Tongliang Liu
Bifrost: Steering Strategic Trajectories to Bridge Contextual Gaps for Self-Improving Agents
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Autonomous agents excel in self-improvement through reflection and iterative refinement, which reuse successful task trajectories as in-context examples to assist subsequent reasoning. However, shifting across tasks often introduces a context mismatch. Hence, existing approaches either discard the trajectories or manipulate them using heuristics, leading to a non-negligible fine-tuning cost or unguaranteed performance. To bridge this gap, we reveal a context-trajectory correlation, where shifts of context are highly parallel with shifts of trajectory. Based on this finding, we propose BrIdge contextual gap FoR imprOvised trajectory STeering (Bifrost), a training-free method that leverages context differences to precisely guide the adaptation of previously solved trajectories towards the target task, mitigating the misalignment caused by context shifts. Our trajectory adaptation is conducted at the representation level using agent hidden states, ensuring trajectory transformation accurately aligns with the target context in a shared space. Across diverse benchmarks, Bifrost consistently outperforms existing trajectory reuse and finetuned self-improvement methods, demonstrating that agents can effectively leverage past experiences despite substantial context shifts.
Intellectual Property Protection for 3D Gaussian Splatting Assets: A Survey
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has become a mainstream representation for real-time 3D scene synthesis, enabling applications in virtual and augmented reality, robotics, and 3D content creation. Its rising commercial value and explicit parametric structure raise emerging intellectual property (IP) protection concerns, prompting a surge of research on 3DGS IP protection. However, current progress remains fragmented, lacking a unified view of the underlying mechanisms, protection paradigms, and robustness challenges. To address this gap, we present the first systematic survey on 3DGS IP protection and introduce a bottom-up framework that examines (i) underlying Gaussian-based perturbation mechanisms, (ii) passive and active protection paradigms, and (iii) robustness threats under emerging generative AI era, revealing gaps in technical foundations and robustness characterization and indicating opportunities for deeper investigation. Finally, we outline six research directions across robustness, efficiency, and protection paradigms, offering a roadmap toward reliable and trustworthy IP protection for 3DGS assets.
Unsupervised Synthetic Image Attribution: Alignment and Disentanglement
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:As the quality of synthetic images improves, identifying the underlying concepts of model-generated images is becoming increasingly crucial for copyright protection and ensuring model transparency. Existing methods achieve this attribution goal by training models using annotated pairs of synthetic images and their original training sources. However, obtaining such paired supervision is challenging, as it requires either well-designed synthetic concepts or precise annotations from millions of training sources. To eliminate the need for costly paired annotations, in this paper, we explore the possibility of unsupervised synthetic image attribution. We propose a simple yet effective unsupervised method called Alignment and Disentanglement. Specifically, we begin by performing basic concept alignment using contrastive self-supervised learning. Next, we enhance the model's attribution ability by promoting representation disentanglement with the Infomax loss. This approach is motivated by an interesting observation: contrastive self-supervised models, such as MoCo and DINO, inherently exhibit the ability to perform simple cross-domain alignment. By formulating this observation as a theoretical assumption on cross-covariance, we provide a theoretical explanation of how alignment and disentanglement can approximate the concept-matching process through a decomposition of the canonical correlation analysis objective. On the real-world benchmarks, AbC, we show that our unsupervised method surprisingly outperforms the supervised methods. As a starting point, we expect our intuitive insights and experimental findings to provide a fresh perspective on this challenging task.
Privacy-Preserving Model Transcription with Differentially Private Synthetic Distillation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:While many deep learning models trained on private datasets have been deployed in various practical tasks, they may pose a privacy leakage risk as attackers could recover informative data or label knowledge from models. In this work, we present \emph{privacy-preserving model transcription}, a data-free model-to-model conversion solution to facilitate model deployment with a privacy guarantee. To this end, we propose a cooperative-competitive learning approach termed \emph{differentially private synthetic distillation} that learns to convert a pretrained model (teacher) into its privacy-preserving counterpart (student) via a trainable generator without access to private data. The learning collaborates with three players in a unified framework and performs alternate optimization: i)~the generator is learned to generate synthetic data, ii)~the teacher and student accept the synthetic data and compute differential private labels by flexible data or label noisy perturbation, and iii)~the student is updated with noisy labels and the generator is updated by taking the student as a discriminator for adversarial training. We theoretically prove that our approach can guarantee differential privacy and convergence. The transcribed student has good performance and privacy protection, while the resulting generator can generate private synthetic data for downstream tasks. Extensive experiments clearly demonstrate that our approach outperforms 26 state-of-the-arts.
Mirage2Matter: A Physically Grounded Gaussian World Model from Video
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:The scalability of embodied intelligence is fundamentally constrained by the scarcity of real-world interaction data. While simulation platforms provide a promising alternative, existing approaches often suffer from a substantial visual and physical gap to real environments and rely on expensive sensors, precise robot calibration, or depth measurements, limiting their practicality at scale. We present Simulate Anything, a graphics-driven world modeling and simulation framework that enables efficient generation of high-fidelity embodied training data using only multi-view environment videos and off-the-shelf assets. Our approach reconstructs real-world environments into a photorealistic scene representation using 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), seamlessly capturing fine-grained geometry and appearance from video. We then leverage generative models to recover a physically realistic representation and integrate it into a simulation environment via a precision calibration target, enabling accurate scale alignment between the reconstructed scene and the real world. Together, these components provide a unified, editable, and physically grounded world model. Vision Language Action (VLA) models trained on our simulated data achieve strong zero-shot performance on downstream tasks, matching or even surpassing results obtained with real-world data, highlighting the potential of reconstruction-driven world modeling for scalable and practical embodied intelligence training.
Combating Noisy Labels through Fostering Self- and Neighbor-Consistency
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Label noise is pervasive in various real-world scenarios, posing challenges in supervised deep learning. Deep networks are vulnerable to such label-corrupted samples due to the memorization effect. One major stream of previous methods concentrates on identifying clean data for training. However, these methods often neglect imbalances in label noise across different mini-batches and devote insufficient attention to out-of-distribution noisy data. To this end, we propose a noise-robust method named Jo-SNC (\textbf{Jo}int sample selection and model regularization based on \textbf{S}elf- and \textbf{N}eighbor-\textbf{C}onsistency). Specifically, we propose to employ the Jensen-Shannon divergence to measure the ``likelihood'' of a sample being clean or out-of-distribution. This process factors in the nearest neighbors of each sample to reinforce the reliability of clean sample identification. We design a self-adaptive, data-driven thresholding scheme to adjust per-class selection thresholds. While clean samples undergo conventional training, detected in-distribution and out-of-distribution noisy samples are trained following partial label learning and negative learning, respectively. Finally, we advance the model performance further by proposing a triplet consistency regularization that promotes self-prediction consistency, neighbor-prediction consistency, and feature consistency. Extensive experiments on various benchmark datasets and comprehensive ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our approach over existing state-of-the-art methods.
Investigating The Functional Roles of Attention Heads in Vision Language Models: Evidence for Reasoning Modules
Dec 11, 2025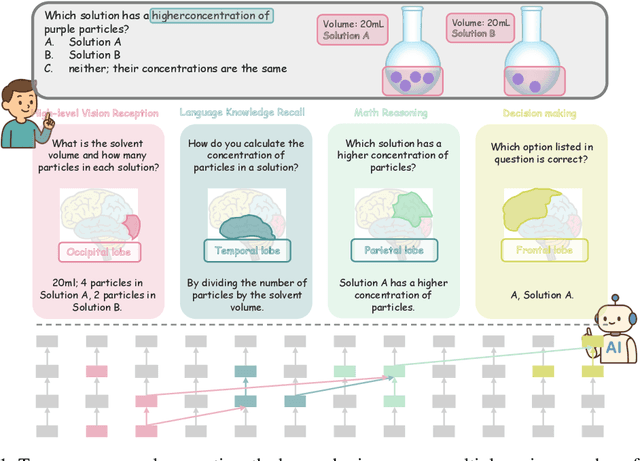
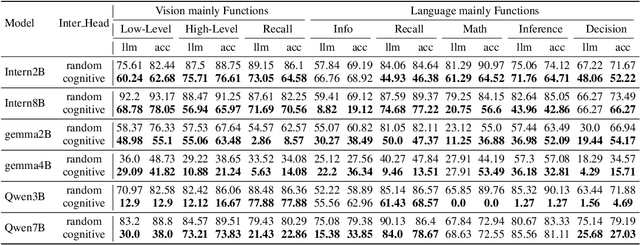
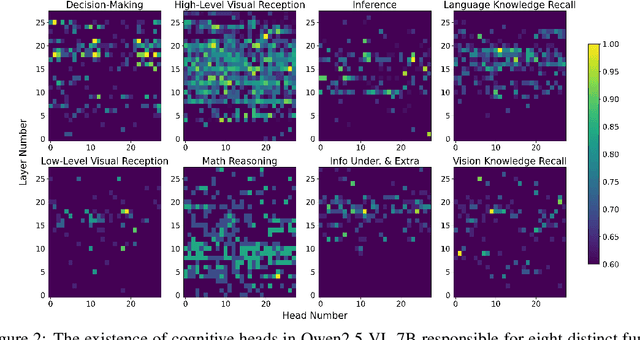
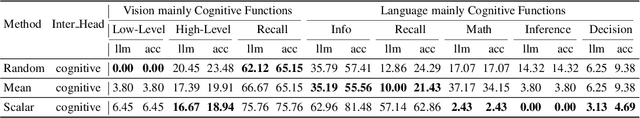
Abstract:Despite excelling on multimodal benchmarks, vision-language models (VLMs) largely remain a black box. In this paper, we propose a novel interpretability framework to systematically analyze the internal mechanisms of VLMs, focusing on the functional roles of attention heads in multimodal reasoning. To this end, we introduce CogVision, a dataset that decomposes complex multimodal questions into step-by-step subquestions designed to simulate human reasoning through a chain-of-thought paradigm, with each subquestion associated with specific receptive or cognitive functions such as high-level visual reception and inference. Using a probing-based methodology, we identify attention heads that specialize in these functions and characterize them as functional heads. Our analysis across diverse VLM families reveals that these functional heads are universally sparse, vary in number and distribution across functions, and mediate interactions and hierarchical organization. Furthermore, intervention experiments demonstrate their critical role in multimodal reasoning: removing functional heads leads to performance degradation, while emphasizing them enhances accuracy. These findings provide new insights into the cognitive organization of VLMs and suggest promising directions for designing models with more human-aligned perceptual and reasoning abilities.
AdLift: Lifting Adversarial Perturbations to Safeguard 3D Gaussian Splatting Assets Against Instruction-Driven Editing
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Recent studies have extended diffusion-based instruction-driven 2D image editing pipelines to 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), enabling faithful manipulation of 3DGS assets and greatly advancing 3DGS content creation. However, it also exposes these assets to serious risks of unauthorized editing and malicious tampering. Although imperceptible adversarial perturbations against diffusion models have proven effective for protecting 2D images, applying them to 3DGS encounters two major challenges: view-generalizable protection and balancing invisibility with protection capability. In this work, we propose the first editing safeguard for 3DGS, termed AdLift, which prevents instruction-driven editing across arbitrary views and dimensions by lifting strictly bounded 2D adversarial perturbations into 3D Gaussian-represented safeguard. To ensure both adversarial perturbations effectiveness and invisibility, these safeguard Gaussians are progressively optimized across training views using a tailored Lifted PGD, which first conducts gradient truncation during back-propagation from the editing model at the rendered image and applies projected gradients to strictly constrain the image-level perturbation. Then, the resulting perturbation is backpropagated to the safeguard Gaussian parameters via an image-to-Gaussian fitting operation. We alternate between gradient truncation and image-to-Gaussian fitting, yielding consistent adversarial-based protection performance across different viewpoints and generalizes to novel views. Empirically, qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that AdLift effectively protects against state-of-the-art instruction-driven 2D image and 3DGS editing.
DINO-Detect: A Simple yet Effective Framework for Blur-Robust AI-Generated Image Detection
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:With growing concerns over image authenticity and digital safety, the field of AI-generated image (AIGI) detection has progressed rapidly. Yet, most AIGI detectors still struggle under real-world degradations, particularly motion blur, which frequently occurs in handheld photography, fast motion, and compressed video. Such blur distorts fine textures and suppresses high-frequency artifacts, causing severe performance drops in real-world settings. We address this limitation with a blur-robust AIGI detection framework based on teacher-student knowledge distillation. A high-capacity teacher (DINOv3), trained on clean (i.e., sharp) images, provides stable and semantically rich representations that serve as a reference for learning. By freezing the teacher to maintain its generalization ability, we distill its feature and logit responses from sharp images to a student trained on blurred counterparts, enabling the student to produce consistent representations under motion degradation. Extensive experiments benchmarks show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance under both motion-blurred and clean conditions, demonstrating improved generalization and real-world applicability. Source codes will be released at: https://github.com/JiaLiangShen/Dino-Detect-for-blur-robust-AIGC-Detection.
MedDCR: Learning to Design Agentic Workflows for Medical Coding
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Medical coding converts free-text clinical notes into standardized diagnostic and procedural codes, which are essential for billing, hospital operations, and medical research. Unlike ordinary text classification, it requires multi-step reasoning: extracting diagnostic concepts, applying guideline constraints, mapping to hierarchical codebooks, and ensuring cross-document consistency. Recent advances leverage agentic LLMs, but most rely on rigid, manually crafted workflows that fail to capture the nuance and variability of real-world documentation, leaving open the question of how to systematically learn effective workflows. We present MedDCR, a closed-loop framework that treats workflow design as a learning problem. A Designer proposes workflows, a Coder executes them, and a Reflector evaluates predictions and provides constructive feedback, while a memory archive preserves prior designs for reuse and iterative refinement. On benchmark datasets, MedDCR outperforms state-of-the-art baselines and produces interpretable, adaptable workflows that better reflect real coding practice, improving both the reliability and trustworthiness of automated systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge