Junwei Zheng
EReLiFM: Evidential Reliability-Aware Residual Flow Meta-Learning for Open-Set Domain Generalization under Noisy Labels
Oct 14, 2025


Abstract:Open-Set Domain Generalization (OSDG) aims to enable deep learning models to recognize unseen categories in new domains, which is crucial for real-world applications. Label noise hinders open-set domain generalization by corrupting source-domain knowledge, making it harder to recognize known classes and reject unseen ones. While existing methods address OSDG under Noisy Labels (OSDG-NL) using hyperbolic prototype-guided meta-learning, they struggle to bridge domain gaps, especially with limited clean labeled data. In this paper, we propose Evidential Reliability-Aware Residual Flow Meta-Learning (EReLiFM). We first introduce an unsupervised two-stage evidential loss clustering method to promote label reliability awareness. Then, we propose a residual flow matching mechanism that models structured domain- and category-conditioned residuals, enabling diverse and uncertainty-aware transfer paths beyond interpolation-based augmentation. During this meta-learning process, the model is optimized such that the update direction on the clean set maximizes the loss decrease on the noisy set, using pseudo labels derived from the most confident predicted class for supervision. Experimental results show that EReLiFM outperforms existing methods on OSDG-NL, achieving state-of-the-art performance. The source code is available at https://github.com/KPeng9510/ERELIFM.
MICA: Multi-Agent Industrial Coordination Assistant
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Industrial workflows demand adaptive and trustworthy assistance that can operate under limited computing, connectivity, and strict privacy constraints. In this work, we present MICA (Multi-Agent Industrial Coordination Assistant), a perception-grounded and speech-interactive system that delivers real-time guidance for assembly, troubleshooting, part queries, and maintenance. MICA coordinates five role-specialized language agents, audited by a safety checker, to ensure accurate and compliant support. To achieve robust step understanding, we introduce Adaptive Step Fusion (ASF), which dynamically blends expert reasoning with online adaptation from natural speech feedback. Furthermore, we establish a new multi-agent coordination benchmark across representative task categories and propose evaluation metrics tailored to industrial assistance, enabling systematic comparison of different coordination topologies. Our experiments demonstrate that MICA consistently improves task success, reliability, and responsiveness over baseline structures, while remaining deployable on practical offline hardware. Together, these contributions highlight MICA as a step toward deployable, privacy-preserving multi-agent assistants for dynamic factory environments. The source code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/Kratos-Wen/MICA.
HopaDIFF: Holistic-Partial Aware Fourier Conditioned Diffusion for Referring Human Action Segmentation in Multi-Person Scenarios
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Action segmentation is a core challenge in high-level video understanding, aiming to partition untrimmed videos into segments and assign each a label from a predefined action set. Existing methods primarily address single-person activities with fixed action sequences, overlooking multi-person scenarios. In this work, we pioneer textual reference-guided human action segmentation in multi-person settings, where a textual description specifies the target person for segmentation. We introduce the first dataset for Referring Human Action Segmentation, i.e., RHAS133, built from 133 movies and annotated with 137 fine-grained actions with 33h video data, together with textual descriptions for this new task. Benchmarking existing action recognition methods on RHAS133 using VLM-based feature extractors reveals limited performance and poor aggregation of visual cues for the target person. To address this, we propose a holistic-partial aware Fourier-conditioned diffusion framework, i.e., HopaDIFF, leveraging a novel cross-input gate attentional xLSTM to enhance holistic-partial long-range reasoning and a novel Fourier condition to introduce more fine-grained control to improve the action segmentation generation. HopaDIFF achieves state-of-the-art results on RHAS133 in diverse evaluation settings. The code is available at https://github.com/KPeng9510/HopaDIFF.git.
SAMBLE: Shape-Specific Point Cloud Sampling for an Optimal Trade-Off Between Local Detail and Global Uniformity
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Driven by the increasing demand for accurate and efficient representation of 3D data in various domains, point cloud sampling has emerged as a pivotal research topic in 3D computer vision. Recently, learning-to-sample methods have garnered growing interest from the community, particularly for their ability to be jointly trained with downstream tasks. However, previous learning-based sampling methods either lead to unrecognizable sampling patterns by generating a new point cloud or biased sampled results by focusing excessively on sharp edge details. Moreover, they all overlook the natural variations in point distribution across different shapes, applying a similar sampling strategy to all point clouds. In this paper, we propose a Sparse Attention Map and Bin-based Learning method (termed SAMBLE) to learn shape-specific sampling strategies for point cloud shapes. SAMBLE effectively achieves an improved balance between sampling edge points for local details and preserving uniformity in the global shape, resulting in superior performance across multiple common point cloud downstream tasks, even in scenarios with few-point sampling.
Exploring Video-Based Driver Activity Recognition under Noisy Labels
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:As an open research topic in the field of deep learning, learning with noisy labels has attracted much attention and grown rapidly over the past ten years. Learning with label noise is crucial for driver distraction behavior recognition, as real-world video data often contains mislabeled samples, impacting model reliability and performance. However, label noise learning is barely explored in the driver activity recognition field. In this paper, we propose the first label noise learning approach for the driver activity recognition task. Based on the cluster assumption, we initially enable the model to learn clustering-friendly low-dimensional representations from given videos and assign the resultant embeddings into clusters. We subsequently perform co-refinement within each cluster to smooth the classifier outputs. Furthermore, we propose a flexible sample selection strategy that combines two selection criteria without relying on any hyperparameters to filter clean samples from the training dataset. We also incorporate a self-adaptive parameter into the sample selection process to enforce balancing across classes. A comprehensive variety of experiments on the public Drive&Act dataset for all granularity levels demonstrates the superior performance of our method in comparison with other label-denoising methods derived from the image classification field. The source code is available at https://github.com/ilonafan/DAR-noisy-labels.
Scene-agnostic Pose Regression for Visual Localization
Mar 25, 2025



Abstract:Absolute Pose Regression (APR) predicts 6D camera poses but lacks the adaptability to unknown environments without retraining, while Relative Pose Regression (RPR) generalizes better yet requires a large image retrieval database. Visual Odometry (VO) generalizes well in unseen environments but suffers from accumulated error in open trajectories. To address this dilemma, we introduce a new task, Scene-agnostic Pose Regression (SPR), which can achieve accurate pose regression in a flexible way while eliminating the need for retraining or databases. To benchmark SPR, we created a large-scale dataset, 360SPR, with over 200K photorealistic panoramas, 3.6M pinhole images and camera poses in 270 scenes at three different sensor heights. Furthermore, a SPR-Mamba model is initially proposed to address SPR in a dual-branch manner. Extensive experiments and studies demonstrate the effectiveness of our SPR paradigm, dataset, and model. In the unknown scenes of both 360SPR and 360Loc datasets, our method consistently outperforms APR, RPR and VO. The dataset and code are available at https://junweizheng93.github.io/publications/SPR/SPR.html.
Graph-based Document Structure Analysis
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:When reading a document, glancing at the spatial layout of a document is an initial step to understand it roughly. Traditional document layout analysis (DLA) methods, however, offer only a superficial parsing of documents, focusing on basic instance detection and often failing to capture the nuanced spatial and logical relations between instances. These limitations hinder DLA-based models from achieving a gradually deeper comprehension akin to human reading. In this work, we propose a novel graph-based Document Structure Analysis (gDSA) task. This task requires that model not only detects document elements but also generates spatial and logical relations in form of a graph structure, allowing to understand documents in a holistic and intuitive manner. For this new task, we construct a relation graph-based document structure analysis dataset (GraphDoc) with 80K document images and 4.13M relation annotations, enabling training models to complete multiple tasks like reading order, hierarchical structures analysis, and complex inter-element relation inference. Furthermore, a document relation graph generator (DRGG) is proposed to address the gDSA task, which achieves performance with 57.6% at mAP$_g$@0.5 for a strong benchmark baseline on this novel task and dataset. We hope this graphical representation of document structure can mark an innovative advancement in document structure analysis and understanding. The new dataset and code will be made publicly available at https://yufanchen96.github.io/projects/GraphDoc.
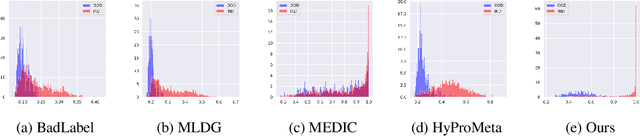
Mitigating Label Noise using Prompt-Based Hyperbolic Meta-Learning in Open-Set Domain Generalization
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:Open-Set Domain Generalization (OSDG) is a challenging task requiring models to accurately predict familiar categories while minimizing confidence for unknown categories to effectively reject them in unseen domains. While the OSDG field has seen considerable advancements, the impact of label noise--a common issue in real-world datasets--has been largely overlooked. Label noise can mislead model optimization, thereby exacerbating the challenges of open-set recognition in novel domains. In this study, we take the first step towards addressing Open-Set Domain Generalization under Noisy Labels (OSDG-NL) by constructing dedicated benchmarks derived from widely used OSDG datasets, including PACS and DigitsDG. We evaluate baseline approaches by integrating techniques from both label denoising and OSDG methodologies, highlighting the limitations of existing strategies in handling label noise effectively. To address these limitations, we propose HyProMeta, a novel framework that integrates hyperbolic category prototypes for label noise-aware meta-learning alongside a learnable new-category agnostic prompt designed to enhance generalization to unseen classes. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of HyProMeta compared to state-of-the-art methods across the newly established benchmarks. The source code of this work is released at https://github.com/KPeng9510/HyProMeta.
ObjectFinder: Open-Vocabulary Assistive System for Interactive Object Search by Blind People
Dec 04, 2024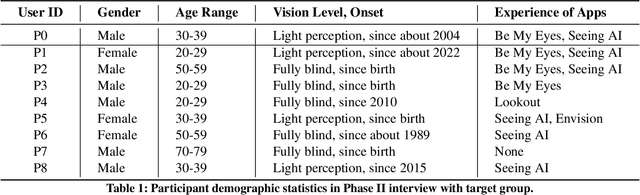
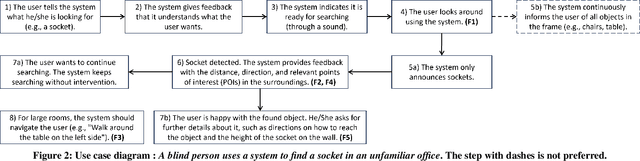

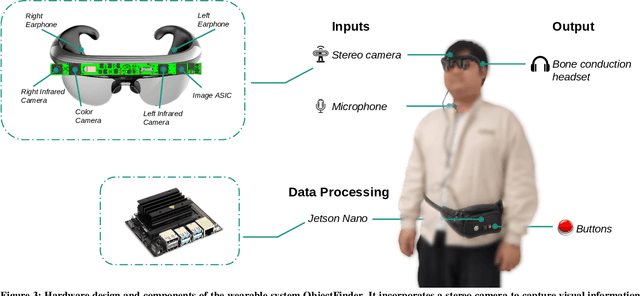
Abstract:Assistive technology can be leveraged by blind people when searching for objects in their daily lives. We created ObjectFinder, an open-vocabulary interactive object-search prototype, which combines object detection with scene description and navigation. It enables blind persons to detect and navigate to objects of their choice. Our approach used co-design for the development of the prototype. We further conducted need-finding interviews to better understand challenges in object search, followed by a study with the ObjectFinder prototype in a laboratory setting simulating a living room and an office, with eight blind users. Additionally, we compared the prototype with BeMyEyes and Lookout for object search. We found that most participants felt more independent with ObjectFinder and preferred it over the baselines when deployed on more efficient hardware, as it enhances mental mapping and allows for active target definition. Moreover, we identified factors for future directions for the development of object-search systems.
Deformable Mamba for Wide Field of View Segmentation
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Wide-FoV cameras, like fisheye and panoramic setups, are essential for broader perception but introduce significant distortions in 180{\deg} and 360{\deg} images, complicating dense prediction tasks. For instance, existing MAMBA models lacking distortion-aware capacity cannot perform well in panoramic semantic segmentation. To address this problem, this work presents Deformable Mamba, a unified framework specifically designed to address imaging distortions within the context of panoramic and fisheye semantic segmentation. At the core is a decoder constructed with a series of Deformable Mamba Fusion (DMF) blocks, making the whole framework more deformable, efficient, and accurate, when handling extreme distortions. Extensive evaluations across five datasets demonstrate that our method consistently improves segmentation accuracy compared to the previous state-of-the-art methods tailored for specific FoVs. Notably, Deformable Mamba achieves a +2.5% performance improvement on the 360{\deg} Stanford2D3D dataset, and shows better results across FoVs from 60{\deg} to 360{\deg}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge