Kailun Yang
TRACER: Texture-Robust Affordance Chain-of-Thought for Deformable-Object Refinement
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:The central challenge in robotic manipulation of deformable objects lies in aligning high-level semantic instructions with physical interaction points under complex appearance and texture variations. Due to near-infinite degrees of freedom, complex dynamics, and heterogeneous patterns, existing vision-based affordance prediction methods often suffer from boundary overflow and fragmented functional regions. To address these issues, we propose TRACER, a Texture-Robust Affordance Chain-of-thought with dEformable-object Refinement framework, which establishes a cross-hierarchical mapping from hierarchical semantic reasoning to appearance-robust and physically consistent functional region refinement. Specifically, a Tree-structured Affordance Chain-of-Thought (TA-CoT) is formulated to decompose high-level task intentions into hierarchical sub-task semantics, providing consistent guidance across various execution stages. To ensure spatial integrity, a Spatial-Constrained Boundary Refinement (SCBR) mechanism is introduced to suppress prediction spillover, guiding the perceptual response to converge toward authentic interaction manifolds. Furthermore, an Interactive Convergence Refinement Flow (ICRF) is developed to aggregate discrete pixels corrupted by appearance noise, significantly enhancing the spatial continuity and physical plausibility of the identified functional regions. Extensive experiments conducted on the Fine-AGDDO15 dataset and a real-world robotic platform demonstrate that TRACER significantly improves affordance grounding precision across diverse textures and patterns inherent to deformable objects. More importantly, it enhances the success rate of long-horizon tasks, effectively bridging the gap between high-level semantic reasoning and low-level physical execution. The source code and dataset will be made publicly available at https://github.com/Dikay1/TRACER.
Learning Fine-Grained Correspondence with Cross-Perspective Perception for Open-Vocabulary 6D Object Pose Estimation
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Open-vocabulary 6D object pose estimation empowers robots to manipulate arbitrary unseen objects guided solely by natural language. However, a critical limitation of existing approaches is their reliance on unconstrained global matching strategies. In open-world scenarios, trying to match anchor features against the entire query image space introduces excessive ambiguity, as target features are easily confused with background distractors. To resolve this, we propose Fine-grained Correspondence Pose Estimation (FiCoP), a framework that transitions from noise-prone global matching to spatially-constrained patch-level correspondence. Our core innovation lies in leveraging a patch-to-patch correlation matrix as a structural prior to narrowing the matching scope, effectively filtering out irrelevant clutter to prevent it from degrading pose estimation. Firstly, we introduce an object-centric disentanglement preprocessing to isolate the semantic target from environmental noise. Secondly, a Cross-Perspective Global Perception (CPGP) module is proposed to fuse dual-view features, establishing structural consensus through explicit context reasoning. Finally, we design a Patch Correlation Predictor (PCP) that generates a precise block-wise association map, acting as a spatial filter to enforce fine-grained, noise-resilient matching. Experiments on the REAL275 and Toyota-Light datasets demonstrate that FiCoP improves Average Recall by 8.0% and 6.1%, respectively, compared to the state-of-the-art method, highlighting its capability to deliver robust and generalized perception for robotic agents operating in complex, unconstrained open-world environments. The source code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/zjjqinyu/FiCoP.
Towards Real-world Lens Active Alignment with Unlabeled Data via Domain Adaptation
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Active Alignment (AA) is a key technology for the large-scale automated assembly of high-precision optical systems. Compared with labor-intensive per-model on-device calibration, a digital-twin pipeline built on optical simulation offers a substantial advantage in generating large-scale labeled data. However, complex imaging conditions induce a domain gap between simulation and real-world images, limiting the generalization of simulation-trained models. To address this, we propose augmenting a simulation baseline with minimal unlabeled real-world images captured at random misalignment positions, mitigating the gap from a domain adaptation perspective. We introduce Domain Adaptive Active Alignment (DA3), which utilizes an autoregressive domain transformation generator and an adversarial-based feature alignment strategy to distill real-world domain information via self-supervised learning. This enables the extraction of domain-invariant image degradation features to facilitate robust misalignment prediction. Experiments on two lens types reveal that DA3 improves accuracy by 46% over a purely simulation pipeline. Notably, it approaches the performance achieved with precisely labeled real-world data collected on 3 lens samples, while reducing on-device data collection time by 98.7%. The results demonstrate that domain adaptation effectively endows simulation-trained models with robust real-world performance, validating the digital-twin pipeline as a practical solution to significantly enhance the efficiency of large-scale optical assembly.
OccSTeP: Benchmarking 4D Occupancy Spatio-Temporal Persistence
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Autonomous driving requires a persistent understanding of 3D scenes that is robust to temporal disturbances and accounts for potential future actions. We introduce a new concept of 4D Occupancy Spatio-Temporal Persistence (OccSTeP), which aims to address two tasks: (1) reactive forecasting: ''what will happen next'' and (2) proactive forecasting: "what would happen given a specific future action". For the first time, we create a new OccSTeP benchmark with challenging scenarios (e.g., erroneous semantic labels and dropped frames). To address this task, we propose OccSTeP-WM, a tokenizer-free world model that maintains a dense voxel-based scene state and incrementally fuses spatio-temporal context over time. OccSTeP-WM leverages a linear-complexity attention backbone and a recurrent state-space module to capture long-range spatial dependencies while continually updating the scene memory with ego-motion compensation. This design enables online inference and robust performance even when historical sensor input is missing or noisy. Extensive experiments prove the effectiveness of the OccSTeP concept and our OccSTeP-WM, yielding an average semantic mIoU of 23.70% (+6.56% gain) and occupancy IoU of 35.89% (+9.26% gain). The data and code will be open source at https://github.com/FaterYU/OccSTeP.
OneOcc: Semantic Occupancy Prediction for Legged Robots with a Single Panoramic Camera
Nov 05, 2025Abstract:Robust 3D semantic occupancy is crucial for legged/humanoid robots, yet most semantic scene completion (SSC) systems target wheeled platforms with forward-facing sensors. We present OneOcc, a vision-only panoramic SSC framework designed for gait-introduced body jitter and 360{\deg} continuity. OneOcc combines: (i) Dual-Projection fusion (DP-ER) to exploit the annular panorama and its equirectangular unfolding, preserving 360{\deg} continuity and grid alignment; (ii) Bi-Grid Voxelization (BGV) to reason in Cartesian and cylindrical-polar spaces, reducing discretization bias and sharpening free/occupied boundaries; (iii) a lightweight decoder with Hierarchical AMoE-3D for dynamic multi-scale fusion and better long-range/occlusion reasoning; and (iv) plug-and-play Gait Displacement Compensation (GDC) learning feature-level motion correction without extra sensors. We also release two panoramic occupancy benchmarks: QuadOcc (real quadruped, first-person 360{\deg}) and Human360Occ (H3O) (CARLA human-ego 360{\deg} with RGB, Depth, semantic occupancy; standardized within-/cross-city splits). OneOcc sets new state-of-the-art (SOTA): on QuadOcc it beats strong vision baselines and popular LiDAR ones; on H3O it gains +3.83 mIoU (within-city) and +8.08 (cross-city). Modules are lightweight, enabling deployable full-surround perception for legged/humanoid robots. Datasets and code will be publicly available at https://github.com/MasterHow/OneOcc.
EReLiFM: Evidential Reliability-Aware Residual Flow Meta-Learning for Open-Set Domain Generalization under Noisy Labels
Oct 14, 2025
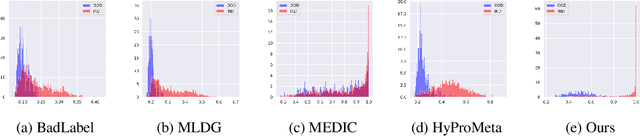


Abstract:Open-Set Domain Generalization (OSDG) aims to enable deep learning models to recognize unseen categories in new domains, which is crucial for real-world applications. Label noise hinders open-set domain generalization by corrupting source-domain knowledge, making it harder to recognize known classes and reject unseen ones. While existing methods address OSDG under Noisy Labels (OSDG-NL) using hyperbolic prototype-guided meta-learning, they struggle to bridge domain gaps, especially with limited clean labeled data. In this paper, we propose Evidential Reliability-Aware Residual Flow Meta-Learning (EReLiFM). We first introduce an unsupervised two-stage evidential loss clustering method to promote label reliability awareness. Then, we propose a residual flow matching mechanism that models structured domain- and category-conditioned residuals, enabling diverse and uncertainty-aware transfer paths beyond interpolation-based augmentation. During this meta-learning process, the model is optimized such that the update direction on the clean set maximizes the loss decrease on the noisy set, using pseudo labels derived from the most confident predicted class for supervision. Experimental results show that EReLiFM outperforms existing methods on OSDG-NL, achieving state-of-the-art performance. The source code is available at https://github.com/KPeng9510/ERELIFM.
MICA: Multi-Agent Industrial Coordination Assistant
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Industrial workflows demand adaptive and trustworthy assistance that can operate under limited computing, connectivity, and strict privacy constraints. In this work, we present MICA (Multi-Agent Industrial Coordination Assistant), a perception-grounded and speech-interactive system that delivers real-time guidance for assembly, troubleshooting, part queries, and maintenance. MICA coordinates five role-specialized language agents, audited by a safety checker, to ensure accurate and compliant support. To achieve robust step understanding, we introduce Adaptive Step Fusion (ASF), which dynamically blends expert reasoning with online adaptation from natural speech feedback. Furthermore, we establish a new multi-agent coordination benchmark across representative task categories and propose evaluation metrics tailored to industrial assistance, enabling systematic comparison of different coordination topologies. Our experiments demonstrate that MICA consistently improves task success, reliability, and responsiveness over baseline structures, while remaining deployable on practical offline hardware. Together, these contributions highlight MICA as a step toward deployable, privacy-preserving multi-agent assistants for dynamic factory environments. The source code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/Kratos-Wen/MICA.
PANORAMA: The Rise of Omnidirectional Vision in the Embodied AI Era
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Omnidirectional vision, using 360-degree vision to understand the environment, has become increasingly critical across domains like robotics, industrial inspection, and environmental monitoring. Compared to traditional pinhole vision, omnidirectional vision provides holistic environmental awareness, significantly enhancing the completeness of scene perception and the reliability of decision-making. However, foundational research in this area has historically lagged behind traditional pinhole vision. This talk presents an emerging trend in the embodied AI era: the rapid development of omnidirectional vision, driven by growing industrial demand and academic interest. We highlight recent breakthroughs in omnidirectional generation, omnidirectional perception, omnidirectional understanding, and related datasets. Drawing on insights from both academia and industry, we propose an ideal panoramic system architecture in the embodied AI era, PANORAMA, which consists of four key subsystems. Moreover, we offer in-depth opinions related to emerging trends and cross-community impacts at the intersection of panoramic vision and embodied AI, along with the future roadmap and open challenges. This overview synthesizes state-of-the-art advancements and outlines challenges and opportunities for future research in building robust, general-purpose omnidirectional AI systems in the embodied AI era.
Hallucinating 360°: Panoramic Street-View Generation via Local Scenes Diffusion and Probabilistic Prompting
Jul 09, 2025



Abstract:Panoramic perception holds significant potential for autonomous driving, enabling vehicles to acquire a comprehensive 360{\deg} surround view in a single shot. However, autonomous driving is a data-driven task. Complete panoramic data acquisition requires complex sampling systems and annotation pipelines, which are time-consuming and labor-intensive. Although existing street view generation models have demonstrated strong data regeneration capabilities, they can only learn from the fixed data distribution of existing datasets and cannot achieve high-quality, controllable panoramic generation. In this paper, we propose the first panoramic generation method Percep360 for autonomous driving. Percep360 enables coherent generation of panoramic data with control signals based on the stitched panoramic data. Percep360 focuses on two key aspects: coherence and controllability. Specifically, to overcome the inherent information loss caused by the pinhole sampling process, we propose the Local Scenes Diffusion Method (LSDM). LSDM reformulates the panorama generation as a spatially continuous diffusion process, bridging the gaps between different data distributions. Additionally, to achieve the controllable generation of panoramic images, we propose a Probabilistic Prompting Method (PPM). PPM dynamically selects the most relevant control cues, enabling controllable panoramic image generation. We evaluate the effectiveness of the generated images from three perspectives: image quality assessment (i.e., no-reference and with reference), controllability, and their utility in real-world Bird's Eye View (BEV) segmentation. Notably, the generated data consistently outperforms the original stitched images in no-reference quality metrics and enhances downstream perception models. The source code will be publicly available at https://github.com/Bryant-Teng/Percep360.
HopaDIFF: Holistic-Partial Aware Fourier Conditioned Diffusion for Referring Human Action Segmentation in Multi-Person Scenarios
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Action segmentation is a core challenge in high-level video understanding, aiming to partition untrimmed videos into segments and assign each a label from a predefined action set. Existing methods primarily address single-person activities with fixed action sequences, overlooking multi-person scenarios. In this work, we pioneer textual reference-guided human action segmentation in multi-person settings, where a textual description specifies the target person for segmentation. We introduce the first dataset for Referring Human Action Segmentation, i.e., RHAS133, built from 133 movies and annotated with 137 fine-grained actions with 33h video data, together with textual descriptions for this new task. Benchmarking existing action recognition methods on RHAS133 using VLM-based feature extractors reveals limited performance and poor aggregation of visual cues for the target person. To address this, we propose a holistic-partial aware Fourier-conditioned diffusion framework, i.e., HopaDIFF, leveraging a novel cross-input gate attentional xLSTM to enhance holistic-partial long-range reasoning and a novel Fourier condition to introduce more fine-grained control to improve the action segmentation generation. HopaDIFF achieves state-of-the-art results on RHAS133 in diverse evaluation settings. The code is available at https://github.com/KPeng9510/HopaDIFF.git.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge