Zheng Lian
SayNext-Bench: Why Do LLMs Struggle with Next-Utterance Prediction?
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:We explore the use of large language models (LLMs) for next-utterance prediction in human dialogue. Despite recent advances in LLMs demonstrating their ability to engage in natural conversations with users, we show that even leading models surprisingly struggle to predict a human speaker's next utterance. Instead, humans can readily anticipate forthcoming utterances based on multimodal cues, such as gestures, gaze, and emotional tone, from the context. To systematically examine whether LLMs can reproduce this ability, we propose SayNext-Bench, a benchmark that evaluates LLMs and Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) on anticipating context-conditioned responses from multimodal cues spanning a variety of real-world scenarios. To support this benchmark, we build SayNext-PC, a novel large-scale dataset containing dialogues with rich multimodal cues. Building on this, we further develop a dual-route prediction MLLM, SayNext-Chat, that incorporates cognitively inspired design to emulate predictive processing in conversation. Experimental results demonstrate that our model outperforms state-of-the-art MLLMs in terms of lexical overlap, semantic similarity, and emotion consistency. Our results prove the feasibility of next-utterance prediction with LLMs from multimodal cues and emphasize the (i) indispensable role of multimodal cues and (ii) actively predictive processing as the foundation of natural human interaction, which is missing in current MLLMs. We hope that this exploration offers a new research entry toward more human-like, context-sensitive AI interaction for human-centered AI. Our benchmark and model can be accessed at https://saynext.github.io/.
Emotion-LLaMAv2 and MMEVerse: A New Framework and Benchmark for Multimodal Emotion Understanding
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Understanding human emotions from multimodal signals poses a significant challenge in affective computing and human-robot interaction. While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have excelled in general vision-language tasks, their capabilities in emotional reasoning remain limited. The field currently suffers from a scarcity of large-scale datasets with high-quality, descriptive emotion annotations and lacks standardized benchmarks for evaluation. Our preliminary framework, Emotion-LLaMA, pioneered instruction-tuned multimodal learning for emotion reasoning but was restricted by explicit face detectors, implicit fusion strategies, and low-quality training data with limited scale. To address these limitations, we present Emotion-LLaMAv2 and the MMEVerse benchmark, establishing an end-to-end pipeline together with a standardized evaluation setting for emotion recognition and reasoning. Emotion-LLaMAv2 introduces three key advances. First, an end-to-end multiview encoder eliminates external face detection and captures nuanced emotional cues via richer spatial and temporal multiview tokens. Second, a Conv Attention pre-fusion module is designed to enable simultaneous local and global multimodal feature interactions external to the LLM backbone. Third, a perception-to-cognition curriculum instruction tuning scheme within the LLaMA2 backbone unifies emotion recognition and free-form emotion reasoning. To support large-scale training and reproducible evaluation, MMEVerse aggregates twelve publicly available emotion datasets, including IEMOCAP, MELD, DFEW, and MAFW, into a unified multimodal instruction format. The data are re-annotated via a multi-agent pipeline involving Qwen2 Audio, Qwen2.5 VL, and GPT 4o, producing 130k training clips and 36k testing clips across 18 evaluation benchmarks.
A Unified Evaluation Framework for Multi-Annotator Tendency Learning
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Recent works have emerged in multi-annotator learning that shift focus from Consensus-oriented Learning (CoL), which aggregates multiple annotations into a single ground-truth prediction, to Individual Tendency Learning (ITL), which models annotator-specific labeling behavior patterns (i.e., tendency) to provide explanation analysis for understanding annotator decisions. However, no evaluation framework currently exists to assess whether ITL methods truly capture individual tendencies and provide meaningful behavioral explanations. To address this gap, we propose the first unified evaluation framework with two novel metrics: (1) Difference of Inter-annotator Consistency (DIC) quantifies how well models capture annotator tendencies by comparing predicted inter-annotator similarity structures with ground-truth; (2) Behavior Alignment Explainability (BAE) evaluates how well model explanations reflect annotator behavior and decision relevance by aligning explainability-derived with ground-truth labeling similarity structures via Multidimensional Scaling (MDS). Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our proposed evaluation framework.
Learning Transferable Facial Emotion Representations from Large-Scale Semantically Rich Captions
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Current facial emotion recognition systems are predominately trained to predict a fixed set of predefined categories or abstract dimensional values. This constrained form of supervision hinders generalization and applicability, as it reduces the rich and nuanced spectrum of emotions into oversimplified labels or scales. In contrast, natural language provides a more flexible, expressive, and interpretable way to represent emotions, offering a much broader source of supervision. Yet, leveraging semantically rich natural language captions as supervisory signals for facial emotion representation learning remains relatively underexplored, primarily due to two key challenges: 1) the lack of large-scale caption datasets with rich emotional semantics, and 2) the absence of effective frameworks tailored to harness such rich supervision. To this end, we introduce EmoCap100K, a large-scale facial emotion caption dataset comprising over 100,000 samples, featuring rich and structured semantic descriptions that capture both global affective states and fine-grained local facial behaviors. Building upon this dataset, we further propose EmoCapCLIP, which incorporates a joint global-local contrastive learning framework enhanced by a cross-modal guided positive mining module. This design facilitates the comprehensive exploitation of multi-level caption information while accommodating semantic similarities between closely related expressions. Extensive evaluations on over 20 benchmarks covering five tasks demonstrate the superior performance of our method, highlighting the promise of learning facial emotion representations from large-scale semantically rich captions. The code and data will be available at https://github.com/sunlicai/EmoCapCLIP.
QuMAB: Query-based Multi-annotator Behavior Pattern Learning
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Multi-annotator learning traditionally aggregates diverse annotations to approximate a single ground truth, treating disagreements as noise. However, this paradigm faces fundamental challenges: subjective tasks often lack absolute ground truth, and sparse annotation coverage makes aggregation statistically unreliable. We introduce a paradigm shift from sample-wise aggregation to annotator-wise behavior modeling. By treating annotator disagreements as valuable information rather than noise, modeling annotator-specific behavior patterns can reconstruct unlabeled data to reduce annotation cost, enhance aggregation reliability, and explain annotator decision behavior. To this end, we propose QuMATL (Query-based Multi-Annotator Behavior Pattern Learning), which uses light-weight queries to model individual annotators while capturing inter-annotator correlations as implicit regularization, preventing overfitting to sparse individual data while maintaining individualization and improving generalization, with a visualization of annotator focus regions offering an explainable analysis of behavior understanding. We contribute two large-scale datasets with dense per-annotator labels: STREET (4,300 labels/annotator) and AMER (average 3,118 labels/annotator), the first multimodal multi-annotator dataset.
Are MLMs Trapped in the Visual Room?
May 29, 2025Abstract:Can multi-modal large models (MLMs) that can ``see'' an image be said to ``understand'' it? Drawing inspiration from Searle's Chinese Room, we propose the \textbf{Visual Room} argument: a system may process and describe every detail of visual inputs by following algorithmic rules, without genuinely comprehending the underlying intention. This dilemma challenges the prevailing assumption that perceptual mastery implies genuine understanding. In implementation, we introduce a two-tier evaluation framework spanning perception and cognition. The perception component evaluates whether MLMs can accurately capture the surface-level details of visual contents, where the cognitive component examines their ability to infer sarcasm polarity. To support this framework, We further introduce a high-quality multi-modal sarcasm dataset comprising both 924 static images and 100 dynamic videos. All sarcasm labels are annotated by the original authors and verified by independent reviewers to ensure clarity and consistency. We evaluate eight state-of-the-art (SoTA) MLMs. Our results highlight three key findings: (1) MLMs perform well on perception tasks; (2) even with correct perception, models exhibit an average error rate of ~16.1\% in sarcasm understanding, revealing a significant gap between seeing and understanding; (3) error analysis attributes this gap to deficiencies in emotional reasoning, commonsense inference, and context alignment. This work provides empirical grounding for the proposed Visual Room argument and offers a new evaluation paradigm for MLMs.
MMAR: A Challenging Benchmark for Deep Reasoning in Speech, Audio, Music, and Their Mix
May 19, 2025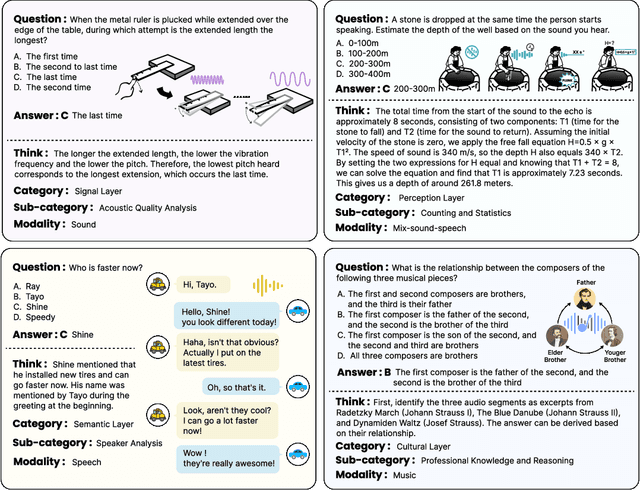
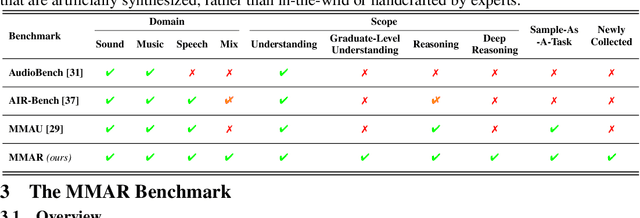
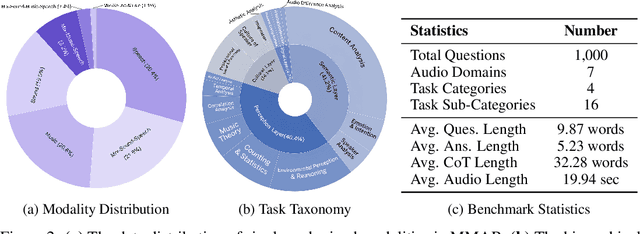
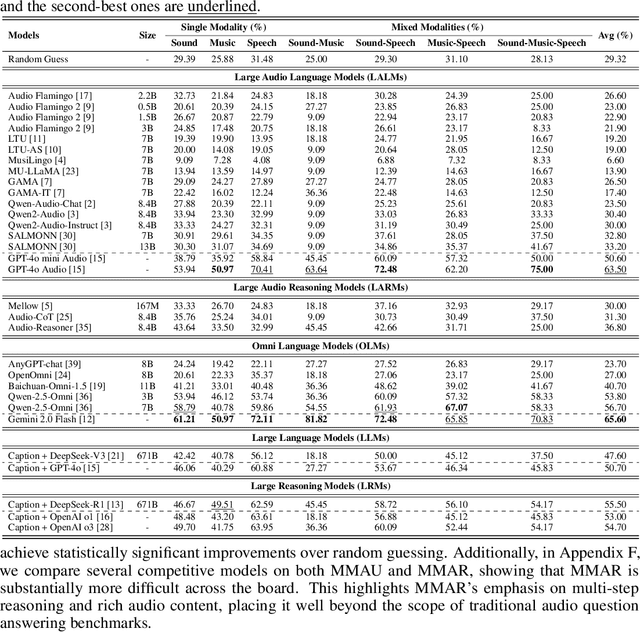
Abstract:We introduce MMAR, a new benchmark designed to evaluate the deep reasoning capabilities of Audio-Language Models (ALMs) across massive multi-disciplinary tasks. MMAR comprises 1,000 meticulously curated audio-question-answer triplets, collected from real-world internet videos and refined through iterative error corrections and quality checks to ensure high quality. Unlike existing benchmarks that are limited to specific domains of sound, music, or speech, MMAR extends them to a broad spectrum of real-world audio scenarios, including mixed-modality combinations of sound, music, and speech. Each question in MMAR is hierarchically categorized across four reasoning layers: Signal, Perception, Semantic, and Cultural, with additional sub-categories within each layer to reflect task diversity and complexity. To further foster research in this area, we annotate every question with a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) rationale to promote future advancements in audio reasoning. Each item in the benchmark demands multi-step deep reasoning beyond surface-level understanding. Moreover, a part of the questions requires graduate-level perceptual and domain-specific knowledge, elevating the benchmark's difficulty and depth. We evaluate MMAR using a broad set of models, including Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs), Large Audio Reasoning Models (LARMs), Omni Language Models (OLMs), Large Language Models (LLMs), and Large Reasoning Models (LRMs), with audio caption inputs. The performance of these models on MMAR highlights the benchmark's challenging nature, and our analysis further reveals critical limitations of understanding and reasoning capabilities among current models. We hope MMAR will serve as a catalyst for future advances in this important but little-explored area.
$\mathcal{A}LLM4ADD$: Unlocking the Capabilities of Audio Large Language Models for Audio Deepfake Detection
May 16, 2025
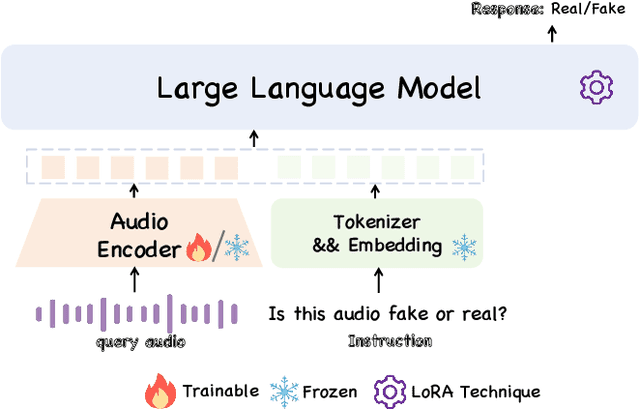
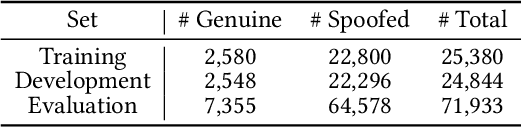
Abstract:Audio deepfake detection (ADD) has grown increasingly important due to the rise of high-fidelity audio generative models and their potential for misuse. Given that audio large language models (ALLMs) have made significant progress in various audio processing tasks, a heuristic question arises: Can ALLMs be leveraged to solve ADD?. In this paper, we first conduct a comprehensive zero-shot evaluation of ALLMs on ADD, revealing their ineffectiveness in detecting fake audio. To enhance their performance, we propose $\mathcal{A}LLM4ADD$, an ALLM-driven framework for ADD. Specifically, we reformulate ADD task as an audio question answering problem, prompting the model with the question: "Is this audio fake or real?". We then perform supervised fine-tuning to enable the ALLM to assess the authenticity of query audio. Extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate that our ALLM-based method can achieve superior performance in fake audio detection, particularly in data-scarce scenarios. As a pioneering study, we anticipate that this work will inspire the research community to leverage ALLMs to develop more effective ADD systems.
Emotion-Qwen: Training Hybrid Experts for Unified Emotion and General Vision-Language Understanding
May 10, 2025Abstract:Emotion understanding in videos aims to accurately recognize and interpret individuals' emotional states by integrating contextual, visual, textual, and auditory cues. While Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have demonstrated significant progress in general vision-language (VL) tasks, their performance in emotion-specific scenarios remains limited. Moreover, fine-tuning LMMs on emotion-related tasks often leads to catastrophic forgetting, hindering their ability to generalize across diverse tasks. To address these challenges, we present Emotion-Qwen, a tailored multimodal framework designed to enhance both emotion understanding and general VL reasoning. Emotion-Qwen incorporates a sophisticated Hybrid Compressor based on the Mixture of Experts (MoE) paradigm, which dynamically routes inputs to balance emotion-specific and general-purpose processing. The model is pre-trained in a three-stage pipeline on large-scale general and emotional image datasets to support robust multimodal representations. Furthermore, we construct the Video Emotion Reasoning (VER) dataset, comprising more than 40K bilingual video clips with fine-grained descriptive annotations, to further enrich Emotion-Qwen's emotional reasoning capability. Experimental results demonstrate that Emotion-Qwen achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple emotion recognition benchmarks, while maintaining competitive results on general VL tasks. Code and models are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Emotion-Qwen-Anonymous.
EmoBench-M: Benchmarking Emotional Intelligence for Multimodal Large Language Models
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:With the integration of Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) into robotic systems and various AI applications, embedding emotional intelligence (EI) capabilities into these models is essential for enabling robots to effectively address human emotional needs and interact seamlessly in real-world scenarios. Existing static, text-based, or text-image benchmarks overlook the multimodal complexities of real-world interactions and fail to capture the dynamic, multimodal nature of emotional expressions, making them inadequate for evaluating MLLMs' EI. Based on established psychological theories of EI, we build EmoBench-M, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate the EI capability of MLLMs across 13 valuation scenarios from three key dimensions: foundational emotion recognition, conversational emotion understanding, and socially complex emotion analysis. Evaluations of both open-source and closed-source MLLMs on EmoBench-M reveal a significant performance gap between them and humans, highlighting the need to further advance their EI capabilities. All benchmark resources, including code and datasets, are publicly available at https://emo-gml.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge