Jiayun Wang
Resolution-Independent Neural Operators for Multi-Rate Sparse-View CT
Dec 13, 2025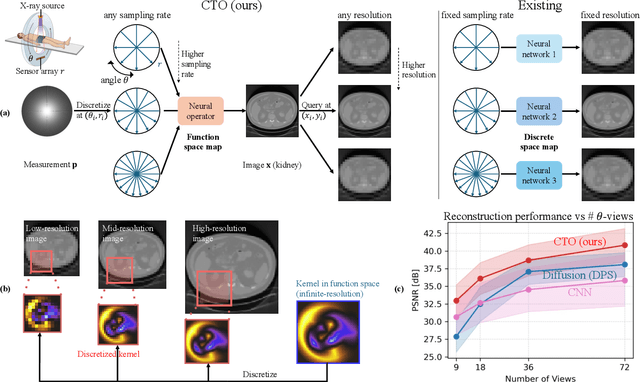
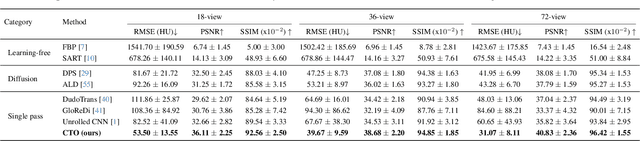
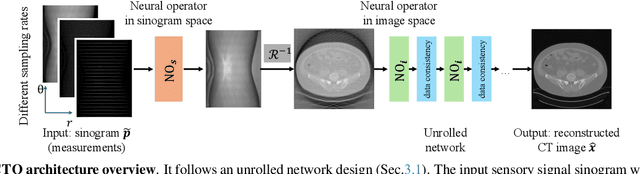
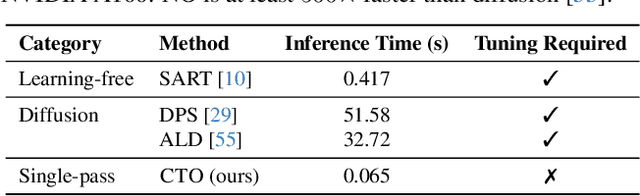
Abstract:Sparse-view Computed Tomography (CT) reconstructs images from a limited number of X-ray projections to reduce radiation and scanning time, which makes reconstruction an ill-posed inverse problem. Deep learning methods achieve high-fidelity reconstructions but often overfit to a fixed acquisition setup, failing to generalize across sampling rates and image resolutions. For example, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) use the same learned kernels across resolutions, leading to artifacts when data resolution changes. We propose Computed Tomography neural Operator (CTO), a unified CT reconstruction framework that extends to continuous function space, enabling generalization (without retraining) across sampling rates and image resolutions. CTO operates jointly in the sinogram and image domains through rotation-equivariant Discrete-Continuous convolutions parametrized in the function space, making it inherently resolution- and sampling-agnostic. Empirically, CTO enables consistent multi-sampling-rate and cross-resolution performance, with on average >4dB PSNR gain over CNNs. Compared to state-of-the-art diffusion methods, CTO is 500$\times$ faster in inference time with on average 3dB gain. Empirical results also validate our design choices behind CTO's sinogram-space operator learning and rotation-equivariant convolution. Overall, CTO outperforms state-of-the-art baselines across sampling rates and resolutions, offering a scalable and generalizable solution that makes automated CT reconstruction more practical for deployment.
Ultrasound Lung Aeration Map via Physics-Aware Neural Operators
Jan 02, 2025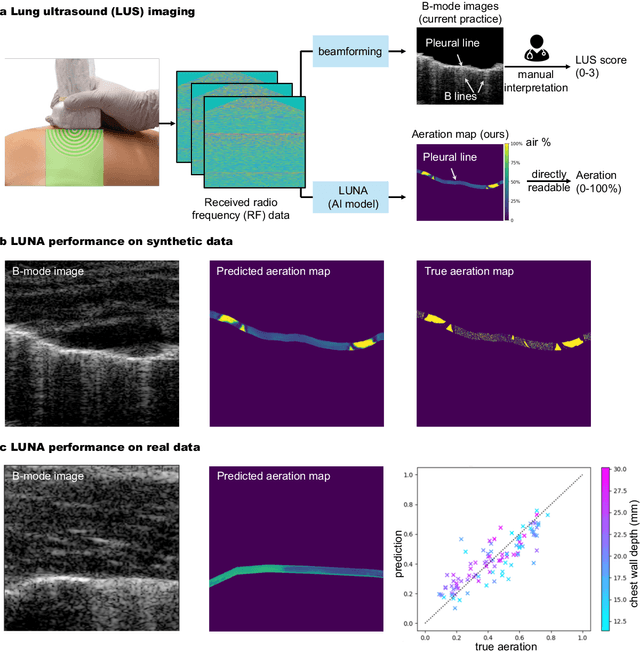
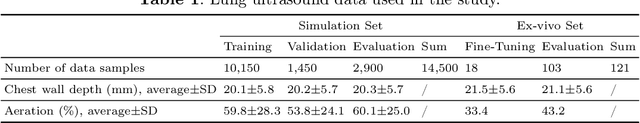
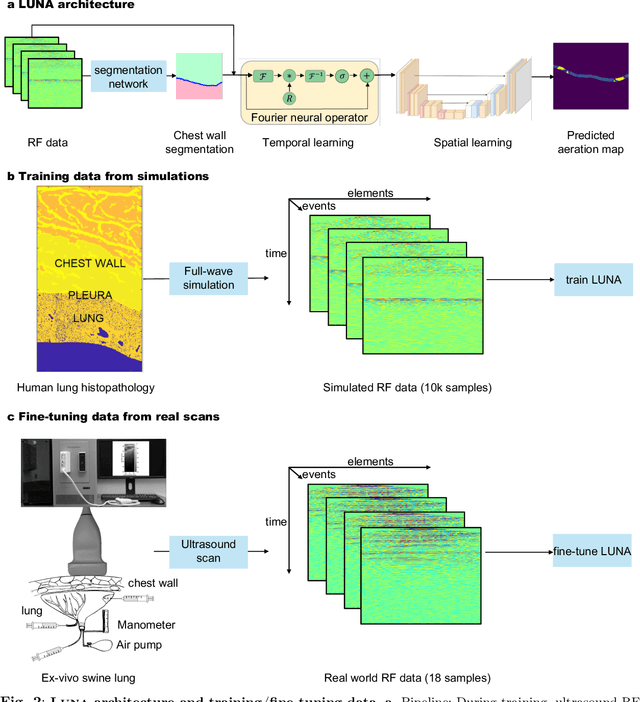
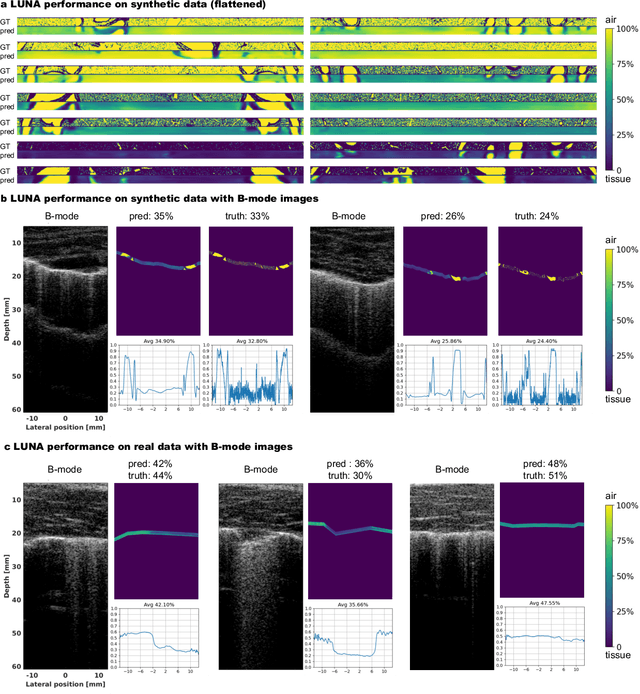
Abstract:Lung ultrasound is a growing modality in clinics for diagnosing and monitoring acute and chronic lung diseases due to its low cost and accessibility. Lung ultrasound works by emitting diagnostic pulses, receiving pressure waves and converting them into radio frequency (RF) data, which are then processed into B-mode images with beamformers for radiologists to interpret. However, unlike conventional ultrasound for soft tissue anatomical imaging, lung ultrasound interpretation is complicated by complex reverberations from the pleural interface caused by the inability of ultrasound to penetrate air. The indirect B-mode images make interpretation highly dependent on reader expertise, requiring years of training, which limits its widespread use despite its potential for high accuracy in skilled hands. To address these challenges and democratize ultrasound lung imaging as a reliable diagnostic tool, we propose LUNA, an AI model that directly reconstructs lung aeration maps from RF data, bypassing the need for traditional beamformers and indirect interpretation of B-mode images. LUNA uses a Fourier neural operator, which processes RF data efficiently in Fourier space, enabling accurate reconstruction of lung aeration maps. LUNA offers a quantitative, reader-independent alternative to traditional semi-quantitative lung ultrasound scoring methods. The development of LUNA involves synthetic and real data: We simulate synthetic data with an experimentally validated approach and scan ex vivo swine lungs as real data. Trained on abundant simulated data and fine-tuned with a small amount of real-world data, LUNA achieves robust performance, demonstrated by an aeration estimation error of 9% in ex-vivo lung scans. We demonstrate the potential of reconstructing lung aeration maps from RF data, providing a foundation for improving lung ultrasound reproducibility and diagnostic utility.
Open Vocabulary Monocular 3D Object Detection
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:In this work, we pioneer the study of open-vocabulary monocular 3D object detection, a novel task that aims to detect and localize objects in 3D space from a single RGB image without limiting detection to a predefined set of categories. We formalize this problem, establish baseline methods, and introduce a class-agnostic approach that leverages open-vocabulary 2D detectors and lifts 2D bounding boxes into 3D space. Our approach decouples the recognition and localization of objects in 2D from the task of estimating 3D bounding boxes, enabling generalization across unseen categories. Additionally, we propose a target-aware evaluation protocol to address inconsistencies in existing datasets, improving the reliability of model performance assessment. Extensive experiments on the Omni3D dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in zero-shot 3D detection for novel object categories, validating its robust generalization capabilities. Our method and evaluation protocols contribute towards the development of open-vocabulary object detection models that can effectively operate in real-world, category-diverse environments.
Beyond Closure Models: Learning Chaotic-Systems via Physics-Informed Neural Operators
Aug 09, 2024Abstract:Accurately predicting the long-term behavior of chaotic systems is crucial for various applications such as climate modeling. However, achieving such predictions typically requires iterative computations over a dense spatiotemporal grid to account for the unstable nature of chaotic systems, which is expensive and impractical in many real-world situations. An alternative approach to such a full-resolved simulation is using a coarse grid and then correcting its errors through a \textit{closure model}, which approximates the overall information from fine scales not captured in the coarse-grid simulation. Recently, ML approaches have been used for closure modeling, but they typically require a large number of training samples from expensive fully-resolved simulations (FRS). In this work, we prove an even more fundamental limitation, i.e., the standard approach to learning closure models suffers from a large approximation error for generic problems, no matter how large the model is, and it stems from the non-uniqueness of the mapping. We propose an alternative end-to-end learning approach using a physics-informed neural operator (PINO) that overcomes this limitation by not using a closure model or a coarse-grid solver. We first train the PINO model on data from a coarse-grid solver and then fine-tune it with (a small amount of) FRS and physics-based losses on a fine grid. The discretization-free nature of neural operators means that they do not suffer from the restriction of a coarse grid that closure models face, and they can provably approximate the long-term statistics of chaotic systems. In our experiments, our PINO model achieves a 120x speedup compared to FRS with a relative error $\sim 5\%$. In contrast, the closure model coupled with a coarse-grid solver is $58$x slower than PINO while having a much higher error $\sim205\%$ when the closure model is trained on the same FRS dataset.
Trajectory Regularization Enhances Self-Supervised Geometric Representation
Mar 22, 2024Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) has proven effective in learning high-quality representations for various downstream tasks, with a primary focus on semantic tasks. However, its application in geometric tasks remains underexplored, partially due to the absence of a standardized evaluation method for geometric representations. To address this gap, we introduce a new pose-estimation benchmark for assessing SSL geometric representations, which demands training without semantic or pose labels and achieving proficiency in both semantic and geometric downstream tasks. On this benchmark, we study enhancing SSL geometric representations without sacrificing semantic classification accuracy. We find that leveraging mid-layer representations improves pose-estimation performance by 10-20%. Further, we introduce an unsupervised trajectory-regularization loss, which improves performance by an additional 4% and improves generalization ability on out-of-distribution data. We hope the proposed benchmark and methods offer new insights and improvements in self-supervised geometric representation learning.
Deep Multimodal Fusion for Surgical Feedback Classification
Dec 06, 2023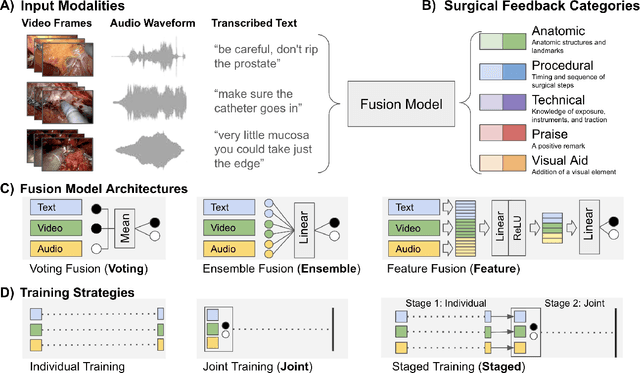

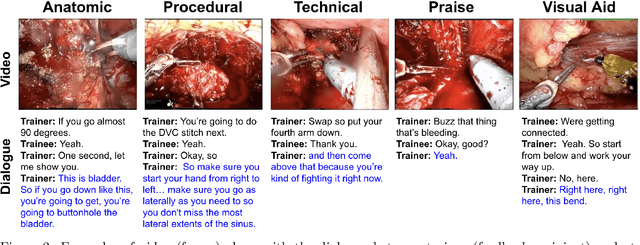
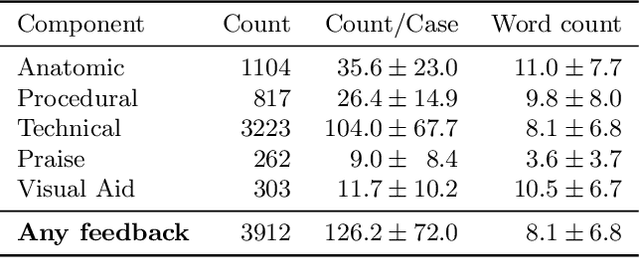
Abstract:Quantification of real-time informal feedback delivered by an experienced surgeon to a trainee during surgery is important for skill improvements in surgical training. Such feedback in the live operating room is inherently multimodal, consisting of verbal conversations (e.g., questions and answers) as well as non-verbal elements (e.g., through visual cues like pointing to anatomic elements). In this work, we leverage a clinically-validated five-category classification of surgical feedback: "Anatomic", "Technical", "Procedural", "Praise" and "Visual Aid". We then develop a multi-label machine learning model to classify these five categories of surgical feedback from inputs of text, audio, and video modalities. The ultimate goal of our work is to help automate the annotation of real-time contextual surgical feedback at scale. Our automated classification of surgical feedback achieves AUCs ranging from 71.5 to 77.6 with the fusion improving performance by 3.1%. We also show that high-quality manual transcriptions of feedback audio from experts improve AUCs to between 76.5 and 96.2, which demonstrates a clear path toward future improvements. Empirically, we find that the Staged training strategy, with first pre-training each modality separately and then training them jointly, is more effective than training different modalities altogether. We also present intuitive findings on the importance of modalities for different feedback categories. This work offers an important first look at the feasibility of automated classification of real-world live surgical feedback based on text, audio, and video modalities.
Tracking the Dynamics of the Tear Film Lipid Layer
Dec 07, 2022Abstract:Dry Eye Disease (DED) is one of the most common ocular diseases: over five percent of US adults suffer from DED. Tear film instability is a known factor for DED, and is thought to be regulated in large part by the thin lipid layer that covers and stabilizes the tear film. In order to aid eye related disease diagnosis, this work proposes a novel paradigm in using computer vision techniques to numerically analyze the tear film lipid layer (TFLL) spread. Eleven videos of the tear film lipid layer spread are collected with a micro-interferometer and a subset are annotated. A tracking algorithm relying on various pillar computer vision techniques is developed. Our method can be found at https://easytear-dev.github.io/.
Unsupervised Scene Sketch to Photo Synthesis
Sep 06, 2022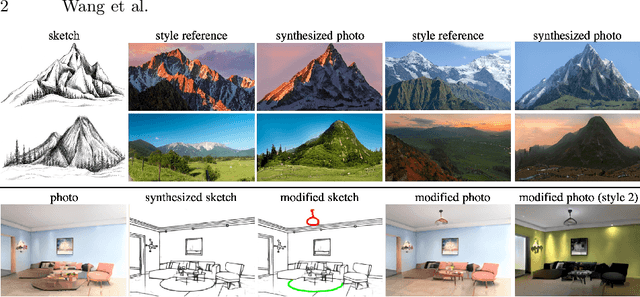
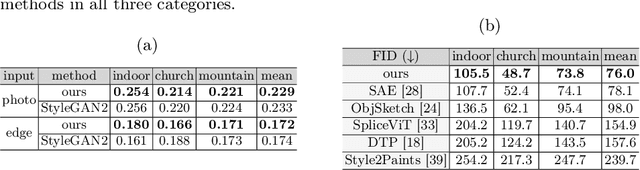
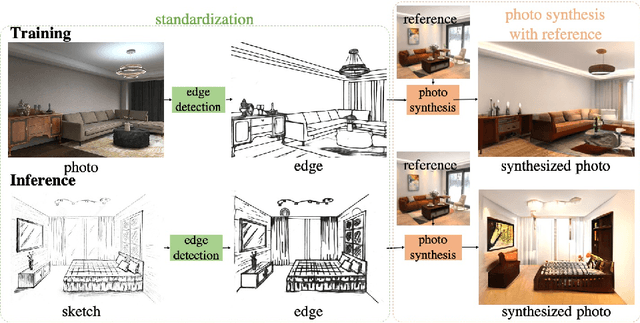

Abstract:Sketches make an intuitive and powerful visual expression as they are fast executed freehand drawings. We present a method for synthesizing realistic photos from scene sketches. Without the need for sketch and photo pairs, our framework directly learns from readily available large-scale photo datasets in an unsupervised manner. To this end, we introduce a standardization module that provides pseudo sketch-photo pairs during training by converting photos and sketches to a standardized domain, i.e. the edge map. The reduced domain gap between sketch and photo also allows us to disentangle them into two components: holistic scene structures and low-level visual styles such as color and texture. Taking this advantage, we synthesize a photo-realistic image by combining the structure of a sketch and the visual style of a reference photo. Extensive experimental results on perceptual similarity metrics and human perceptual studies show the proposed method could generate realistic photos with high fidelity from scene sketches and outperform state-of-the-art photo synthesis baselines. We also demonstrate that our framework facilitates a controllable manipulation of photo synthesis by editing strokes of corresponding sketches, delivering more fine-grained details than previous approaches that rely on region-level editing.
Open Long-Tailed Recognition in a Dynamic World
Aug 17, 2022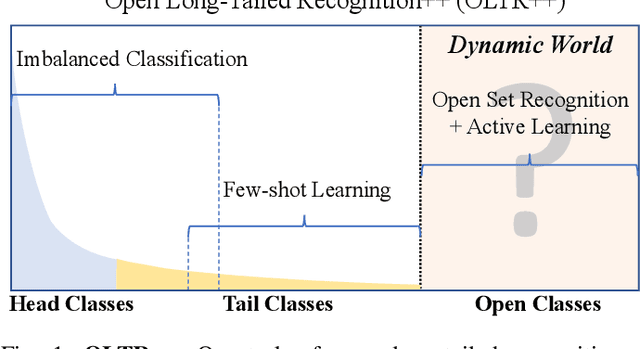
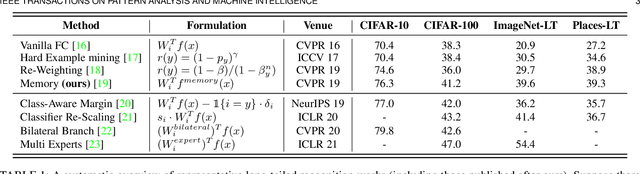
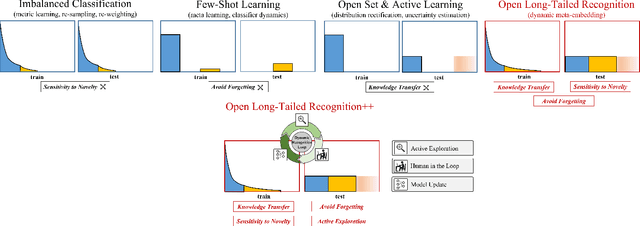
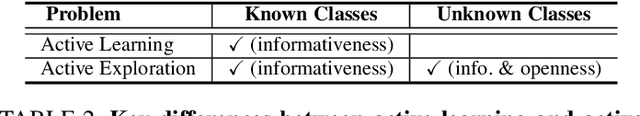
Abstract:Real world data often exhibits a long-tailed and open-ended (with unseen classes) distribution. A practical recognition system must balance between majority (head) and minority (tail) classes, generalize across the distribution, and acknowledge novelty upon the instances of unseen classes (open classes). We define Open Long-Tailed Recognition++ (OLTR++) as learning from such naturally distributed data and optimizing for the classification accuracy over a balanced test set which includes both known and open classes. OLTR++ handles imbalanced classification, few-shot learning, open-set recognition, and active learning in one integrated algorithm, whereas existing classification approaches often focus only on one or two aspects and deliver poorly over the entire spectrum. The key challenges are: 1) how to share visual knowledge between head and tail classes, 2) how to reduce confusion between tail and open classes, and 3) how to actively explore open classes with learned knowledge. Our algorithm, OLTR++, maps images to a feature space such that visual concepts can relate to each other through a memory association mechanism and a learned metric (dynamic meta-embedding) that both respects the closed world classification of seen classes and acknowledges the novelty of open classes. Additionally, we propose an active learning scheme based on visual memory, which learns to recognize open classes in a data-efficient manner for future expansions. On three large-scale open long-tailed datasets we curated from ImageNet (object-centric), Places (scene-centric), and MS1M (face-centric) data, as well as three standard benchmarks (CIFAR-10-LT, CIFAR-100-LT, and iNaturalist-18), our approach, as a unified framework, consistently demonstrates competitive performance. Notably, our approach also shows strong potential for the active exploration of open classes and the fairness analysis of minority groups.
Recurrent Parameter Generators
Jul 15, 2021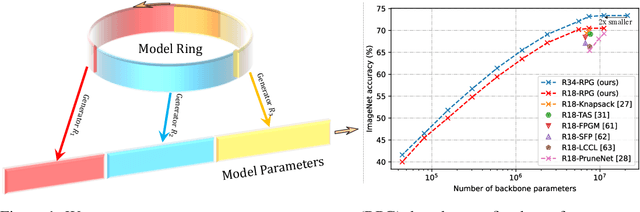
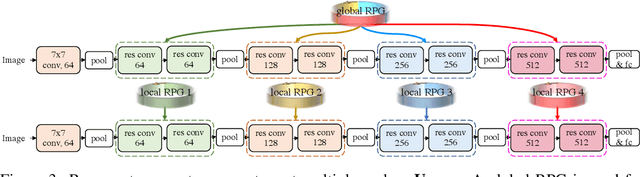
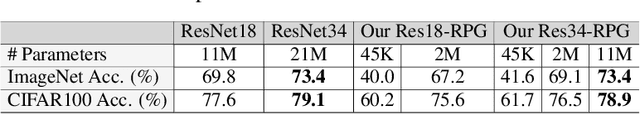
Abstract:We present a generic method for recurrently using the same parameters for many different convolution layers to build a deep network. Specifically, for a network, we create a recurrent parameter generator (RPG), from which the parameters of each convolution layer are generated. Though using recurrent models to build a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) is not entirely new, our method achieves significant performance gain compared to the existing works. We demonstrate how to build a one-layer neural network to achieve similar performance compared to other traditional CNN models on various applications and datasets. Such a method allows us to build an arbitrarily complex neural network with any amount of parameters. For example, we build a ResNet34 with model parameters reduced by more than $400$ times, which still achieves $41.6\%$ ImageNet top-1 accuracy. Furthermore, we demonstrate the RPG can be applied at different scales, such as layers, blocks, or even sub-networks. Specifically, we use the RPG to build a ResNet18 network with the number of weights equivalent to one convolutional layer of a conventional ResNet and show this model can achieve $67.2\%$ ImageNet top-1 accuracy. The proposed method can be viewed as an inverse approach to model compression. Rather than removing the unused parameters from a large model, it aims to squeeze more information into a small number of parameters. Extensive experiment results are provided to demonstrate the power of the proposed recurrent parameter generator.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge