Hao Gu
Learning While Staying Curious: Entropy-Preserving Supervised Fine-Tuning via Adaptive Self-Distillation for Large Reasoning Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:The standard post-training recipe for large reasoning models, supervised fine-tuning followed by reinforcement learning (SFT-then-RL), may limit the benefits of the RL stage: while SFT imitates expert demonstrations, it often causes overconfidence and reduces generation diversity, leaving RL with a narrowed solution space to explore. Adding entropy regularization during SFT is not a cure-all; it tends to flatten token distributions toward uniformity, increasing entropy without improving meaningful exploration capability. In this paper, we propose CurioSFT, an entropy-preserving SFT method designed to enhance exploration capabilities through intrinsic curiosity. It consists of (a) Self-Exploratory Distillation, which distills the model toward a self-generated, temperature-scaled teacher to encourage exploration within its capability; and (b) Entropy-Guided Temperature Selection, which adaptively adjusts distillation strength to mitigate knowledge forgetting by amplifying exploration at reasoning tokens while stabilizing factual tokens. Extensive experiments on mathematical reasoning tasks demonstrate that, in SFT stage, CurioSFT outperforms the vanilla SFT by 2.5 points on in-distribution tasks and 2.9 points on out-of-distribution tasks. We also verify that exploration capabilities preserved during SFT successfully translate into concrete gains in RL stage, yielding an average improvement of 5.0 points.
Spectral Imbalance Causes Forgetting in Low-Rank Continual Adaptation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Parameter-efficient continual learning aims to adapt pre-trained models to sequential tasks without forgetting previously acquired knowledge. Most existing approaches treat continual learning as avoiding interference with past updates, rather than considering what properties make the current task-specific update naturally preserve previously acquired knowledge. From a knowledge-decomposition perspective, we observe that low-rank adaptations exhibit highly imbalanced singular value spectra: a few dominant components absorb most of the adaptation energy, thereby (i) more likely to disrupt previously acquired knowledge and (ii) making the update more vulnerable to interference from subsequent tasks. To enable explicit balance among components, we decouple the magnitude of the task update from its directional structure and formulate it as a constrained optimization problem on a restricted Stiefel manifold. We address this problem using a projected first-order method compatible with standard deep-learning optimizers used in vision-language models. Our method mitigates both backward and forward forgetting, consistently outperforming continual learning baselines. The implementation code is available at https://github.com/haodotgu/EBLoRA.
OV-InstructTTS: Towards Open-Vocabulary Instruct Text-to-Speech
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Instruct Text-to-Speech (InstructTTS) leverages natural language descriptions as style prompts to guide speech synthesis. However, existing InstructTTS methods mainly rely on a direct combination of audio-related labels or their diverse rephrasings, making it difficult to handle flexible, high-level instructions. Such rigid control is insufficient for users such as content creators who wish to steer generation with descriptive instructions. To address these constraints, we introduce OV-InstructTTS, a new paradigm for open-vocabulary InstructTTS. We propose a comprehensive solution comprising a newly curated dataset, OV-Speech, and a novel reasoning-driven framework. The OV-Speech dataset pairs speech with open-vocabulary instructions, each augmented with a reasoning process that connects high-level instructions to acoustic features. The reasoning-driven framework infers emotional, acoustic, and paralinguistic information from open-vocabulary instructions before synthesizing speech. Evaluations show that this reasoning-driven approach significantly improves instruction-following fidelity and speech expressiveness. We believe this work can inspire the next user-friendly InstructTTS systems with stronger generalization and real-world applicability. The dataset and demos are publicly available on our project page.
R4ec: A Reasoning, Reflection, and Refinement Framework for Recommendation Systems
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Harnessing Large Language Models (LLMs) for recommendation systems has emerged as a prominent avenue, drawing substantial research interest. However, existing approaches primarily involve basic prompt techniques for knowledge acquisition, which resemble System-1 thinking. This makes these methods highly sensitive to errors in the reasoning path, where even a small mistake can lead to an incorrect inference. To this end, in this paper, we propose $R^{4}$ec, a reasoning, reflection and refinement framework that evolves the recommendation system into a weak System-2 model. Specifically, we introduce two models: an actor model that engages in reasoning, and a reflection model that judges these responses and provides valuable feedback. Then the actor model will refine its response based on the feedback, ultimately leading to improved responses. We employ an iterative reflection and refinement process, enabling LLMs to facilitate slow and deliberate System-2-like thinking. Ultimately, the final refined knowledge will be incorporated into a recommendation backbone for prediction. We conduct extensive experiments on Amazon-Book and MovieLens-1M datasets to demonstrate the superiority of $R^{4}$ec. We also deploy $R^{4}$ec on a large scale online advertising platform, showing 2.2\% increase of revenue. Furthermore, we investigate the scaling properties of the actor model and reflection model.
Hierarchical Tree Search-based User Lifelong Behavior Modeling on Large Language Model
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have garnered significant attention in Recommendation Systems (RS) due to their extensive world knowledge and robust reasoning capabilities. However, a critical challenge lies in enabling LLMs to effectively comprehend and extract insights from massive user behaviors. Current approaches that directly leverage LLMs for user interest learning face limitations in handling long sequential behaviors, effectively extracting interest, and applying interest in practical scenarios. To address these issues, we propose a Hierarchical Tree Search-based User Lifelong Behavior Modeling framework (HiT-LBM). HiT-LBM integrates Chunked User Behavior Extraction (CUBE) and Hierarchical Tree Search for Interest (HTS) to capture diverse interests and interest evolution of user. CUBE divides user lifelong behaviors into multiple chunks and learns the interest and interest evolution within each chunk in a cascading manner. HTS generates candidate interests through hierarchical expansion and searches for the optimal interest with process rating model to ensure information gain for each behavior chunk. Additionally, we design Temporal-Ware Interest Fusion (TIF) to integrate interests from multiple behavior chunks, constructing a comprehensive representation of user lifelong interests. The representation can be embedded into any recommendation model to enhance performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, showing that it surpasses state-of-the-art methods.
Hearing from Silence: Reasoning Audio Descriptions from Silent Videos via Vision-Language Model
May 19, 2025Abstract:Humans can intuitively infer sounds from silent videos, but whether multimodal large language models can perform modal-mismatch reasoning without accessing target modalities remains relatively unexplored. Current text-assisted-video-to-audio (VT2A) methods excel in video foley tasks but struggle to acquire audio descriptions during inference. We introduce the task of Reasoning Audio Descriptions from Silent Videos (SVAD) to address this challenge and investigate vision-language models' (VLMs) capabilities on this task. To further enhance the VLMs' reasoning capacity for the SVAD task, we construct a CoT-AudioCaps dataset and propose a Chain-of-Thought-based supervised fine-tuning strategy. Experiments on SVAD and subsequent VT2A tasks demonstrate our method's effectiveness in two key aspects: significantly improving VLMs' modal-mismatch reasoning for SVAD and effectively addressing the challenge of acquiring audio descriptions during VT2A inference.
$\mathcal{A}LLM4ADD$: Unlocking the Capabilities of Audio Large Language Models for Audio Deepfake Detection
May 16, 2025
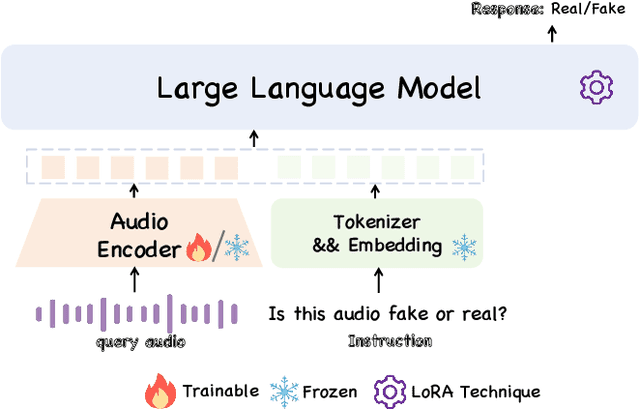
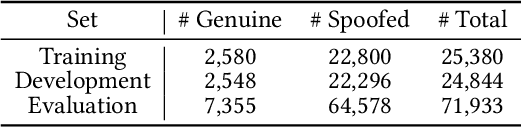
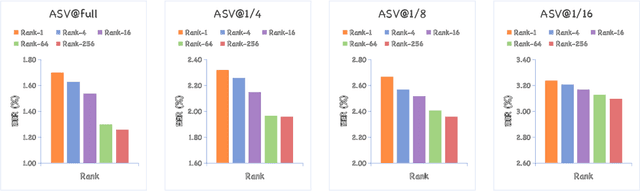
Abstract:Audio deepfake detection (ADD) has grown increasingly important due to the rise of high-fidelity audio generative models and their potential for misuse. Given that audio large language models (ALLMs) have made significant progress in various audio processing tasks, a heuristic question arises: Can ALLMs be leveraged to solve ADD?. In this paper, we first conduct a comprehensive zero-shot evaluation of ALLMs on ADD, revealing their ineffectiveness in detecting fake audio. To enhance their performance, we propose $\mathcal{A}LLM4ADD$, an ALLM-driven framework for ADD. Specifically, we reformulate ADD task as an audio question answering problem, prompting the model with the question: "Is this audio fake or real?". We then perform supervised fine-tuning to enable the ALLM to assess the authenticity of query audio. Extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate that our ALLM-based method can achieve superior performance in fake audio detection, particularly in data-scarce scenarios. As a pioneering study, we anticipate that this work will inspire the research community to leverage ALLMs to develop more effective ADD systems.
Relative Contrastive Learning for Sequential Recommendation with Similarity-based Positive Pair Selection
Apr 27, 2025Abstract:Contrastive Learning (CL) enhances the training of sequential recommendation (SR) models through informative self-supervision signals. Existing methods often rely on data augmentation strategies to create positive samples and promote representation invariance. Some strategies such as item reordering and item substitution may inadvertently alter user intent. Supervised Contrastive Learning (SCL) based methods find an alternative to augmentation-based CL methods by selecting same-target sequences (interaction sequences with the same target item) to form positive samples. However, SCL-based methods suffer from the scarcity of same-target sequences and consequently lack enough signals for contrastive learning. In this work, we propose to use similar sequences (with different target items) as additional positive samples and introduce a Relative Contrastive Learning (RCL) framework for sequential recommendation. RCL comprises a dual-tiered positive sample selection module and a relative contrastive learning module. The former module selects same-target sequences as strong positive samples and selects similar sequences as weak positive samples. The latter module employs a weighted relative contrastive loss, ensuring that each sequence is represented closer to its strong positive samples than its weak positive samples. We apply RCL on two mainstream deep learning-based SR models, and our empirical results reveal that RCL can achieve 4.88% improvement averagely than the state-of-the-art SR methods on five public datasets and one private dataset.
Delta Decompression for MoE-based LLMs Compression
Feb 24, 2025



Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures in large language models (LLMs) achieve exceptional performance, but face prohibitive storage and memory requirements. To address these challenges, we present $D^2$-MoE, a new delta decompression compressor for reducing the parameters of MoE LLMs. Based on observations of expert diversity, we decompose their weights into a shared base weight and unique delta weights. Specifically, our method first merges each expert's weight into the base weight using the Fisher information matrix to capture shared components. Then, we compress delta weights through Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) by exploiting their low-rank properties. Finally, we introduce a semi-dynamical structured pruning strategy for the base weights, combining static and dynamic redundancy analysis to achieve further parameter reduction while maintaining input adaptivity. In this way, our $D^2$-MoE successfully compact MoE LLMs to high compression ratios without additional training. Extensive experiments highlight the superiority of our approach, with over 13% performance gains than other compressors on Mixtral|Phi-3.5|DeepSeek|Qwen2 MoE LLMs at 40$\sim$60% compression rates. Codes are available in https://github.com/lliai/D2MoE.
Region-Based Optimization in Continual Learning for Audio Deepfake Detection
Dec 16, 2024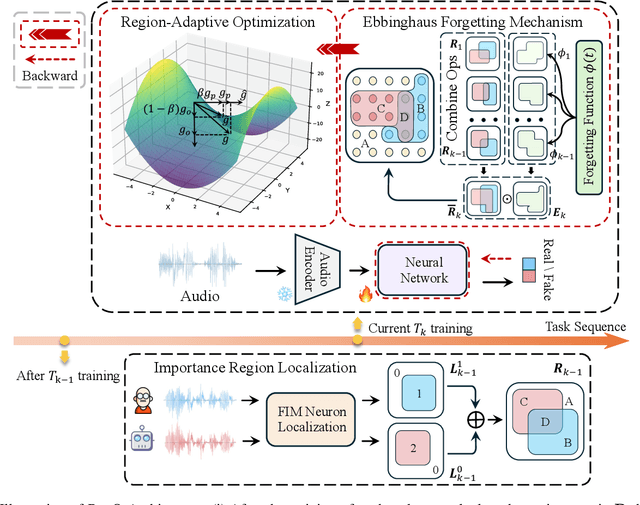
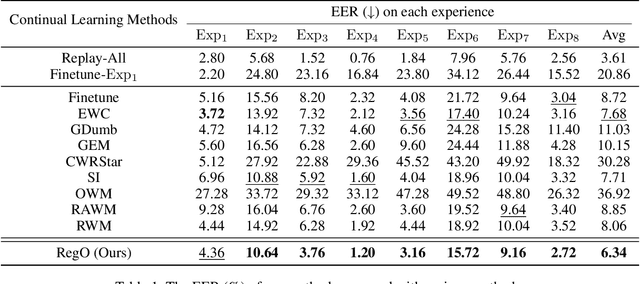
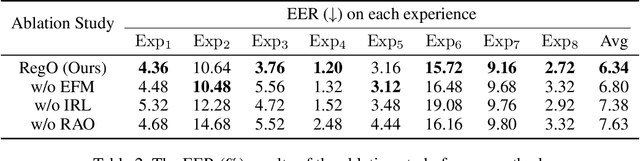
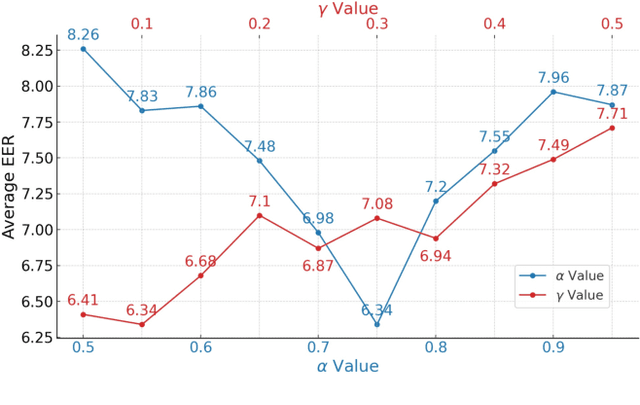
Abstract:Rapid advancements in speech synthesis and voice conversion bring convenience but also new security risks, creating an urgent need for effective audio deepfake detection. Although current models perform well, their effectiveness diminishes when confronted with the diverse and evolving nature of real-world deepfakes. To address this issue, we propose a continual learning method named Region-Based Optimization (RegO) for audio deepfake detection. Specifically, we use the Fisher information matrix to measure important neuron regions for real and fake audio detection, dividing them into four regions. First, we directly fine-tune the less important regions to quickly adapt to new tasks. Next, we apply gradient optimization in parallel for regions important only to real audio detection, and in orthogonal directions for regions important only to fake audio detection. For regions that are important to both, we use sample proportion-based adaptive gradient optimization. This region-adaptive optimization ensures an appropriate trade-off between memory stability and learning plasticity. Additionally, to address the increase of redundant neurons from old tasks, we further introduce the Ebbinghaus forgetting mechanism to release them, thereby promoting the capability of the model to learn more generalized discriminative features. Experimental results show our method achieves a 21.3% improvement in EER over the state-of-the-art continual learning approach RWM for audio deepfake detection. Moreover, the effectiveness of RegO extends beyond the audio deepfake detection domain, showing potential significance in other tasks, such as image recognition. The code is available at https://github.com/cyjie429/RegO
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge