Danda Pani Paudel
Advances and Innovations in the Multi-Agent Robotic System (MARS) Challenge
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in multimodal large language models and vision-languageaction models have significantly driven progress in Embodied AI. As the field transitions toward more complex task scenarios, multi-agent system frameworks are becoming essential for achieving scalable, efficient, and collaborative solutions. This shift is fueled by three primary factors: increasing agent capabilities, enhancing system efficiency through task delegation, and enabling advanced human-agent interactions. To address the challenges posed by multi-agent collaboration, we propose the Multi-Agent Robotic System (MARS) Challenge, held at the NeurIPS 2025 Workshop on SpaVLE. The competition focuses on two critical areas: planning and control, where participants explore multi-agent embodied planning using vision-language models (VLMs) to coordinate tasks and policy execution to perform robotic manipulation in dynamic environments. By evaluating solutions submitted by participants, the challenge provides valuable insights into the design and coordination of embodied multi-agent systems, contributing to the future development of advanced collaborative AI systems.
Chorus: Multi-Teacher Pretraining for Holistic 3D Gaussian Scene Encoding
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:While 3DGS has emerged as a high-fidelity scene representation, encoding rich, general-purpose features directly from its primitives remains under-explored. We address this gap by introducing Chorus, a multi-teacher pretraining framework that learns a holistic feed-forward 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) scene encoder by distilling complementary signals from 2D foundation models. Chorus employs a shared 3D encoder and teacher-specific projectors to learn from language-aligned, generalist, and object-aware teachers, encouraging a shared embedding space that captures signals from high-level semantics to fine-grained structure. We evaluate Chorus on a wide range of tasks: open-vocabulary semantic and instance segmentation, linear and decoder probing, as well as data-efficient supervision. Besides 3DGS, we also test Chorus on several benchmarks that only support point clouds by pretraining a variant using only Gaussians' centers, colors, estimated normals as inputs. Interestingly, this encoder shows strong transfer and outperforms the point clouds baseline while using 39.9 times fewer training scenes. Finally, we propose a render-and-distill adaptation that facilitates out-of-domain finetuning. Our code and model will be released upon publication.
ConceptPose: Training-Free Zero-Shot Object Pose Estimation using Concept Vectors
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Object pose estimation is a fundamental task in computer vision and robotics, yet most methods require extensive, dataset-specific training. Concurrently, large-scale vision language models show remarkable zero-shot capabilities. In this work, we bridge these two worlds by introducing ConceptPose, a framework for object pose estimation that is both training-free and model-free. ConceptPose leverages a vision-language-model (VLM) to create open-vocabulary 3D concept maps, where each point is tagged with a concept vector derived from saliency maps. By establishing robust 3D-3D correspondences across concept maps, our approach allows precise estimation of 6DoF relative pose. Without any object or dataset-specific training, our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on common zero shot relative pose estimation benchmarks, significantly outperforming existing methods by over 62% in ADD(-S) score, including those that utilize extensive dataset-specific training.
Autonomous Vehicle Path Planning by Searching With Differentiable Simulation
Nov 14, 2025



Abstract:Planning allows an agent to safely refine its actions before executing them in the real world. In autonomous driving, this is crucial to avoid collisions and navigate in complex, dense traffic scenarios. One way to plan is to search for the best action sequence. However, this is challenging when all necessary components - policy, next-state predictor, and critic - have to be learned. Here we propose Differentiable Simulation for Search (DSS), a framework that leverages the differentiable simulator Waymax as both a next state predictor and a critic. It relies on the simulator's hardcoded dynamics, making state predictions highly accurate, while utilizing the simulator's differentiability to effectively search across action sequences. Our DSS agent optimizes its actions using gradient descent over imagined future trajectories. We show experimentally that DSS - the combination of planning gradients and stochastic search - significantly improves tracking and path planning accuracy compared to sequence prediction, imitation learning, model-free RL, and other planning methods.
Multimodal Spatial Reasoning in the Large Model Era: A Survey and Benchmarks
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Humans possess spatial reasoning abilities that enable them to understand spaces through multimodal observations, such as vision and sound. Large multimodal reasoning models extend these abilities by learning to perceive and reason, showing promising performance across diverse spatial tasks. However, systematic reviews and publicly available benchmarks for these models remain limited. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of multimodal spatial reasoning tasks with large models, categorizing recent progress in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) and introducing open benchmarks for evaluation. We begin by outlining general spatial reasoning, focusing on post-training techniques, explainability, and architecture. Beyond classical 2D tasks, we examine spatial relationship reasoning, scene and layout understanding, as well as visual question answering and grounding in 3D space. We also review advances in embodied AI, including vision-language navigation and action models. Additionally, we consider emerging modalities such as audio and egocentric video, which contribute to novel spatial understanding through new sensors. We believe this survey establishes a solid foundation and offers insights into the growing field of multimodal spatial reasoning. Updated information about this survey, codes and implementation of the open benchmarks can be found at https://github.com/zhengxuJosh/Awesome-Spatial-Reasoning.
EReLiFM: Evidential Reliability-Aware Residual Flow Meta-Learning for Open-Set Domain Generalization under Noisy Labels
Oct 14, 2025
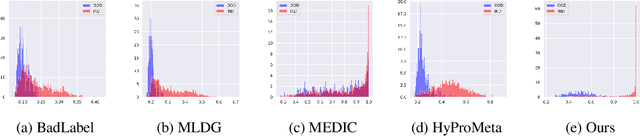


Abstract:Open-Set Domain Generalization (OSDG) aims to enable deep learning models to recognize unseen categories in new domains, which is crucial for real-world applications. Label noise hinders open-set domain generalization by corrupting source-domain knowledge, making it harder to recognize known classes and reject unseen ones. While existing methods address OSDG under Noisy Labels (OSDG-NL) using hyperbolic prototype-guided meta-learning, they struggle to bridge domain gaps, especially with limited clean labeled data. In this paper, we propose Evidential Reliability-Aware Residual Flow Meta-Learning (EReLiFM). We first introduce an unsupervised two-stage evidential loss clustering method to promote label reliability awareness. Then, we propose a residual flow matching mechanism that models structured domain- and category-conditioned residuals, enabling diverse and uncertainty-aware transfer paths beyond interpolation-based augmentation. During this meta-learning process, the model is optimized such that the update direction on the clean set maximizes the loss decrease on the noisy set, using pseudo labels derived from the most confident predicted class for supervision. Experimental results show that EReLiFM outperforms existing methods on OSDG-NL, achieving state-of-the-art performance. The source code is available at https://github.com/KPeng9510/ERELIFM.
PANORAMA: The Rise of Omnidirectional Vision in the Embodied AI Era
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Omnidirectional vision, using 360-degree vision to understand the environment, has become increasingly critical across domains like robotics, industrial inspection, and environmental monitoring. Compared to traditional pinhole vision, omnidirectional vision provides holistic environmental awareness, significantly enhancing the completeness of scene perception and the reliability of decision-making. However, foundational research in this area has historically lagged behind traditional pinhole vision. This talk presents an emerging trend in the embodied AI era: the rapid development of omnidirectional vision, driven by growing industrial demand and academic interest. We highlight recent breakthroughs in omnidirectional generation, omnidirectional perception, omnidirectional understanding, and related datasets. Drawing on insights from both academia and industry, we propose an ideal panoramic system architecture in the embodied AI era, PANORAMA, which consists of four key subsystems. Moreover, we offer in-depth opinions related to emerging trends and cross-community impacts at the intersection of panoramic vision and embodied AI, along with the future roadmap and open challenges. This overview synthesizes state-of-the-art advancements and outlines challenges and opportunities for future research in building robust, general-purpose omnidirectional AI systems in the embodied AI era.
Incremental Object Detection with Prompt-based Methods
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Visual prompt-based methods have seen growing interest in incremental learning (IL) for image classification. These approaches learn additional embedding vectors while keeping the model frozen, making them efficient to train. However, no prior work has applied such methods to incremental object detection (IOD), leaving their generalizability unclear. In this paper, we analyze three different prompt-based methods under a complex domain-incremental learning setting. We additionally provide a wide range of reference baselines for comparison. Empirically, we show that the prompt-based approaches we tested underperform in this setting. However, a strong yet practical method, combining visual prompts with replaying a small portion of previous data, achieves the best results. Together with additional experiments on prompt length and initialization, our findings offer valuable insights for advancing prompt-based IL in IOD.
From Scan to Action: Leveraging Realistic Scans for Embodied Scene Understanding
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Real-world 3D scene-level scans offer realism and can enable better real-world generalizability for downstream applications. However, challenges such as data volume, diverse annotation formats, and tool compatibility limit their use. This paper demonstrates a methodology to effectively leverage these scans and their annotations. We propose a unified annotation integration using USD, with application-specific USD flavors. We identify challenges in utilizing holistic real-world scan datasets and present mitigation strategies. The efficacy of our approach is demonstrated through two downstream applications: LLM-based scene editing, enabling effective LLM understanding and adaptation of the data (80% success), and robotic simulation, achieving an 87% success rate in policy learning.
GaussianVLM: Scene-centric 3D Vision-Language Models using Language-aligned Gaussian Splats for Embodied Reasoning and Beyond
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:As multimodal language models advance, their application to 3D scene understanding is a fast-growing frontier, driving the development of 3D Vision-Language Models (VLMs). Current methods show strong dependence on object detectors, introducing processing bottlenecks and limitations in taxonomic flexibility. To address these limitations, we propose a scene-centric 3D VLM for 3D Gaussian splat scenes that employs language- and task-aware scene representations. Our approach directly embeds rich linguistic features into the 3D scene representation by associating language with each Gaussian primitive, achieving early modality alignment. To process the resulting dense representations, we introduce a dual sparsifier that distills them into compact, task-relevant tokens via task-guided and location-guided pathways, producing sparse, task-aware global and local scene tokens. Notably, we present the first Gaussian splatting-based VLM, leveraging photorealistic 3D representations derived from standard RGB images, demonstrating strong generalization: it improves performance of prior 3D VLM five folds, in out-of-the-domain settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge