack the on-policy exploration capabilities required to decouple step-level credit from global outcomes. To address these challenges, we propose ProRAG, a process-supervised reinforcement learning framework designed to integrate learned step-level supervision into the online optimization loop. Our framework consists of four stages: (1) Supervised Policy Warmup to initialize the model with a structured reasoning format; (2) construction of an MCTS-based Process Reward Model (PRM) to quantify intermediate reasoning quality; (3) PRM-Guided Reasoning Refinement to align the policy with fine-grained process preferences; and (4) Process-Supervised Reinforcement Learning with a dual-granularity advantage mechanism. By aggregating step-level process rewards with global outcome signals, ProRAG provides precise feedback for every action. Extensive experiments on five multi-hop reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that ProRAG achieves superior overall performance compared to strong outcome-based and process-aware RL baselines, particularly on complex long-horizon tasks, validating the effectiveness of fine-grained process supervision. The code and model are available at https://github.com/lilinwz/ProRAG.
Entropy-Guided k-Guard Sampling for Long-Horizon Autoregressive Video Generation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) architectures have achieved significant successes in LLMs, inspiring explorations for video generation. In LLMs, top-p/top-k sampling strategies work exceptionally well: language tokens have high semantic density and low redundancy, so a fixed size of token candidates already strikes a balance between semantic accuracy and generation diversity. In contrast, video tokens have low semantic density and high spatio-temporal redundancy. This mismatch makes static top-k/top-p strategies ineffective for video decoders: they either introduce unnecessary randomness for low-uncertainty regions (static backgrounds) or get stuck in early errors for high-uncertainty regions (foreground objects). Prediction errors will accumulate as more frames are generated and eventually severely degrade long-horizon quality. To address this, we propose Entropy-Guided k-Guard (ENkG) sampling, a simple yet effective strategy that adapts sampling to token-wise dispersion, quantified by the entropy of each token's predicted distribution. ENkG uses adaptive token candidate sizes: for low-entropy regions, it employs fewer candidates to suppress redundant noise and preserve structural integrity; for high-entropy regions, it uses more candidates to mitigate error compounding. ENkG is model-agnostic, training-free, and adds negligible overhead. Experiments demonstrate consistent improvements in perceptual quality and structural stability compared to static top-k/top-p strategies.
NextFlow: Unified Sequential Modeling Activates Multimodal Understanding and Generation
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:We present NextFlow, a unified decoder-only autoregressive transformer trained on 6 trillion interleaved text-image discrete tokens. By leveraging a unified vision representation within a unified autoregressive architecture, NextFlow natively activates multimodal understanding and generation capabilities, unlocking abilities of image editing, interleaved content and video generation. Motivated by the distinct nature of modalities - where text is strictly sequential and images are inherently hierarchical - we retain next-token prediction for text but adopt next-scale prediction for visual generation. This departs from traditional raster-scan methods, enabling the generation of 1024x1024 images in just 5 seconds - orders of magnitude faster than comparable AR models. We address the instabilities of multi-scale generation through a robust training recipe. Furthermore, we introduce a prefix-tuning strategy for reinforcement learning. Experiments demonstrate that NextFlow achieves state-of-the-art performance among unified models and rivals specialized diffusion baselines in visual quality.
OpenGround: Active Cognition-based Reasoning for Open-World 3D Visual Grounding
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:3D visual grounding aims to locate objects based on natural language descriptions in 3D scenes. Existing methods rely on a pre-defined Object Lookup Table (OLT) to query Visual Language Models (VLMs) for reasoning about object locations, which limits the applications in scenarios with undefined or unforeseen targets. To address this problem, we present OpenGround, a novel zero-shot framework for open-world 3D visual grounding. Central to OpenGround is the Active Cognition-based Reasoning (ACR) module, which is designed to overcome the fundamental limitation of pre-defined OLTs by progressively augmenting the cognitive scope of VLMs. The ACR module performs human-like perception of the target via a cognitive task chain and actively reasons about contextually relevant objects, thereby extending VLM cognition through a dynamically updated OLT. This allows OpenGround to function with both pre-defined and open-world categories. We also propose a new dataset named OpenTarget, which contains over 7000 object-description pairs to evaluate our method in open-world scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OpenGround achieves competitive performance on Nr3D, state-of-the-art on ScanRefer, and delivers a substantial 17.6% improvement on OpenTarget. Project Page at https://why-102.github.io/openground.io/.
AIM: Software and Hardware Co-design for Architecture-level IR-drop Mitigation in High-performance PIM
Nov 06, 2025



Abstract:SRAM Processing-in-Memory (PIM) has emerged as the most promising implementation for high-performance PIM, delivering superior computing density, energy efficiency, and computational precision. However, the pursuit of higher performance necessitates more complex circuit designs and increased operating frequencies, which exacerbate IR-drop issues. Severe IR-drop can significantly degrade chip performance and even threaten reliability. Conventional circuit-level IR-drop mitigation methods, such as back-end optimizations, are resource-intensive and often compromise power, performance, and area (PPA). To address these challenges, we propose AIM, comprehensive software and hardware co-design for architecture-level IR-drop mitigation in high-performance PIM. Initially, leveraging the bit-serial and in-situ dataflow processing properties of PIM, we introduce Rtog and HR, which establish a direct correlation between PIM workloads and IR-drop. Building on this foundation, we propose LHR and WDS, enabling extensive exploration of architecture-level IR-drop mitigation while maintaining computational accuracy through software optimization. Subsequently, we develop IR-Booster, a dynamic adjustment mechanism that integrates software-level HR information with hardware-based IR-drop monitoring to adapt the V-f pairs of the PIM macro, achieving enhanced energy efficiency and performance. Finally, we propose the HR-aware task mapping method, bridging software and hardware designs to achieve optimal improvement. Post-layout simulation results on a 7nm 256-TOPS PIM chip demonstrate that AIM achieves up to 69.2% IR-drop mitigation, resulting in 2.29x energy efficiency improvement and 1.152x speedup.
SAMRI: Segment Anything Model for MRI
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Accurate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) segmentation is crucial for clinical decision-making, but remains labor-intensive when performed manually. Convolutional neural network (CNN)-based methods can be accurate and efficient, but often generalize poorly to MRI's variable contrast, intensity inhomogeneity, and protocols. Although the transformer-based Segment Anything Model (SAM) has demonstrated remarkable generalizability in natural images, existing adaptations often treat MRI as another imaging modality, overlooking these modality-specific challenges. We present SAMRI, an MRI-specialized SAM trained and validated on 1.1 million labeled MR slices spanning whole-body organs and pathologies. We demonstrate that SAM can be effectively adapted to MRI by simply fine-tuning its mask decoder using a two-stage strategy, reducing training time by 94% and trainable parameters by 96% versus full-model retraining. Across diverse MRI segmentation tasks, SAMRI achieves a mean Dice of 0.87, delivering state-of-the-art accuracy across anatomical regions and robust generalization on unseen structures, particularly small and clinically important structures.
CoAR: Concept Injection into Autoregressive Models for Personalized Text-to-Image Generation
Aug 10, 2025



Abstract:The unified autoregressive (AR) model excels at multimodal understanding and generation, but its potential for customized image generation remains underexplored. Existing customized generation methods rely on full fine-tuning or adapters, making them costly and prone to overfitting or catastrophic forgetting. In this paper, we propose \textbf{CoAR}, a novel framework for injecting subject concepts into the unified AR models while keeping all pre-trained parameters completely frozen. CoAR learns effective, specific subject representations with only a minimal number of parameters using a Layerwise Multimodal Context Learning strategy. To address overfitting and language drift, we further introduce regularization that preserves the pre-trained distribution and anchors context tokens to improve subject fidelity and re-contextualization. Additionally, CoAR supports training-free subject customization in a user-provided style. Experiments demonstrate that CoAR achieves superior performance on both subject-driven personalization and style personalization, while delivering significant gains in computational and memory efficiency. Notably, CoAR tunes less than \textbf{0.05\%} of the parameters while achieving competitive performance compared to recent Proxy-Tuning. Code: https://github.com/KZF-kzf/CoAR
OMS: On-the-fly, Multi-Objective, Self-Reflective Ad Keyword Generation via LLM Agent
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Keyword decision in Sponsored Search Advertising is critical to the success of ad campaigns. While LLM-based methods offer automated keyword generation, they face three major limitations: reliance on large-scale query-keyword pair data, lack of online multi-objective performance monitoring and optimization, and weak quality control in keyword selection. These issues hinder the agentic use of LLMs in fully automating keyword decisions by monitoring and reasoning over key performance indicators such as impressions, clicks, conversions, and CTA effectiveness. To overcome these challenges, we propose OMS, a keyword generation framework that is On-the-fly (requires no training data, monitors online performance, and adapts accordingly), Multi-objective (employs agentic reasoning to optimize keywords based on multiple performance metrics), and Self-reflective (agentically evaluates keyword quality). Experiments on benchmarks and real-world ad campaigns show that OMS outperforms existing methods; ablation and human evaluations confirm the effectiveness of each component and the quality of generated keywords.
DyST-XL: Dynamic Layout Planning and Content Control for Compositional Text-to-Video Generation
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:Compositional text-to-video generation, which requires synthesizing dynamic scenes with multiple interacting entities and precise spatial-temporal relationships, remains a critical challenge for diffusion-based models. Existing methods struggle with layout discontinuity, entity identity drift, and implausible interaction dynamics due to unconstrained cross-attention mechanisms and inadequate physics-aware reasoning. To address these limitations, we propose DyST-XL, a \textbf{training-free} framework that enhances off-the-shelf text-to-video models (e.g., CogVideoX-5B) through frame-aware control. DyST-XL integrates three key innovations: (1) A Dynamic Layout Planner that leverages large language models (LLMs) to parse input prompts into entity-attribute graphs and generates physics-aware keyframe layouts, with intermediate frames interpolated via trajectory optimization; (2) A Dual-Prompt Controlled Attention Mechanism that enforces localized text-video alignment through frame-aware attention masking, achieving the precise control over individual entities; and (3) An Entity-Consistency Constraint strategy that propagates first-frame feature embeddings to subsequent frames during denoising, preserving object identity without manual annotation. Experiments demonstrate that DyST-XL excels in compositional text-to-video generation, significantly improving performance on complex prompts and bridging a crucial gap in training-free video synthesis.
DreamFuse: Adaptive Image Fusion with Diffusion Transformer
Apr 11, 2025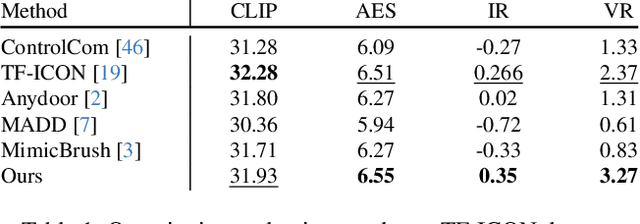
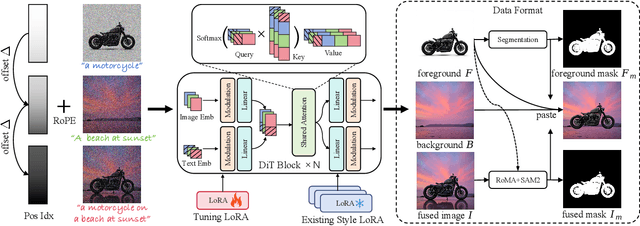
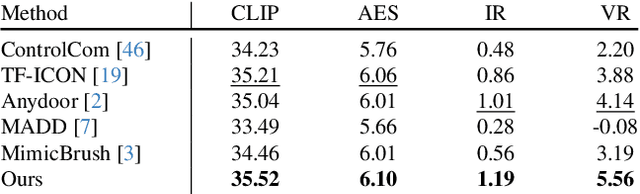
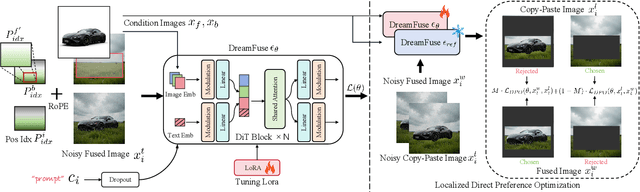
Abstract:Image fusion seeks to seamlessly integrate foreground objects with background scenes, producing realistic and harmonious fused images. Unlike existing methods that directly insert objects into the background, adaptive and interactive fusion remains a challenging yet appealing task. It requires the foreground to adjust or interact with the background context, enabling more coherent integration. To address this, we propose an iterative human-in-the-loop data generation pipeline, which leverages limited initial data with diverse textual prompts to generate fusion datasets across various scenarios and interactions, including placement, holding, wearing, and style transfer. Building on this, we introduce DreamFuse, a novel approach based on the Diffusion Transformer (DiT) model, to generate consistent and harmonious fused images with both foreground and background information. DreamFuse employs a Positional Affine mechanism to inject the size and position of the foreground into the background, enabling effective foreground-background interaction through shared attention. Furthermore, we apply Localized Direct Preference Optimization guided by human feedback to refine DreamFuse, enhancing background consistency and foreground harmony. DreamFuse achieves harmonious fusion while generalizing to text-driven attribute editing of the fused results. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches across multiple metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge