Le Song
MemR$^3$: Memory Retrieval via Reflective Reasoning for LLM Agents
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Memory systems have been designed to leverage past experiences in Large Language Model (LLM) agents. However, many deployed memory systems primarily optimize compression and storage, with comparatively less emphasis on explicit, closed-loop control of memory retrieval. From this observation, we build memory retrieval as an autonomous, accurate, and compatible agent system, named MemR$^3$, which has two core mechanisms: 1) a router that selects among retrieve, reflect, and answer actions to optimize answer quality; 2) a global evidence-gap tracker that explicitly renders the answering process transparent and tracks the evidence collection process. This design departs from the standard retrieve-then-answer pipeline by introducing a closed-loop control mechanism that enables autonomous decision-making. Empirical results on the LoCoMo benchmark demonstrate that MemR$^3$ surpasses strong baselines on LLM-as-a-Judge score, and particularly, it improves existing retrievers across four categories with an overall improvement on RAG (+7.29%) and Zep (+1.94%) using GPT-4.1-mini backend, offering a plug-and-play controller for existing memory stores.
HD-Prot: A Protein Language Model for Joint Sequence-Structure Modeling with Continuous Structure Tokens
Dec 17, 2025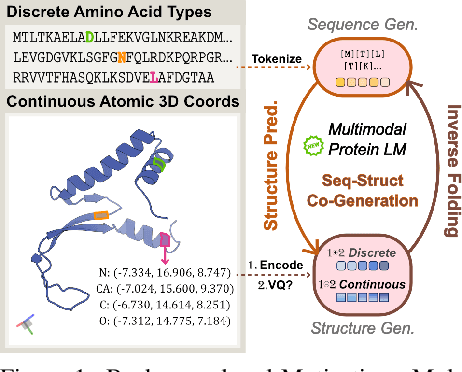
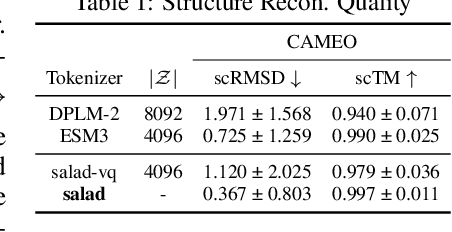
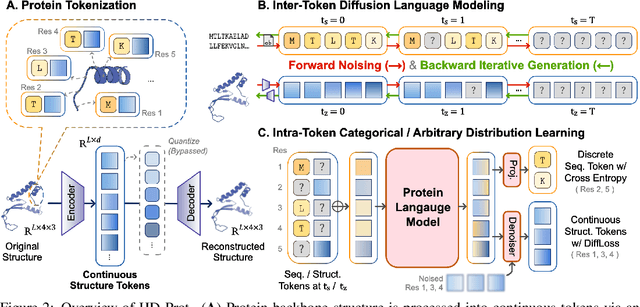
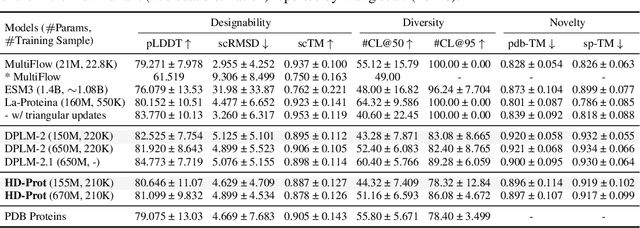
Abstract:Proteins inherently possess a consistent sequence-structure duality. The abundance of protein sequence data, which can be readily represented as discrete tokens, has driven fruitful developments in protein language models (pLMs). A key remaining challenge, however, is how to effectively integrate continuous structural knowledge into pLMs. Current methods often discretize protein structures to accommodate the language modeling framework, which inevitably results in the loss of fine-grained information and limits the performance potential of multimodal pLMs. In this paper, we argue that such concerns can be circumvented: a sequence-based pLM can be extended to incorporate the structure modality through continuous tokens, i.e., high-fidelity protein structure latents that avoid vector quantization. Specifically, we propose a hybrid diffusion protein language model, HD-Prot, which embeds a continuous-valued diffusion head atop a discrete pLM, enabling seamless operation with both discrete and continuous tokens for joint sequence-structure modeling. It captures inter-token dependencies across modalities through a unified absorbing diffusion process, and estimates per-token distributions via categorical prediction for sequences and continuous diffusion for structures. Extensive empirical results show that HD-Prot achieves competitive performance in unconditional sequence-structure co-generation, motif-scaffolding, protein structure prediction, and inverse folding tasks, performing on par with state-of-the-art multimodal pLMs despite being developed under limited computational resources. It highlights the viability of simultaneously estimating categorical and continuous distributions within a unified language model architecture, offering a promising alternative direction for multimodal pLMs.
MedKGent: A Large Language Model Agent Framework for Constructing Temporally Evolving Medical Knowledge Graph
Aug 17, 2025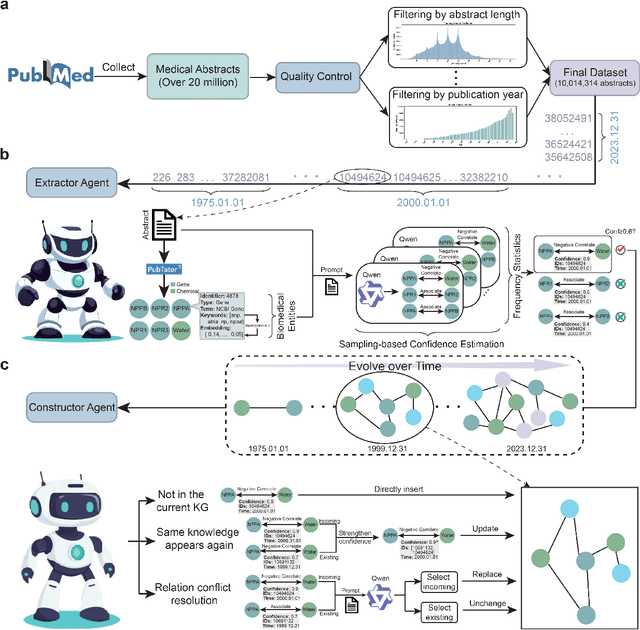
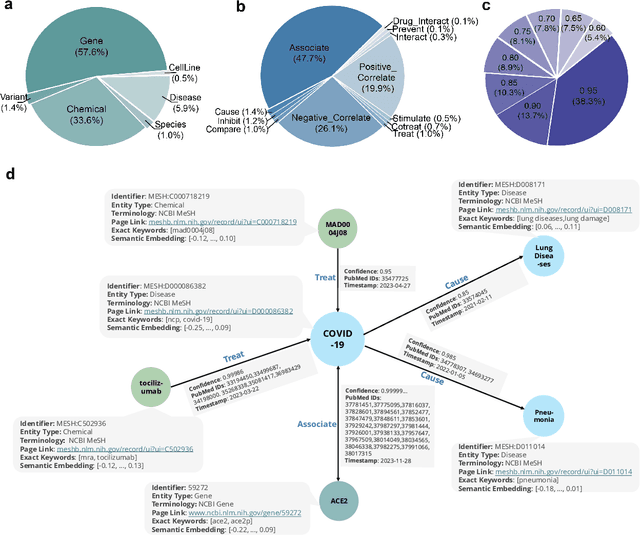
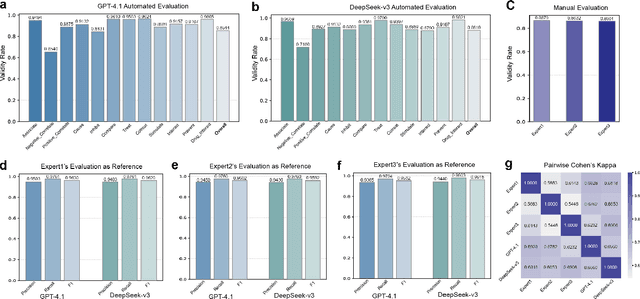
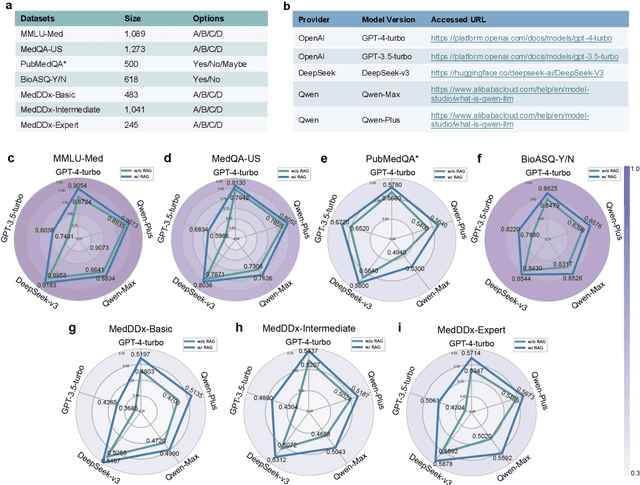
Abstract:The rapid expansion of medical literature presents growing challenges for structuring and integrating domain knowledge at scale. Knowledge Graphs (KGs) offer a promising solution by enabling efficient retrieval, automated reasoning, and knowledge discovery. However, current KG construction methods often rely on supervised pipelines with limited generalizability or naively aggregate outputs from Large Language Models (LLMs), treating biomedical corpora as static and ignoring the temporal dynamics and contextual uncertainty of evolving knowledge. To address these limitations, we introduce MedKGent, a LLM agent framework for constructing temporally evolving medical KGs. Leveraging over 10 million PubMed abstracts published between 1975 and 2023, we simulate the emergence of biomedical knowledge via a fine-grained daily time series. MedKGent incrementally builds the KG in a day-by-day manner using two specialized agents powered by the Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct model. The Extractor Agent identifies knowledge triples and assigns confidence scores via sampling-based estimation, which are used to filter low-confidence extractions and inform downstream processing. The Constructor Agent incrementally integrates the retained triples into a temporally evolving graph, guided by confidence scores and timestamps to reinforce recurring knowledge and resolve conflicts. The resulting KG contains 156,275 entities and 2,971,384 relational triples. Quality assessments by two SOTA LLMs and three domain experts demonstrate an accuracy approaching 90\%, with strong inter-rater agreement. To evaluate downstream utility, we conduct RAG across seven medical question answering benchmarks using five leading LLMs, consistently observing significant improvements over non-augmented baselines. Case studies further demonstrate the KG's value in literature-based drug repurposing via confidence-aware causal inference.
Pruning Spurious Subgraphs for Graph Out-of-Distribtuion Generalization
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) often encounter significant performance degradation under distribution shifts between training and test data, hindering their applicability in real-world scenarios. Recent studies have proposed various methods to address the out-of-distribution generalization challenge, with many methods in the graph domain focusing on directly identifying an invariant subgraph that is predictive of the target label. However, we argue that identifying the edges from the invariant subgraph directly is challenging and error-prone, especially when some spurious edges exhibit strong correlations with the targets. In this paper, we propose PrunE, the first pruning-based graph OOD method that eliminates spurious edges to improve OOD generalizability. By pruning spurious edges, \mine{} retains the invariant subgraph more comprehensively, which is critical for OOD generalization. Specifically, PrunE employs two regularization terms to prune spurious edges: 1) graph size constraint to exclude uninformative spurious edges, and 2) $\epsilon$-probability alignment to further suppress the occurrence of spurious edges. Through theoretical analysis and extensive experiments, we show that PrunE achieves superior OOD performance and outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods significantly. Codes are available at: \href{https://github.com/tianyao-aka/PrunE-GraphOOD}{https://github.com/tianyao-aka/PrunE-GraphOOD}.
LifelongAgentBench: Evaluating LLM Agents as Lifelong Learners
May 17, 2025Abstract:Lifelong learning is essential for intelligent agents operating in dynamic environments. Current large language model (LLM)-based agents, however, remain stateless and unable to accumulate or transfer knowledge over time. Existing benchmarks treat agents as static systems and fail to evaluate lifelong learning capabilities. We present LifelongAgentBench, the first unified benchmark designed to systematically assess the lifelong learning ability of LLM agents. It provides skill-grounded, interdependent tasks across three interactive environments, Database, Operating System, and Knowledge Graph, with automatic label verification, reproducibility, and modular extensibility. Extensive experiments reveal that conventional experience replay has limited effectiveness for LLM agents due to irrelevant information and context length constraints. We further introduce a group self-consistency mechanism that significantly improves lifelong learning performance. We hope LifelongAgentBench will advance the development of adaptive, memory-capable LLM agents.
From System 1 to System 2: A Survey of Reasoning Large Language Models
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Achieving human-level intelligence requires refining the transition from the fast, intuitive System 1 to the slower, more deliberate System 2 reasoning. While System 1 excels in quick, heuristic decisions, System 2 relies on logical reasoning for more accurate judgments and reduced biases. Foundational Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at fast decision-making but lack the depth for complex reasoning, as they have not yet fully embraced the step-by-step analysis characteristic of true System 2 thinking. Recently, reasoning LLMs like OpenAI's o1/o3 and DeepSeek's R1 have demonstrated expert-level performance in fields such as mathematics and coding, closely mimicking the deliberate reasoning of System 2 and showcasing human-like cognitive abilities. This survey begins with a brief overview of the progress in foundational LLMs and the early development of System 2 technologies, exploring how their combination has paved the way for reasoning LLMs. Next, we discuss how to construct reasoning LLMs, analyzing their features, the core methods enabling advanced reasoning, and the evolution of various reasoning LLMs. Additionally, we provide an overview of reasoning benchmarks, offering an in-depth comparison of the performance of representative reasoning LLMs. Finally, we explore promising directions for advancing reasoning LLMs and maintain a real-time \href{https://github.com/zzli2022/Awesome-Slow-Reason-System}{GitHub Repository} to track the latest developments. We hope this survey will serve as a valuable resource to inspire innovation and drive progress in this rapidly evolving field.
Beyond Profile: From Surface-Level Facts to Deep Persona Simulation in LLMs
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Previous approaches to persona simulation large language models (LLMs) have typically relied on learning basic biographical information, or using limited role-play dialogue datasets to capture a character's responses. However, a holistic representation of an individual goes beyond surface-level facts or conversations to deeper thoughts and thinking. In this work, we introduce CharacterBot, a model designed to replicate both the linguistic patterns and distinctive thought processes of a character. Using Lu Xun, a renowned Chinese writer, as a case study, we propose four training tasks derived from his 17 essay collections. These include a pre-training task focused on mastering external linguistic structures and knowledge, as well as three fine-tuning tasks: multiple-choice question answering, generative question answering, and style transfer, each aligning the LLM with Lu Xun's internal ideation and writing style. To optimize learning across these tasks, we introduce a CharLoRA parameter updating mechanism, where a general linguistic style expert collaborates with other task-specific experts to better study both the language style and the understanding of deeper thoughts. We evaluate CharacterBot on three tasks for linguistic accuracy and opinion comprehension, demonstrating that it significantly outperforms the baselines on our adapted metrics. We hope that this work inspires future research on deep character persona simulation LLM.
Computational Protein Science in the Era of Large Language Models (LLMs)
Jan 17, 2025



Abstract:Considering the significance of proteins, computational protein science has always been a critical scientific field, dedicated to revealing knowledge and developing applications within the protein sequence-structure-function paradigm. In the last few decades, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has made significant impacts in computational protein science, leading to notable successes in specific protein modeling tasks. However, those previous AI models still meet limitations, such as the difficulty in comprehending the semantics of protein sequences, and the inability to generalize across a wide range of protein modeling tasks. Recently, LLMs have emerged as a milestone in AI due to their unprecedented language processing & generalization capability. They can promote comprehensive progress in fields rather than solving individual tasks. As a result, researchers have actively introduced LLM techniques in computational protein science, developing protein Language Models (pLMs) that skillfully grasp the foundational knowledge of proteins and can be effectively generalized to solve a diversity of sequence-structure-function reasoning problems. While witnessing prosperous developments, it's necessary to present a systematic overview of computational protein science empowered by LLM techniques. First, we summarize existing pLMs into categories based on their mastered protein knowledge, i.e., underlying sequence patterns, explicit structural and functional information, and external scientific languages. Second, we introduce the utilization and adaptation of pLMs, highlighting their remarkable achievements in promoting protein structure prediction, protein function prediction, and protein design studies. Then, we describe the practical application of pLMs in antibody design, enzyme design, and drug discovery. Finally, we specifically discuss the promising future directions in this fast-growing field.
Toward AI-Driven Digital Organism: Multiscale Foundation Models for Predicting, Simulating and Programming Biology at All Levels
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:We present an approach of using AI to model and simulate biology and life. Why is it important? Because at the core of medicine, pharmacy, public health, longevity, agriculture and food security, environmental protection, and clean energy, it is biology at work. Biology in the physical world is too complex to manipulate and always expensive and risky to tamper with. In this perspective, we layout an engineering viable approach to address this challenge by constructing an AI-Driven Digital Organism (AIDO), a system of integrated multiscale foundation models, in a modular, connectable, and holistic fashion to reflect biological scales, connectedness, and complexities. An AIDO opens up a safe, affordable and high-throughput alternative platform for predicting, simulating and programming biology at all levels from molecules to cells to individuals. We envision that an AIDO is poised to trigger a new wave of better-guided wet-lab experimentation and better-informed first-principle reasoning, which can eventually help us better decode and improve life.
Training Compute-Optimal Protein Language Models
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:We explore optimally training protein language models, an area of significant interest in biological research where guidance on best practices is limited. Most models are trained with extensive compute resources until performance gains plateau, focusing primarily on increasing model sizes rather than optimizing the efficient compute frontier that balances performance and compute budgets. Our investigation is grounded in a massive dataset consisting of 939 million protein sequences. We trained over 300 models ranging from 3.5 million to 10.7 billion parameters on 5 to 200 billion unique tokens, to investigate the relations between model sizes, training token numbers, and objectives. First, we observed the effect of diminishing returns for the Causal Language Model (CLM) and that of overfitting for the Masked Language Model~(MLM) when repeating the commonly used Uniref database. To address this, we included metagenomic protein sequences in the training set to increase the diversity and avoid the plateau or overfitting effects. Second, we obtained the scaling laws of CLM and MLM on Transformer, tailored to the specific characteristics of protein sequence data. Third, we observe a transfer scaling phenomenon from CLM to MLM, further demonstrating the effectiveness of transfer through scaling behaviors based on estimated Effectively Transferred Tokens. Finally, to validate our scaling laws, we compare the large-scale versions of ESM-2 and PROGEN2 on downstream tasks, encompassing evaluations of protein generation as well as structure- and function-related tasks, all within less or equivalent pre-training compute budgets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge