Xinwen Zhang
Federated Stochastic Minimax Optimization under Heavy-Tailed Noises
Nov 06, 2025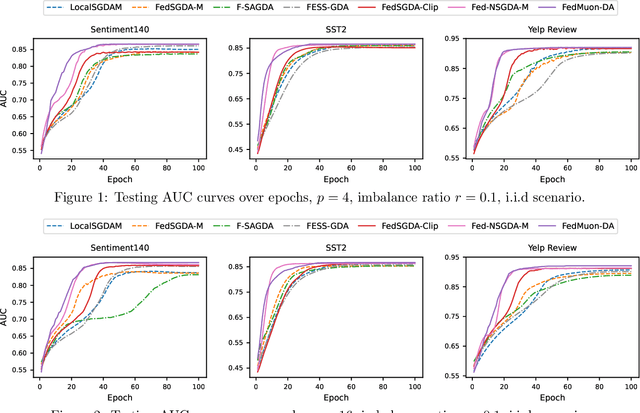
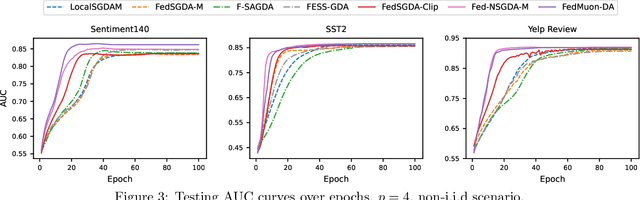
Abstract:Heavy-tailed noise has attracted growing attention in nonconvex stochastic optimization, as numerous empirical studies suggest it offers a more realistic assumption than standard bounded variance assumption. In this work, we investigate nonconvex-PL minimax optimization under heavy-tailed gradient noise in federated learning. We propose two novel algorithms: Fed-NSGDA-M, which integrates normalized gradients, and FedMuon-DA, which leverages the Muon optimizer for local updates. Both algorithms are designed to effectively address heavy-tailed noise in federated minimax optimization, under a milder condition. We theoretically establish that both algorithms achieve a convergence rate of $O({1}/{(TNp)^{\frac{s-1}{2s}}})$. To the best of our knowledge, these are the first federated minimax optimization algorithms with rigorous theoretical guarantees under heavy-tailed noise. Extensive experiments further validate their effectiveness.
SAM 2++: Tracking Anything at Any Granularity
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Video tracking aims at finding the specific target in subsequent frames given its initial state. Due to the varying granularity of target states across different tasks, most existing trackers are tailored to a single task and heavily rely on custom-designed modules within the individual task, which limits their generalization and leads to redundancy in both model design and parameters. To unify video tracking tasks, we present SAM 2++, a unified model towards tracking at any granularity, including masks, boxes, and points. First, to extend target granularity, we design task-specific prompts to encode various task inputs into general prompt embeddings, and a unified decoder to unify diverse task results into a unified form pre-output. Next, to satisfy memory matching, the core operation of tracking, we introduce a task-adaptive memory mechanism that unifies memory across different granularities. Finally, we introduce a customized data engine to support tracking training at any granularity, producing a large and diverse video tracking dataset with rich annotations at three granularities, termed Tracking-Any-Granularity, which represents a comprehensive resource for training and benchmarking on unified tracking. Comprehensive experiments on multiple benchmarks confirm that SAM 2++ sets a new state of the art across diverse tracking tasks at different granularities, establishing a unified and robust tracking framework.
Nonconvex Decentralized Stochastic Bilevel Optimization under Heavy-Tailed Noises
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Existing decentralized stochastic optimization methods assume the lower-level loss function is strongly convex and the stochastic gradient noise has finite variance. These strong assumptions typically are not satisfied in real-world machine learning models. To address these limitations, we develop a novel decentralized stochastic bilevel optimization algorithm for the nonconvex bilevel optimization problem under heavy-tailed noises. Specifically, we develop a normalized stochastic variance-reduced bilevel gradient descent algorithm, which does not rely on any clipping operation. Moreover, we establish its convergence rate by innovatively bounding interdependent gradient sequences under heavy-tailed noises for nonconvex decentralized bilevel optimization problems. As far as we know, this is the first decentralized bilevel optimization algorithm with rigorous theoretical guarantees under heavy-tailed noises. The extensive experimental results confirm the effectiveness of our algorithm in handling heavy-tailed noises.
AniSora: Exploring the Frontiers of Animation Video Generation in the Sora Era
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Animation has gained significant interest in the recent film and TV industry. Despite the success of advanced video generation models like Sora, Kling, and CogVideoX in generating natural videos, they lack the same effectiveness in handling animation videos. Evaluating animation video generation is also a great challenge due to its unique artist styles, violating the laws of physics and exaggerated motions. In this paper, we present a comprehensive system, AniSora, designed for animation video generation, which includes a data processing pipeline, a controllable generation model, and an evaluation dataset. Supported by the data processing pipeline with over 10M high-quality data, the generation model incorporates a spatiotemporal mask module to facilitate key animation production functions such as image-to-video generation, frame interpolation, and localized image-guided animation. We also collect an evaluation benchmark of 948 various animation videos, the evaluation on VBench and human double-blind test demonstrates consistency in character and motion, achieving state-of-the-art results in animation video generation. Our evaluation benchmark will be publicly available at https://github.com/bilibili/Index-anisora.
SynthMix: Mixing up Aligned Synthesis for Medical Cross-Modality Domain Adaptation
May 07, 2023Abstract:The adversarial methods showed advanced performance by producing synthetic images to mitigate the domain shift, a common problem due to the hardship of acquiring labelled data in medical field. Most existing studies focus on modifying the network architecture, but little has worked on the GAN training strategy. In this work, we propose SynthMix, an add-on module with a natural yet effective training policy that can promote synthetic quality without altering the network architecture. Following the adversarial philosophy of GAN, we designed a mix-up synthesis scheme termed SynthMix. It coherently mixed up aligned images of real and synthetic samples to stimulate the generation of fine-grained features, examined by an associated Inspector for the domain-specific details. We evaluated our method on two segmentation benchmarks among three publicly available datasets, where our method showed a significant performance gain compared with existing state-of-the-art approaches.
Federated Compositional Deep AUC Maximization
Apr 20, 2023



Abstract:Federated learning has attracted increasing attention due to the promise of balancing privacy and large-scale learning; numerous approaches have been proposed. However, most existing approaches focus on problems with balanced data, and prediction performance is far from satisfactory for many real-world applications where the number of samples in different classes is highly imbalanced. To address this challenging problem, we developed a novel federated learning method for imbalanced data by directly optimizing the area under curve (AUC) score. In particular, we formulate the AUC maximization problem as a federated compositional minimax optimization problem, develop a local stochastic compositional gradient descent ascent with momentum algorithm, and provide bounds on the computational and communication complexities of our algorithm. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to achieve such favorable theoretical results. Finally, extensive experimental results confirm the efficacy of our method.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Fundus Image Segmentation with Few Labeled Source Data
Oct 10, 2022



Abstract:Deep learning-based segmentation methods have been widely employed for automatic glaucoma diagnosis and prognosis. In practice, fundus images obtained by different fundus cameras vary significantly in terms of illumination and intensity. Although recent unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) methods enhance the models' generalization ability on the unlabeled target fundus datasets, they always require sufficient labeled data from the source domain, bringing auxiliary data acquisition and annotation costs. To further facilitate the data efficiency of the cross-domain segmentation methods on the fundus images, we explore UDA optic disc and cup segmentation problems using few labeled source data in this work. We first design a Searching-based Multi-style Invariant Mechanism to diversify the source data style as well as increase the data amount. Next, a prototype consistency mechanism on the foreground objects is proposed to facilitate the feature alignment for each kind of tissue under different image styles. Moreover, a cross-style self-supervised learning stage is further designed to improve the segmentation performance on the target images. Our method has outperformed several state-of-the-art UDA segmentation methods under the UDA fundus segmentation with few labeled source data.
Imitate then Transcend: Multi-Agent Optimal Execution with Dual-Window Denoise PPO
Jun 21, 2022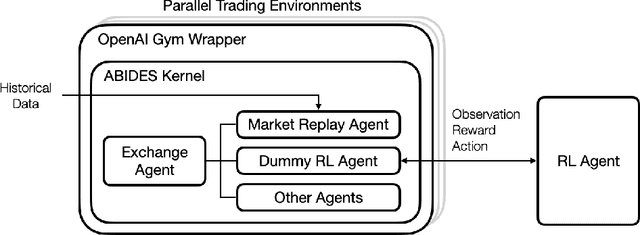
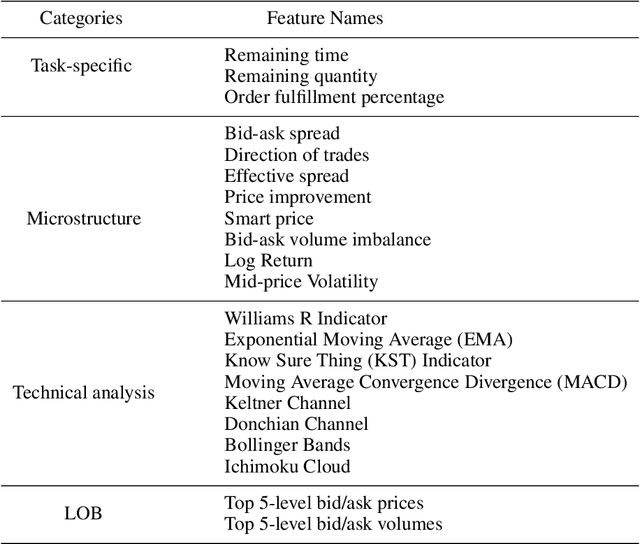
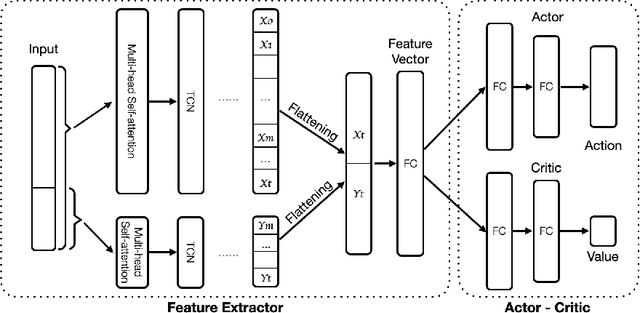
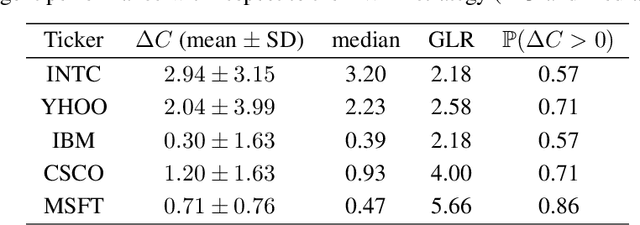
Abstract:A novel framework for solving the optimal execution and placement problems using reinforcement learning (RL) with imitation was proposed. The RL agents trained from the proposed framework consistently outperformed the industry benchmark time-weighted average price (TWAP) strategy in execution cost and showed great generalization across out-of-sample trading dates and tickers. The impressive performance was achieved from three aspects. First, our RL network architecture called Dual-window Denoise PPO enabled efficient learning in a noisy market environment. Second, a reward scheme with imitation learning was designed, and a comprehensive set of market features was studied. Third, our flexible action formulation allowed the RL agent to tackle optimal execution and placement collectively resulting in better performance than solving individual problems separately. The RL agent's performance was evaluated in our multi-agent realistic historical limit order book simulator in which price impact was accurately assessed. In addition, ablation studies were also performed, confirming the superiority of our framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge