Xiaofeng Liu
GTFMN: Guided Texture and Feature Modulation Network for Low-Light Image Enhancement and Super-Resolution
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Low-light image super-resolution (LLSR) is a challenging task due to the coupled degradation of low resolution and poor illumination. To address this, we propose the Guided Texture and Feature Modulation Network (GTFMN), a novel framework that decouples the LLSR task into two sub-problems: illumination estimation and texture restoration. First, our network employs a dedicated Illumination Stream whose purpose is to predict a spatially varying illumination map that accurately captures lighting distribution. Further, this map is utilized as an explicit guide within our novel Illumination Guided Modulation Block (IGM Block) to dynamically modulate features in the Texture Stream. This mechanism achieves spatially adaptive restoration, enabling the network to intensify enhancement in poorly lit regions while preserving details in well-exposed areas. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GTFMN achieves the best performance among competing methods on the OmniNormal5 and OmniNormal15 datasets, outperforming them in both quantitative metrics and visual quality.
U-Harmony: Enhancing Joint Training for Segmentation Models with Universal Harmonization
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:In clinical practice, medical segmentation datasets are often limited and heterogeneous, with variations in modalities, protocols, and anatomical targets across institutions. Existing deep learning models struggle to jointly learn from such diverse data, often sacrificing either generalization or domain-specific knowledge. To overcome these challenges, we propose a joint training method called Universal Harmonization (U-Harmony), which can be integrated into deep learning-based architectures with a domain-gated head, enabling a single segmentation model to learn from heterogeneous datasets simultaneously. By integrating U-Harmony, our approach sequentially normalizes and then denormalizes feature distributions to mitigate domain-specific variations while preserving original dataset-specific knowledge. More appealingly, our framework also supports universal modality adaptation, allowing the seamless learning of new imaging modalities and anatomical classes. Extensive experiments on cross-institutional brain lesion datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, establishing a new benchmark for robust and adaptable 3D medical image segmentation models in real-world clinical settings.
MODE: Efficient Time Series Prediction with Mamba Enhanced by Low-Rank Neural ODEs
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Time series prediction plays a pivotal role across diverse domains such as finance, healthcare, energy systems, and environmental modeling. However, existing approaches often struggle to balance efficiency, scalability, and accuracy, particularly when handling long-range dependencies and irregularly sampled data. To address these challenges, we propose MODE, a unified framework that integrates Low-Rank Neural Ordinary Differential Equations (Neural ODEs) with an Enhanced Mamba architecture. As illustrated in our framework, the input sequence is first transformed by a Linear Tokenization Layer and then processed through multiple Mamba Encoder blocks, each equipped with an Enhanced Mamba Layer that employs Causal Convolution, SiLU activation, and a Low-Rank Neural ODE enhancement to efficiently capture temporal dynamics. This low-rank formulation reduces computational overhead while maintaining expressive power. Furthermore, a segmented selective scanning mechanism, inspired by pseudo-ODE dynamics, adaptively focuses on salient subsequences to improve scalability and long-range sequence modeling. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that MODE surpasses existing baselines in both predictive accuracy and computational efficiency. Overall, our contributions include: (1) a unified and efficient architecture for long-term time series modeling, (2) integration of Mamba's selective scanning with low-rank Neural ODEs for enhanced temporal representation, and (3) substantial improvements in efficiency and scalability enabled by low-rank approximation and dynamic selective scanning.
UniMRSeg: Unified Modality-Relax Segmentation via Hierarchical Self-Supervised Compensation
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal image segmentation faces real-world deployment challenges from incomplete/corrupted modalities degrading performance. While existing methods address training-inference modality gaps via specialized per-combination models, they introduce high deployment costs by requiring exhaustive model subsets and model-modality matching. In this work, we propose a unified modality-relax segmentation network (UniMRSeg) through hierarchical self-supervised compensation (HSSC). Our approach hierarchically bridges representation gaps between complete and incomplete modalities across input, feature and output levels. % First, we adopt modality reconstruction with the hybrid shuffled-masking augmentation, encouraging the model to learn the intrinsic modality characteristics and generate meaningful representations for missing modalities through cross-modal fusion. % Next, modality-invariant contrastive learning implicitly compensates the feature space distance among incomplete-complete modality pairs. Furthermore, the proposed lightweight reverse attention adapter explicitly compensates for the weak perceptual semantics in the frozen encoder. Last, UniMRSeg is fine-tuned under the hybrid consistency constraint to ensure stable prediction under all modality combinations without large performance fluctuations. Without bells and whistles, UniMRSeg significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods under diverse missing modality scenarios on MRI-based brain tumor segmentation, RGB-D semantic segmentation, RGB-D/T salient object segmentation. The code will be released at https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/UniMRSeg.
Fine-grained Video Dubbing Duration Alignment with Segment Supervised Preference Optimization
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Video dubbing aims to translate original speech in visual media programs from the source language to the target language, relying on neural machine translation and text-to-speech technologies. Due to varying information densities across languages, target speech often mismatches the source speech duration, causing audio-video synchronization issues that significantly impact viewer experience. In this study, we approach duration alignment in LLM-based video dubbing machine translation as a preference optimization problem. We propose the Segment Supervised Preference Optimization (SSPO) method, which employs a segment-wise sampling strategy and fine-grained loss to mitigate duration mismatches between source and target lines. Experimental results demonstrate that SSPO achieves superior performance in duration alignment tasks.
* This paper is accepted by ACL2025 (Main)
In-situ Value-aligned Human-Robot Interactions with Physical Constraints
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Equipped with Large Language Models (LLMs), human-centered robots are now capable of performing a wide range of tasks that were previously deemed challenging or unattainable. However, merely completing tasks is insufficient for cognitive robots, who should learn and apply human preferences to future scenarios. In this work, we propose a framework that combines human preferences with physical constraints, requiring robots to complete tasks while considering both. Firstly, we developed a benchmark of everyday household activities, which are often evaluated based on specific preferences. We then introduced In-Context Learning from Human Feedback (ICLHF), where human feedback comes from direct instructions and adjustments made intentionally or unintentionally in daily life. Extensive sets of experiments, testing the ICLHF to generate task plans and balance physical constraints with preferences, have demonstrated the efficiency of our approach.
Power Battery Detection
Aug 11, 2025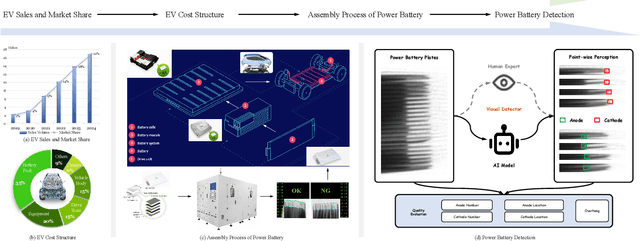
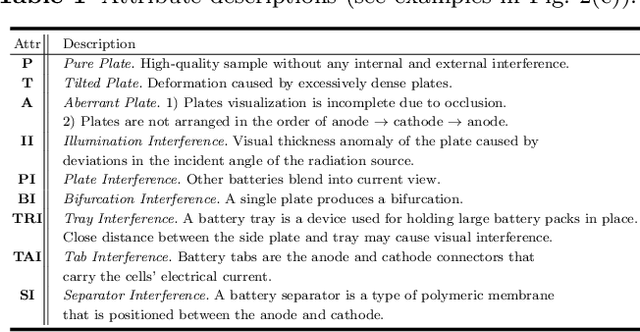
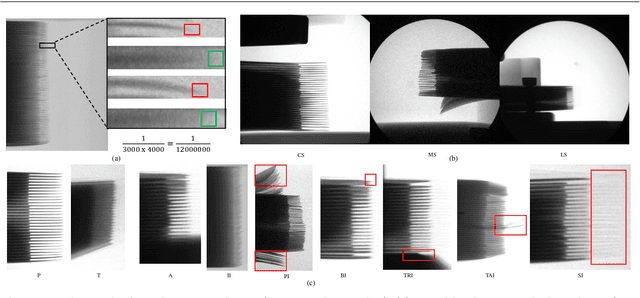

Abstract:Power batteries are essential components in electric vehicles, where internal structural defects can pose serious safety risks. We conduct a comprehensive study on a new task, power battery detection (PBD), which aims to localize the dense endpoints of cathode and anode plates from industrial X-ray images for quality inspection. Manual inspection is inefficient and error-prone, while traditional vision algorithms struggle with densely packed plates, low contrast, scale variation, and imaging artifacts. To address this issue and drive more attention into this meaningful task, we present PBD5K, the first large-scale benchmark for this task, consisting of 5,000 X-ray images from nine battery types with fine-grained annotations and eight types of real-world visual interference. To support scalable and consistent labeling, we develop an intelligent annotation pipeline that combines image filtering, model-assisted pre-labeling, cross-verification, and layered quality evaluation. We formulate PBD as a point-level segmentation problem and propose MDCNeXt, a model designed to extract and integrate multi-dimensional structure clues including point, line, and count information from the plate itself. To improve discrimination between plates and suppress visual interference, MDCNeXt incorporates two state space modules. The first is a prompt-filtered module that learns contrastive relationships guided by task-specific prompts. The second is a density-aware reordering module that refines segmentation in regions with high plate density. In addition, we propose a distance-adaptive mask generation strategy to provide robust supervision under varying spatial distributions of anode and cathode positions. The source code and datasets will be publicly available at \href{https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/X-ray-PBD}{PBD5K}.
When and How Unlabeled Data Provably Improve In-Context Learning
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Recent research shows that in-context learning (ICL) can be effective even when demonstrations have missing or incorrect labels. To shed light on this capability, we examine a canonical setting where the demonstrations are drawn according to a binary Gaussian mixture model (GMM) and a certain fraction of the demonstrations have missing labels. We provide a comprehensive theoretical study to show that: (1) The loss landscape of one-layer linear attention models recover the optimal fully-supervised estimator but completely fail to exploit unlabeled data; (2) In contrast, multilayer or looped transformers can effectively leverage unlabeled data by implicitly constructing estimators of the form $\sum_{i\ge 0} a_i (X^\top X)^iX^\top y$ with $X$ and $y$ denoting features and partially-observed labels (with missing entries set to zero). We characterize the class of polynomials that can be expressed as a function of depth and draw connections to Expectation Maximization, an iterative pseudo-labeling algorithm commonly used in semi-supervised learning. Importantly, the leading polynomial power is exponential in depth, so mild amount of depth/looping suffices. As an application of theory, we propose looping off-the-shelf tabular foundation models to enhance their semi-supervision capabilities. Extensive evaluations on real-world datasets show that our method significantly improves the semisupervised tabular learning performance over the standard single pass inference.
ATR-Bench: A Federated Learning Benchmark for Adaptation, Trust, and Reasoning
May 22, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a promising paradigm for collaborative model training while preserving data privacy across decentralized participants. As FL adoption grows, numerous techniques have been proposed to tackle its practical challenges. However, the lack of standardized evaluation across key dimensions hampers systematic progress and fair comparison of FL methods. In this work, we introduce ATR-Bench, a unified framework for analyzing federated learning through three foundational dimensions: Adaptation, Trust, and Reasoning. We provide an in-depth examination of the conceptual foundations, task formulations, and open research challenges associated with each theme. We have extensively benchmarked representative methods and datasets for adaptation to heterogeneous clients and trustworthiness in adversarial or unreliable environments. Due to the lack of reliable metrics and models for reasoning in FL, we only provide literature-driven insights for this dimension. ATR-Bench lays the groundwork for a systematic and holistic evaluation of federated learning with real-world relevance. We will make our complete codebase publicly accessible and a curated repository that continuously tracks new developments and research in the FL literature.
Oral Imaging for Malocclusion Issues Assessments: OMNI Dataset, Deep Learning Baselines and Benchmarking
May 21, 2025Abstract:Malocclusion is a major challenge in orthodontics, and its complex presentation and diverse clinical manifestations make accurate localization and diagnosis particularly important. Currently, one of the major shortcomings facing the field of dental image analysis is the lack of large-scale, accurately labeled datasets dedicated to malocclusion issues, which limits the development of automated diagnostics in the field of dentistry and leads to a lack of diagnostic accuracy and efficiency in clinical practice. Therefore, in this study, we propose the Oral and Maxillofacial Natural Images (OMNI) dataset, a novel and comprehensive dental image dataset aimed at advancing the study of analyzing dental images for issues of malocclusion. Specifically, the dataset contains 4166 multi-view images with 384 participants in data collection and annotated by professional dentists. In addition, we performed a comprehensive validation of the created OMNI dataset, including three CNN-based methods, two Transformer-based methods, and one GNN-based method, and conducted automated diagnostic experiments for malocclusion issues. The experimental results show that the OMNI dataset can facilitate the automated diagnosis research of malocclusion issues and provide a new benchmark for the research in this field. Our OMNI dataset and baseline code are publicly available at https://github.com/RoundFaceJ/OMNI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge