Jiaming Zhang
SGR3 Model: Scene Graph Retrieval-Reasoning Model in 3D
Mar 04, 2026Abstract:3D scene graphs provide a structured representation of object entities and their relationships, enabling high-level interpretation and reasoning for robots while remaining intuitively understandable to humans. Existing approaches for 3D scene graph generation typically combine scene reconstruction with graph neural networks (GNNs). However, such pipelines require multi-modal data that may not always be available, and their reliance on heuristic graph construction can constrain the prediction of relationship triplets. In this work, we introduce a Scene Graph Retrieval-Reasoning Model in 3D (SGR3 Model), a training-free framework that leverages multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) for semantic scene graph generation. SGR3 Model bypasses the need for explicit 3D reconstruction. Instead, it enhances relational reasoning by incorporating semantically aligned scene graphs retrieved via a ColPali-style cross-modal framework. To improve retrieval robustness, we further introduce a weighted patch-level similarity selection mechanism that mitigates the negative impact of blurry or semantically uninformative regions. Experiments demonstrate that SGR3 Model achieves competitive performance compared to training-free baselines and on par with GNN-based expert models. Moreover, an ablation study on the retrieval module and knowledge base scale reveals that retrieved external information is explicitly integrated into the token generation process, rather than being implicitly internalized through abstraction.
ICON: Indirect Prompt Injection Defense for Agents based on Inference-Time Correction
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) agents are susceptible to Indirect Prompt Injection (IPI) attacks, where malicious instructions in retrieved content hijack the agent's execution. Existing defenses typically rely on strict filtering or refusal mechanisms, which suffer from a critical limitation: over-refusal, prematurely terminating valid agentic workflows. We propose ICON, a probing-to-mitigation framework that neutralizes attacks while preserving task continuity. Our key insight is that IPI attacks leave distinct over-focusing signatures in the latent space. We introduce a Latent Space Trace Prober to detect attacks based on high intensity scores. Subsequently, a Mitigating Rectifier performs surgical attention steering that selectively manipulate adversarial query key dependencies while amplifying task relevant elements to restore the LLM's functional trajectory. Extensive evaluations on multiple backbones show that ICON achieves a competitive 0.4% ASR, matching commercial grade detectors, while yielding a over 50% task utility gain. Furthermore, ICON demonstrates robust Out of Distribution(OOD) generalization and extends effectively to multi-modal agents, establishing a superior balance between security and efficiency.
AdapTools: Adaptive Tool-based Indirect Prompt Injection Attacks on Agentic LLMs
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:The integration of external data services (e.g., Model Context Protocol, MCP) has made large language model-based agents increasingly powerful for complex task execution. However, this advancement introduces critical security vulnerabilities, particularly indirect prompt injection (IPI) attacks. Existing attack methods are limited by their reliance on static patterns and evaluation on simple language models, failing to address the fast-evolving nature of modern AI agents. We introduce AdapTools, a novel adaptive IPI attack framework that selects stealthier attack tools and generates adaptive attack prompts to create a rigorous security evaluation environment. Our approach comprises two key components: (1) Adaptive Attack Strategy Construction, which develops transferable adversarial strategies for prompt optimization, and (2) Attack Enhancement, which identifies stealthy tools capable of circumventing task-relevance defenses. Comprehensive experimental evaluation shows that AdapTools achieves a 2.13 times improvement in attack success rate while degrading system utility by a factor of 1.78. Notably, the framework maintains its effectiveness even against state-of-the-art defense mechanisms. Our method advances the understanding of IPI attacks and provides a useful reference for future research.
Jointly Optimizing Debiased CTR and Uplift for Coupons Marketing: A Unified Causal Framework
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:In online advertising, marketing interventions such as coupons introduce significant confounding bias into Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction. Observed clicks reflect a mixture of users' intrinsic preferences and the uplift induced by these interventions. This causes conventional models to miscalibrate base CTRs, which distorts downstream ranking and billing decisions. Furthermore, marketing interventions often operate as multi-valued treatments with varying magnitudes, introducing additional complexity to CTR prediction. To address these issues, we propose the \textbf{Uni}fied \textbf{M}ulti-\textbf{V}alued \textbf{T}reatment Network (UniMVT). Specifically, UniMVT disentangles confounding factors from treatment-sensitive representations, enabling a full-space counterfactual inference module to jointly reconstruct the debiased base CTR and intensity-response curves. To handle the complexity of multi-valued treatments, UniMVT employs an auxiliary intensity estimation task to capture treatment propensities and devise a unit uplift objective that normalizes the intervention effect. This ensures comparable estimation across the continuous coupon-value spectrum. UniMVT simultaneously achieves debiased CTR prediction for accurate system calibration and precise uplift estimation for incentive allocation. Extensive experiments on synthetic and industrial datasets demonstrate UniMVT's superiority in both predictive accuracy and calibration. Furthermore, real-world A/B tests confirm that UniMVT significantly improves business metrics through more effective coupon distribution.
Bagging-Based Model Merging for Robust General Text Embeddings
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:General-purpose text embedding models underpin a wide range of NLP and information retrieval applications, and are typically trained on large-scale multi-task corpora to encourage broad generalization. However, it remains unclear how different multi-task training strategies compare in practice, and how to efficiently adapt embedding models as new domains and data types continually emerge. In this work, we present a systematic study of multi-task training for text embeddings from two perspectives: data scheduling and model merging. We compare batch-level shuffling, sequential training variants, two-stage training, and multiple merging granularities, and find that simple batch-level shuffling consistently yields the strongest overall performance, suggesting that task conflicts are limited and training datasets are largely complementary. Despite its effectiveness, batch-level shuffling exhibits two practical limitations: suboptimal out-of-domain (OOD) generalization and poor suitability for incremental learning due to expensive full retraining. To address these issues, we propose Bagging-based rObust mOdel Merging (\modelname), which trains multiple embedding models on sampled subsets and merges them into a single model, improving robustness while retaining single-model inference efficiency. Moreover, \modelname naturally supports efficient incremental updates by training lightweight update models on new data with a small historical subset and merging them into the existing model. Experiments across diverse embedding benchmarks demonstrate that \modelname consistently improves both in-domain and OOD performance over full-corpus batch-level shuffling, while substantially reducing training cost in incremental learning settings.
Understanding the Impact of Differentially Private Training on Memorization of Long-Tailed Data
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Recent research shows that modern deep learning models achieve high predictive accuracy partly by memorizing individual training samples. Such memorization raises serious privacy concerns, motivating the widespread adoption of differentially private training algorithms such as DP-SGD. However, a growing body of empirical work shows that DP-SGD often leads to suboptimal generalization performance, particularly on long-tailed data that contain a large number of rare or atypical samples. Despite these observations, a theoretical understanding of this phenomenon remains largely unexplored, and existing differential privacy analysis are difficult to extend to the nonconvex and nonsmooth neural networks commonly used in practice. In this work, we develop the first theoretical framework for analyzing DP-SGD on long-tailed data from a feature learning perspective. We show that the test error of DP-SGD-trained models on the long-tailed subpopulation is significantly larger than the overall test error over the entire dataset. Our analysis further characterizes the training dynamics of DP-SGD, demonstrating how gradient clipping and noise injection jointly adversely affect the model's ability to memorize informative but underrepresented samples. Finally, we validate our theoretical findings through extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
GUITester: Enabling GUI Agents for Exploratory Defect Discovery
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Exploratory GUI testing is essential for software quality but suffers from high manual costs. While Multi-modal Large Language Model (MLLM) agents excel in navigation, they fail to autonomously discover defects due to two core challenges: \textit{Goal-Oriented Masking}, where agents prioritize task completion over reporting anomalies, and \textit{Execution-Bias Attribution}, where system defects are misidentified as agent errors. To address these, we first introduce \textbf{GUITestBench}, the first interactive benchmark for this task, featuring 143 tasks across 26 defects. We then propose \textbf{GUITester}, a multi-agent framework that decouples navigation from verification via two modules: (i) a \textit{Planning-Execution Module (PEM)} that proactively probes for defects via embedded testing intents, and (ii) a \textit{Hierarchical Reflection Module (HRM)} that resolves attribution ambiguity through interaction history analysis. GUITester achieves an F1-score of 48.90\% (Pass@3) on GUITestBench, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines (33.35\%). Our work demonstrates the feasibility of autonomous exploratory testing and provides a robust foundation for future GUI quality assurance~\footnote{Our code is now available in~\href{https://github.com/ADaM-BJTU/GUITestBench}{https://github.com/ADaM-BJTU/GUITestBench}}.
OccSTeP: Benchmarking 4D Occupancy Spatio-Temporal Persistence
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Autonomous driving requires a persistent understanding of 3D scenes that is robust to temporal disturbances and accounts for potential future actions. We introduce a new concept of 4D Occupancy Spatio-Temporal Persistence (OccSTeP), which aims to address two tasks: (1) reactive forecasting: ''what will happen next'' and (2) proactive forecasting: "what would happen given a specific future action". For the first time, we create a new OccSTeP benchmark with challenging scenarios (e.g., erroneous semantic labels and dropped frames). To address this task, we propose OccSTeP-WM, a tokenizer-free world model that maintains a dense voxel-based scene state and incrementally fuses spatio-temporal context over time. OccSTeP-WM leverages a linear-complexity attention backbone and a recurrent state-space module to capture long-range spatial dependencies while continually updating the scene memory with ego-motion compensation. This design enables online inference and robust performance even when historical sensor input is missing or noisy. Extensive experiments prove the effectiveness of the OccSTeP concept and our OccSTeP-WM, yielding an average semantic mIoU of 23.70% (+6.56% gain) and occupancy IoU of 35.89% (+9.26% gain). The data and code will be open source at https://github.com/FaterYU/OccSTeP.
DentalGPT: Incentivizing Multimodal Complex Reasoning in Dentistry
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Reliable interpretation of multimodal data in dentistry is essential for automated oral healthcare, yet current multimodal large language models (MLLMs) struggle to capture fine-grained dental visual details and lack sufficient reasoning ability for precise diagnosis. To address these limitations, we present DentalGPT, a specialized dental MLLM developed through high-quality domain knowledge injection and reinforcement learning. Specifically, the largest annotated multimodal dataset for dentistry to date was constructed by aggregating over 120k dental images paired with detailed descriptions that highlight diagnostically relevant visual features, making it the multimodal dataset with the most extensive collection of dental images to date. Training on this dataset significantly enhances the MLLM's visual understanding of dental conditions, while the subsequent reinforcement learning stage further strengthens its capability for multimodal complex reasoning. Comprehensive evaluations on intraoral and panoramic benchmarks, along with dental subsets of medical VQA benchmarks, show that DentalGPT achieves superior performance in disease classification and dental VQA tasks, outperforming many state-of-the-art MLLMs despite having only 7B parameters. These results demonstrate that high-quality dental data combined with staged adaptation provides an effective pathway for building capable and domain-specialized dental MLLMs.
Disrupting Hierarchical Reasoning: Adversarial Protection for Geographic Privacy in Multimodal Reasoning Models
Dec 09, 2025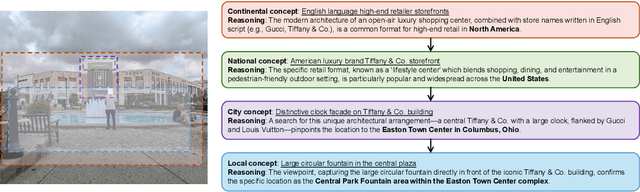
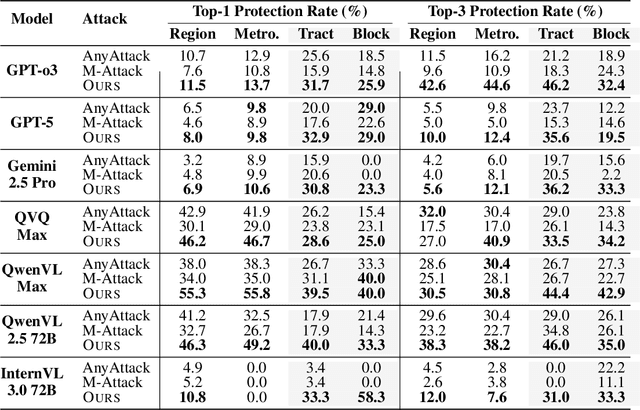
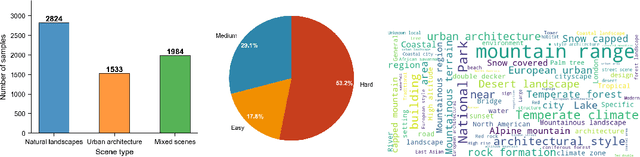
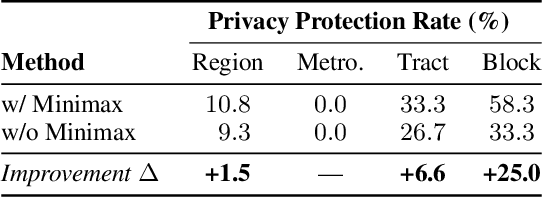
Abstract:Multi-modal large reasoning models (MLRMs) pose significant privacy risks by inferring precise geographic locations from personal images through hierarchical chain-of-thought reasoning. Existing privacy protection techniques, primarily designed for perception-based models, prove ineffective against MLRMs' sophisticated multi-step reasoning processes that analyze environmental cues. We introduce \textbf{ReasonBreak}, a novel adversarial framework specifically designed to disrupt hierarchical reasoning in MLRMs through concept-aware perturbations. Our approach is founded on the key insight that effective disruption of geographic reasoning requires perturbations aligned with conceptual hierarchies rather than uniform noise. ReasonBreak strategically targets critical conceptual dependencies within reasoning chains, generating perturbations that invalidate specific inference steps and cascade through subsequent reasoning stages. To facilitate this approach, we contribute \textbf{GeoPrivacy-6K}, a comprehensive dataset comprising 6,341 ultra-high-resolution images ($\geq$2K) with hierarchical concept annotations. Extensive evaluation across seven state-of-the-art MLRMs (including GPT-o3, GPT-5, Gemini 2.5 Pro) demonstrates ReasonBreak's superior effectiveness, achieving a 14.4\% improvement in tract-level protection (33.8\% vs 19.4\%) and nearly doubling block-level protection (33.5\% vs 16.8\%). This work establishes a new paradigm for privacy protection against reasoning-based threats.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge