Duzhen Zhang
MemR$^3$: Memory Retrieval via Reflective Reasoning for LLM Agents
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Memory systems have been designed to leverage past experiences in Large Language Model (LLM) agents. However, many deployed memory systems primarily optimize compression and storage, with comparatively less emphasis on explicit, closed-loop control of memory retrieval. From this observation, we build memory retrieval as an autonomous, accurate, and compatible agent system, named MemR$^3$, which has two core mechanisms: 1) a router that selects among retrieve, reflect, and answer actions to optimize answer quality; 2) a global evidence-gap tracker that explicitly renders the answering process transparent and tracks the evidence collection process. This design departs from the standard retrieve-then-answer pipeline by introducing a closed-loop control mechanism that enables autonomous decision-making. Empirical results on the LoCoMo benchmark demonstrate that MemR$^3$ surpasses strong baselines on LLM-as-a-Judge score, and particularly, it improves existing retrievers across four categories with an overall improvement on RAG (+7.29%) and Zep (+1.94%) using GPT-4.1-mini backend, offering a plug-and-play controller for existing memory stores.
TinyChemVL: Advancing Chemical Vision-Language Models via Efficient Visual Token Reduction and Complex Reaction Tasks
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:While Vision Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in general visual understanding, their application in the chemical domain has been limited, with previous works predominantly focusing on text and thus overlooking critical visual information, such as molecular structures. Current approaches that directly adopt standard VLMs for chemical tasks suffer from two primary issues: (i) computational inefficiency of processing entire chemical images with non-informative backgrounds. (ii) a narrow scope on molecular-level tasks that restricts progress in chemical reasoning. In this work, we propose \textbf{TinyChemVL}, an efficient and powerful chemical VLM that leverages visual token reduction and reaction-level tasks to improve model efficiency and reasoning capacity. Also, we propose \textbf{ChemRxn-V}, a reaction-level benchmark for assessing vision-based reaction recognition and prediction tasks. Directly predicting reaction products from molecular images poses a non-trivial challenge, as it requires models to integrate both recognition and reasoning capacities. Our results demonstrate that with only 4B parameters, TinyChemVL achieves superior performance on both molecular and reaction tasks while demonstrating faster inference and training speeds compared to existing models. Notably, TinyChemVL outperforms ChemVLM while utilizing only 1/16th of the visual tokens. This work builds efficient yet powerful VLMs for chemical domains by co-designing model architecture and task complexity.
MedKGent: A Large Language Model Agent Framework for Constructing Temporally Evolving Medical Knowledge Graph
Aug 17, 2025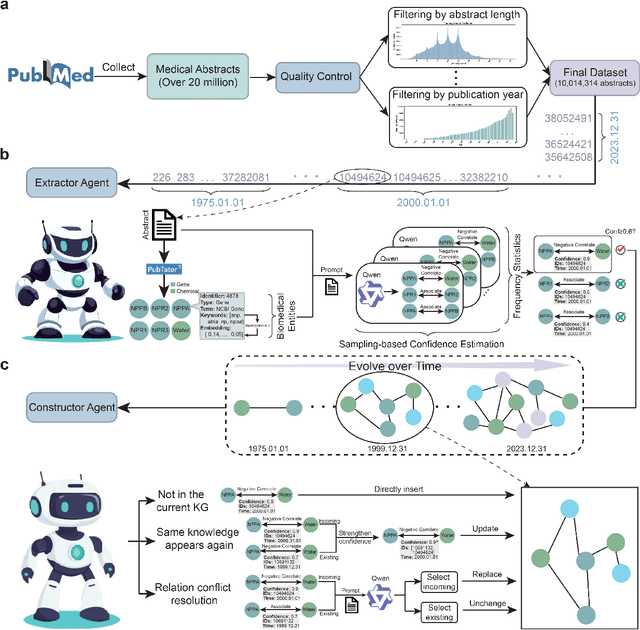
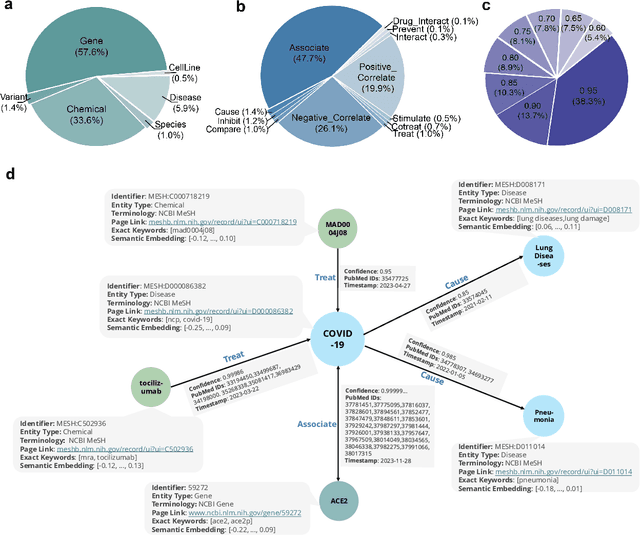
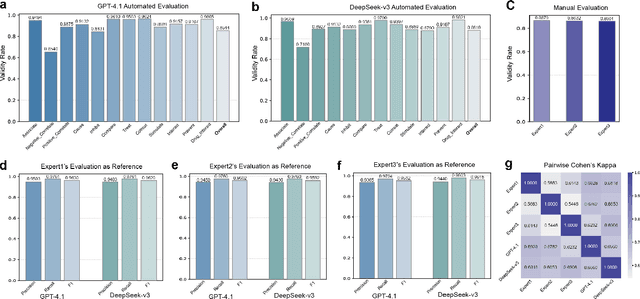
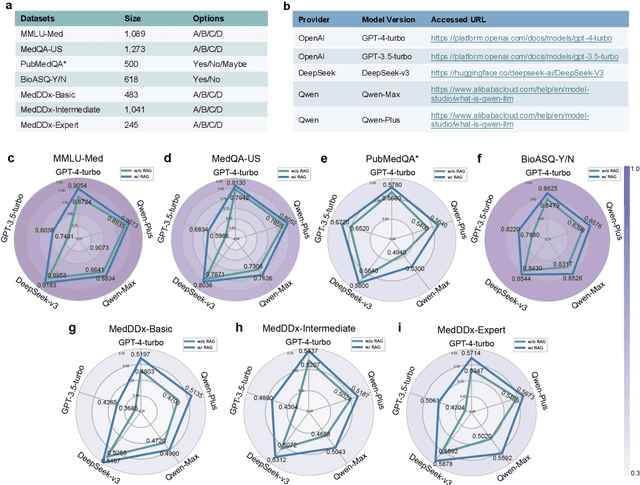
Abstract:The rapid expansion of medical literature presents growing challenges for structuring and integrating domain knowledge at scale. Knowledge Graphs (KGs) offer a promising solution by enabling efficient retrieval, automated reasoning, and knowledge discovery. However, current KG construction methods often rely on supervised pipelines with limited generalizability or naively aggregate outputs from Large Language Models (LLMs), treating biomedical corpora as static and ignoring the temporal dynamics and contextual uncertainty of evolving knowledge. To address these limitations, we introduce MedKGent, a LLM agent framework for constructing temporally evolving medical KGs. Leveraging over 10 million PubMed abstracts published between 1975 and 2023, we simulate the emergence of biomedical knowledge via a fine-grained daily time series. MedKGent incrementally builds the KG in a day-by-day manner using two specialized agents powered by the Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct model. The Extractor Agent identifies knowledge triples and assigns confidence scores via sampling-based estimation, which are used to filter low-confidence extractions and inform downstream processing. The Constructor Agent incrementally integrates the retained triples into a temporally evolving graph, guided by confidence scores and timestamps to reinforce recurring knowledge and resolve conflicts. The resulting KG contains 156,275 entities and 2,971,384 relational triples. Quality assessments by two SOTA LLMs and three domain experts demonstrate an accuracy approaching 90\%, with strong inter-rater agreement. To evaluate downstream utility, we conduct RAG across seven medical question answering benchmarks using five leading LLMs, consistently observing significant improvements over non-augmented baselines. Case studies further demonstrate the KG's value in literature-based drug repurposing via confidence-aware causal inference.
A Survey of Context Engineering for Large Language Models
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:The performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) is fundamentally determined by the contextual information provided during inference. This survey introduces Context Engineering, a formal discipline that transcends simple prompt design to encompass the systematic optimization of information payloads for LLMs. We present a comprehensive taxonomy decomposing Context Engineering into its foundational components and the sophisticated implementations that integrate them into intelligent systems. We first examine the foundational components: context retrieval and generation, context processing and context management. We then explore how these components are architecturally integrated to create sophisticated system implementations: retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), memory systems and tool-integrated reasoning, and multi-agent systems. Through this systematic analysis of over 1300 research papers, our survey not only establishes a technical roadmap for the field but also reveals a critical research gap: a fundamental asymmetry exists between model capabilities. While current models, augmented by advanced context engineering, demonstrate remarkable proficiency in understanding complex contexts, they exhibit pronounced limitations in generating equally sophisticated, long-form outputs. Addressing this gap is a defining priority for future research. Ultimately, this survey provides a unified framework for both researchers and engineers advancing context-aware AI.
Information-Theoretic Complementary Prompts for Improved Continual Text Classification
May 27, 2025Abstract:Continual Text Classification (CTC) aims to continuously classify new text data over time while minimizing catastrophic forgetting of previously acquired knowledge. However, existing methods often focus on task-specific knowledge, overlooking the importance of shared, task-agnostic knowledge. Inspired by the complementary learning systems theory, which posits that humans learn continually through the interaction of two systems -- the hippocampus, responsible for forming distinct representations of specific experiences, and the neocortex, which extracts more general and transferable representations from past experiences -- we introduce Information-Theoretic Complementary Prompts (InfoComp), a novel approach for CTC. InfoComp explicitly learns two distinct prompt spaces: P(rivate)-Prompt and S(hared)-Prompt. These respectively encode task-specific and task-invariant knowledge, enabling models to sequentially learn classification tasks without relying on data replay. To promote more informative prompt learning, InfoComp uses an information-theoretic framework that maximizes mutual information between different parameters (or encoded representations). Within this framework, we design two novel loss functions: (1) to strengthen the accumulation of task-specific knowledge in P-Prompt, effectively mitigating catastrophic forgetting, and (2) to enhance the retention of task-invariant knowledge in S-Prompt, improving forward knowledge transfer. Extensive experiments on diverse CTC benchmarks show that our approach outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods.
AutoReproduce: Automatic AI Experiment Reproduction with Paper Lineage
May 27, 2025Abstract:Efficient experiment reproduction is critical to accelerating progress in artificial intelligence. However, the inherent complexity of method design and training procedures presents substantial challenges for automation. Notably, reproducing experiments often requires implicit domain-specific knowledge not explicitly documented in the original papers. To address this, we introduce the paper lineage algorithm, which identifies and extracts implicit knowledge from the relevant references cited by the target paper. Building on this idea, we propose AutoReproduce, a multi-agent framework capable of automatically reproducing experiments described in research papers in an end-to-end manner. AutoReproduce enhances code executability by generating unit tests alongside the reproduction process. To evaluate the reproduction capability, we construct ReproduceBench, a benchmark annotated with verified implementations, and introduce novel evaluation metrics to assess both the reproduction and execution fidelity. Experimental results demonstrate that AutoReproduce outperforms the existing strong agent baselines on all five evaluation metrics by a peak margin of over $70\%$. In particular, compared to the official implementations, AutoReproduce achieves an average performance gap of $22.1\%$ on $89.74\%$ of the executable experiment runs. The code will be available at https://github.com/AI9Stars/AutoReproduce.
Hearing from Silence: Reasoning Audio Descriptions from Silent Videos via Vision-Language Model
May 19, 2025Abstract:Humans can intuitively infer sounds from silent videos, but whether multimodal large language models can perform modal-mismatch reasoning without accessing target modalities remains relatively unexplored. Current text-assisted-video-to-audio (VT2A) methods excel in video foley tasks but struggle to acquire audio descriptions during inference. We introduce the task of Reasoning Audio Descriptions from Silent Videos (SVAD) to address this challenge and investigate vision-language models' (VLMs) capabilities on this task. To further enhance the VLMs' reasoning capacity for the SVAD task, we construct a CoT-AudioCaps dataset and propose a Chain-of-Thought-based supervised fine-tuning strategy. Experiments on SVAD and subsequent VT2A tasks demonstrate our method's effectiveness in two key aspects: significantly improving VLMs' modal-mismatch reasoning for SVAD and effectively addressing the challenge of acquiring audio descriptions during VT2A inference.
LifelongAgentBench: Evaluating LLM Agents as Lifelong Learners
May 17, 2025Abstract:Lifelong learning is essential for intelligent agents operating in dynamic environments. Current large language model (LLM)-based agents, however, remain stateless and unable to accumulate or transfer knowledge over time. Existing benchmarks treat agents as static systems and fail to evaluate lifelong learning capabilities. We present LifelongAgentBench, the first unified benchmark designed to systematically assess the lifelong learning ability of LLM agents. It provides skill-grounded, interdependent tasks across three interactive environments, Database, Operating System, and Knowledge Graph, with automatic label verification, reproducibility, and modular extensibility. Extensive experiments reveal that conventional experience replay has limited effectiveness for LLM agents due to irrelevant information and context length constraints. We further introduce a group self-consistency mechanism that significantly improves lifelong learning performance. We hope LifelongAgentBench will advance the development of adaptive, memory-capable LLM agents.
Safety in Large Reasoning Models: A Survey
Apr 24, 2025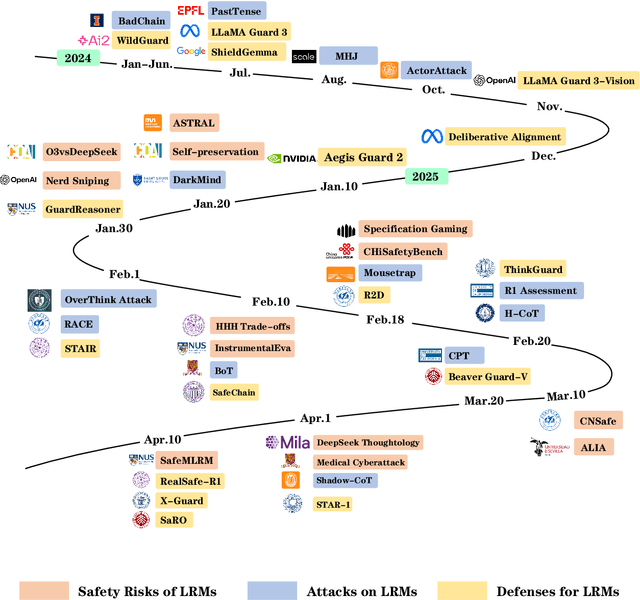
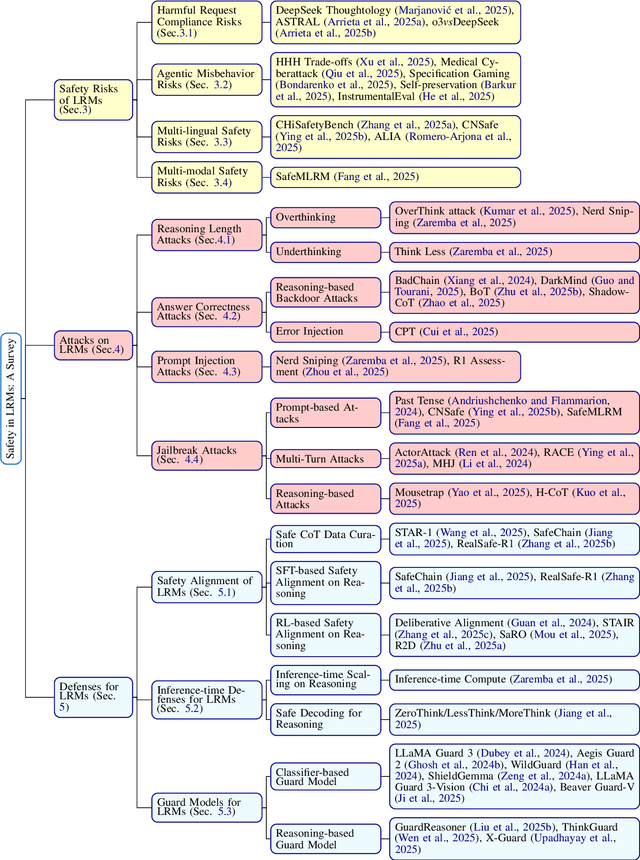
Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) have exhibited extraordinary prowess in tasks like mathematics and coding, leveraging their advanced reasoning capabilities. Nevertheless, as these capabilities progress, significant concerns regarding their vulnerabilities and safety have arisen, which can pose challenges to their deployment and application in real-world settings. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of LRMs, meticulously exploring and summarizing the newly emerged safety risks, attacks, and defense strategies. By organizing these elements into a detailed taxonomy, this work aims to offer a clear and structured understanding of the current safety landscape of LRMs, facilitating future research and development to enhance the security and reliability of these powerful models.
From System 1 to System 2: A Survey of Reasoning Large Language Models
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Achieving human-level intelligence requires refining the transition from the fast, intuitive System 1 to the slower, more deliberate System 2 reasoning. While System 1 excels in quick, heuristic decisions, System 2 relies on logical reasoning for more accurate judgments and reduced biases. Foundational Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at fast decision-making but lack the depth for complex reasoning, as they have not yet fully embraced the step-by-step analysis characteristic of true System 2 thinking. Recently, reasoning LLMs like OpenAI's o1/o3 and DeepSeek's R1 have demonstrated expert-level performance in fields such as mathematics and coding, closely mimicking the deliberate reasoning of System 2 and showcasing human-like cognitive abilities. This survey begins with a brief overview of the progress in foundational LLMs and the early development of System 2 technologies, exploring how their combination has paved the way for reasoning LLMs. Next, we discuss how to construct reasoning LLMs, analyzing their features, the core methods enabling advanced reasoning, and the evolution of various reasoning LLMs. Additionally, we provide an overview of reasoning benchmarks, offering an in-depth comparison of the performance of representative reasoning LLMs. Finally, we explore promising directions for advancing reasoning LLMs and maintain a real-time \href{https://github.com/zzli2022/Awesome-Slow-Reason-System}{GitHub Repository} to track the latest developments. We hope this survey will serve as a valuable resource to inspire innovation and drive progress in this rapidly evolving field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge