Tianwen Qian
CLIP Based Region-Aware Feature Fusion for Automated BBPS Scoring in Colonoscopy Images
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Accurate assessment of bowel cleanliness is essential for effective colonoscopy procedures. The Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) offers a standardized scoring system but suffers from subjectivity and inter-observer variability when performed manually. In this paper, to support robust training and evaluation, we construct a high-quality colonoscopy dataset comprising 2,240 images from 517 subjects, annotated with expert-agreed BBPS scores. We propose a novel automated BBPS scoring framework that leverages the CLIP model with adapter-based transfer learning and a dedicated fecal-feature extraction branch. Our method fuses global visual features with stool-related textual priors to improve the accuracy of bowel cleanliness evaluation without requiring explicit segmentation. Extensive experiments on both our dataset and the public NERTHU dataset demonstrate the superiority of our approach over existing baselines, highlighting its potential for clinical deployment in computer-aided colonoscopy analysis.
Domain-RAG: Retrieval-Guided Compositional Image Generation for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection (CD-FSOD) aims to detect novel objects with only a handful of labeled samples from previously unseen domains. While data augmentation and generative methods have shown promise in few-shot learning, their effectiveness for CD-FSOD remains unclear due to the need for both visual realism and domain alignment. Existing strategies, such as copy-paste augmentation and text-to-image generation, often fail to preserve the correct object category or produce backgrounds coherent with the target domain, making them non-trivial to apply directly to CD-FSOD. To address these challenges, we propose Domain-RAG, a training-free, retrieval-guided compositional image generation framework tailored for CD-FSOD. Domain-RAG consists of three stages: domain-aware background retrieval, domain-guided background generation, and foreground-background composition. Specifically, the input image is first decomposed into foreground and background regions. We then retrieve semantically and stylistically similar images to guide a generative model in synthesizing a new background, conditioned on both the original and retrieved contexts. Finally, the preserved foreground is composed with the newly generated domain-aligned background to form the generated image. Without requiring any additional supervision or training, Domain-RAG produces high-quality, domain-consistent samples across diverse tasks, including CD-FSOD, remote sensing FSOD, and camouflaged FSOD. Extensive experiments show consistent improvements over strong baselines and establish new state-of-the-art results. Codes will be released upon acceptance.
OmniGenBench: A Benchmark for Omnipotent Multimodal Generation across 50+ Tasks
May 24, 2025



Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in large multimodal models (LMMs), such as the impressive GPT-4o-Native, have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in following general-purpose instructions for image generation. However, current benchmarks often lack the necessary breadth and depth to fully evaluate the diverse capabilities of these models. To overcome this limitation, we introduce OmniGenBench, a novel and comprehensive benchmark meticulously designed to assess the instruction-following abilities of state-of-the-art LMMs across both perception-centric and cognition-centric dimensions. Our OmniGenBench includes 57 diverse sub-tasks grounded in real-world scenarios, systematically categorized according to the specific model capabilities they demand. For rigorous evaluation, we further employ a dual-mode protocol. This protocol utilizes off-the-shelf visual parsing tools for perception-centric tasks and a powerful LLM-based judger for cognition-centric tasks to assess the alignment between generated images and user instructions. Using OmniGenBench, we evaluate mainstream generative models, including prevalent models like GPT-4o, Gemini-2.0-Flash, and Seedream, and provide in-depth comparisons and analyses of their performance.Code and data are available at https://github.com/emilia113/OmniGenBench.
HSACNet: Hierarchical Scale-Aware Consistency Regularized Semi-Supervised Change Detection
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Semi-supervised change detection (SSCD) aims to detect changes between bi-temporal remote sensing images by utilizing limited labeled data and abundant unlabeled data. Existing methods struggle in complex scenarios, exhibiting poor performance when confronted with noisy data. They typically neglect intra-layer multi-scale features while emphasizing inter-layer fusion, harming the integrity of change objects with different scales. In this paper, we propose HSACNet, a Hierarchical Scale-Aware Consistency regularized Network for SSCD. Specifically, we integrate Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2), using its Hiera backbone as the encoder to extract inter-layer multi-scale features and applying adapters for parameter-efficient fine-tuning. Moreover, we design a Scale-Aware Differential Attention Module (SADAM) that can precisely capture intra-layer multi-scale change features and suppress noise. Additionally, a dual-augmentation consistency regularization strategy is adopted to effectively utilize the unlabeled data. Extensive experiments across four CD benchmarks demonstrate that our HSACNet achieves state-of-the-art performance, with reduced parameters and computational cost.
NeighborRetr: Balancing Hub Centrality in Cross-Modal Retrieval
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Cross-modal retrieval aims to bridge the semantic gap between different modalities, such as visual and textual data, enabling accurate retrieval across them. Despite significant advancements with models like CLIP that align cross-modal representations, a persistent challenge remains: the hubness problem, where a small subset of samples (hubs) dominate as nearest neighbors, leading to biased representations and degraded retrieval accuracy. Existing methods often mitigate hubness through post-hoc normalization techniques, relying on prior data distributions that may not be practical in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we directly mitigate hubness during training and introduce NeighborRetr, a novel method that effectively balances the learning of hubs and adaptively adjusts the relations of various kinds of neighbors. Our approach not only mitigates the hubness problem but also enhances retrieval performance, achieving state-of-the-art results on multiple cross-modal retrieval benchmarks. Furthermore, NeighborRetr demonstrates robust generalization to new domains with substantial distribution shifts, highlighting its effectiveness in real-world applications. We make our code publicly available at: https://github.com/zzezze/NeighborRetr .
Prompt as Free Lunch: Enhancing Diversity in Source-Free Cross-domain Few-shot Learning through Semantic-Guided Prompting
Dec 01, 2024



Abstract:The source-free cross-domain few-shot learning (CD-FSL) task aims to transfer pretrained models to target domains utilizing minimal samples, eliminating the need for source domain data. Addressing this issue requires models to have robust generalization abilities and strong feature representation, aligning with the characteristics of large-scale pretrained models. However, large-scale models tend to lose representational ability in cross-domain scenarios due to limited sample diversity. \zlh{Given the abundant diversity provided by semantic modality, this paper leverages textual modality to enhance training sample diversity with CLP model}, meanwhile improving model transfer efficiency. Specifically, we propose the SeGD-VPT framework, which is divided into two phases. The first step aims to increase feature diversity by adding diversity prompts to each support sample, thereby generating varying input and enhancing sample diversity. Furthermore, we use diversity descriptions of classes to guide semantically meaningful learning of diversity prompts, proposing random combinations and selections of texts to increase textual diversity. Additionally, deep prompt tuning is introduced to enhance the model's transfer capability. After training of the first step, support samples with different diversity prompts are input into the CLIP backbone to generate enhanced features. After generation, the second phase trains classifiers using the generated features. Extensive experimental results across several benchmarks verify our method is comparable to SOTA source-utilized models and attain the best performance under the source-free CD-FSL setting.
NuScenes-QA: A Multi-modal Visual Question Answering Benchmark for Autonomous Driving Scenario
May 24, 2023Abstract:We introduce a novel visual question answering (VQA) task in the context of autonomous driving, aiming to answer natural language questions based on street-view clues. Compared to traditional VQA tasks, VQA in autonomous driving scenario presents more challenges. Firstly, the raw visual data are multi-modal, including images and point clouds captured by camera and LiDAR, respectively. Secondly, the data are multi-frame due to the continuous, real-time acquisition. Thirdly, the outdoor scenes exhibit both moving foreground and static background. Existing VQA benchmarks fail to adequately address these complexities. To bridge this gap, we propose NuScenes-QA, the first benchmark for VQA in the autonomous driving scenario, encompassing 34K visual scenes and 460K question-answer pairs. Specifically, we leverage existing 3D detection annotations to generate scene graphs and design question templates manually. Subsequently, the question-answer pairs are generated programmatically based on these templates. Comprehensive statistics prove that our NuScenes-QA is a balanced large-scale benchmark with diverse question formats. Built upon it, we develop a series of baselines that employ advanced 3D detection and VQA techniques. Our extensive experiments highlight the challenges posed by this new task. Codes and dataset are available at https://github.com/qiantianwen/NuScenes-QA.
Locate before Answering: Answer Guided Question Localization for Video Question Answering
Oct 05, 2022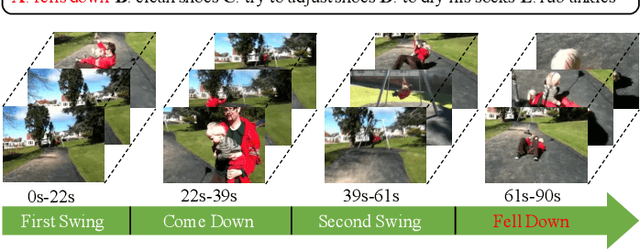
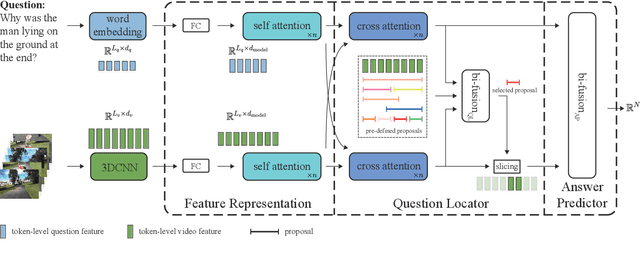
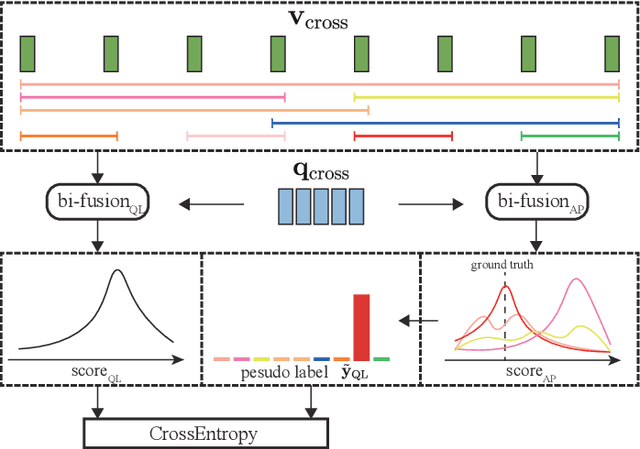
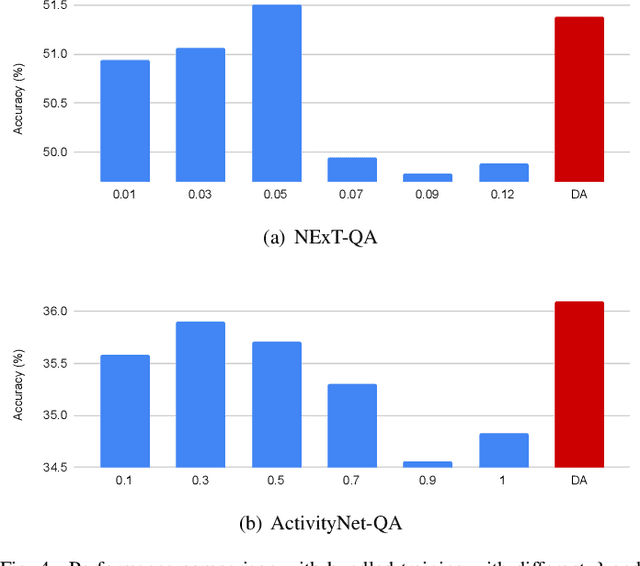
Abstract:Video question answering (VideoQA) is an essential task in vision-language understanding, which has attracted numerous research attention recently. Nevertheless, existing works mostly achieve promising performances on short videos of duration within 15 seconds. For VideoQA on minute-level long-term videos, those methods are likely to fail because of lacking the ability to deal with noise and redundancy caused by scene changes and multiple actions in the video. Considering the fact that the question often remains concentrated in a short temporal range, we propose to first locate the question to a segment in the video and then infer the answer using the located segment only. Under this scheme, we propose "Locate before Answering" (LocAns), a novel approach that integrates a question locator and an answer predictor into an end-to-end model. During the training phase, the available answer label not only serves as the supervision signal of the answer predictor, but also is used to generate pseudo temporal labels for the question locator. Moreover, we design a decoupled alternative training strategy to update the two modules separately. In the experiments, LocAns achieves state-of-the-art performance on two modern long-term VideoQA datasets NExT-QA and ActivityNet-QA, and its qualitative examples show the reliable performance of the question localization.
Video Moment Retrieval from Text Queries via Single Frame Annotation
Apr 26, 2022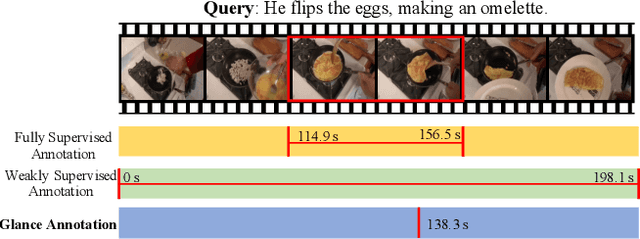
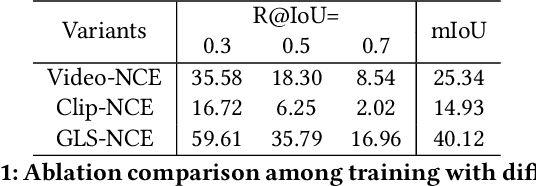
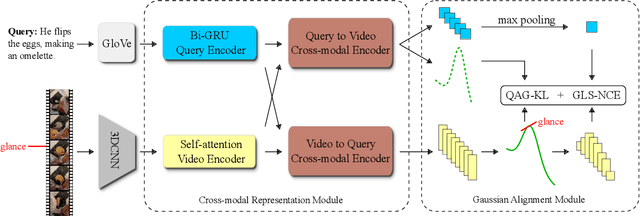
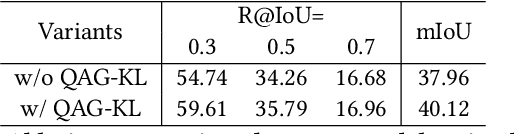
Abstract:Video moment retrieval aims at finding the start and end timestamps of a moment (part of a video) described by a given natural language query. Fully supervised methods need complete temporal boundary annotations to achieve promising results, which is costly since the annotator needs to watch the whole moment. Weakly supervised methods only rely on the paired video and query, but the performance is relatively poor. In this paper, we look closer into the annotation process and propose a new paradigm called "glance annotation". This paradigm requires the timestamp of only one single random frame, which we refer to as a "glance", within the temporal boundary of the fully supervised counterpart. We argue this is beneficial because comparing to weak supervision, trivial cost is added yet more potential in performance is provided. Under the glance annotation setting, we propose a method named as Video moment retrieval via Glance Annotation (ViGA) based on contrastive learning. ViGA cuts the input video into clips and contrasts between clips and queries, in which glance guided Gaussian distributed weights are assigned to all clips. Our extensive experiments indicate that ViGA achieves better results than the state-of-the-art weakly supervised methods by a large margin, even comparable to fully supervised methods in some cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge