Liyun Zhang
3DGesPolicy: Phoneme-Aware Holistic Co-Speech Gesture Generation Based on Action Control
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Generating holistic co-speech gestures that integrate full-body motion with facial expressions suffers from semantically incoherent coordination on body motion and spatially unstable meaningless movements due to existing part-decomposed or frame-level regression methods, We introduce 3DGesPolicy, a novel action-based framework that reformulates holistic gesture generation as a continuous trajectory control problem through diffusion policy from robotics. By modeling frame-to-frame variations as unified holistic actions, our method effectively learns inter-frame holistic gesture motion patterns and ensures both spatially and semantically coherent movement trajectories that adhere to realistic motion manifolds. To further bridge the gap in expressive alignment, we propose a Gesture-Audio-Phoneme (GAP) fusion module that can deeply integrate and refine multi-modal signals, ensuring structured and fine-grained alignment between speech semantics, body motion, and facial expressions. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments on the BEAT2 dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our 3DGesPolicy across other state-of-the-art methods in generating natural, expressive, and highly speech-aligned holistic gestures.
A Unified Evaluation Framework for Multi-Annotator Tendency Learning
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Recent works have emerged in multi-annotator learning that shift focus from Consensus-oriented Learning (CoL), which aggregates multiple annotations into a single ground-truth prediction, to Individual Tendency Learning (ITL), which models annotator-specific labeling behavior patterns (i.e., tendency) to provide explanation analysis for understanding annotator decisions. However, no evaluation framework currently exists to assess whether ITL methods truly capture individual tendencies and provide meaningful behavioral explanations. To address this gap, we propose the first unified evaluation framework with two novel metrics: (1) Difference of Inter-annotator Consistency (DIC) quantifies how well models capture annotator tendencies by comparing predicted inter-annotator similarity structures with ground-truth; (2) Behavior Alignment Explainability (BAE) evaluates how well model explanations reflect annotator behavior and decision relevance by aligning explainability-derived with ground-truth labeling similarity structures via Multidimensional Scaling (MDS). Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our proposed evaluation framework.
QuMAB: Query-based Multi-annotator Behavior Pattern Learning
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Multi-annotator learning traditionally aggregates diverse annotations to approximate a single ground truth, treating disagreements as noise. However, this paradigm faces fundamental challenges: subjective tasks often lack absolute ground truth, and sparse annotation coverage makes aggregation statistically unreliable. We introduce a paradigm shift from sample-wise aggregation to annotator-wise behavior modeling. By treating annotator disagreements as valuable information rather than noise, modeling annotator-specific behavior patterns can reconstruct unlabeled data to reduce annotation cost, enhance aggregation reliability, and explain annotator decision behavior. To this end, we propose QuMATL (Query-based Multi-Annotator Behavior Pattern Learning), which uses light-weight queries to model individual annotators while capturing inter-annotator correlations as implicit regularization, preventing overfitting to sparse individual data while maintaining individualization and improving generalization, with a visualization of annotator focus regions offering an explainable analysis of behavior understanding. We contribute two large-scale datasets with dense per-annotator labels: STREET (4,300 labels/annotator) and AMER (average 3,118 labels/annotator), the first multimodal multi-annotator dataset.
Push the Limit of Multi-modal Emotion Recognition by Prompting LLMs with Receptive-Field-Aware Attention Weighting
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Understanding the emotions in a dialogue usually requires external knowledge to accurately understand the contents. As the LLMs become more and more powerful, we do not want to settle on the limited ability of the pre-trained language model. However, the LLMs either can only process text modality or are too expensive to process the multimedia information. We aim to utilize both the power of LLMs and the supplementary features from the multimedia modalities. In this paper, we present a framework, Lantern, that can improve the performance of a certain vanilla model by prompting large language models with receptive-field-aware attention weighting. This framework trained a multi-task vanilla model to produce probabilities of emotion classes and dimension scores. These predictions are fed into the LLMs as references to adjust the predicted probabilities of each emotion class with its external knowledge and contextual understanding. We slice the dialogue into different receptive fields, and each sample is included in exactly t receptive fields. Finally, the predictions of LLMs are merged with a receptive-field-aware attention-driven weighting module. In the experiments, vanilla models CORECT and SDT are deployed in Lantern with GPT-4 or Llama-3.1-405B. The experiments in IEMOCAP with 4-way and 6-way settings demonstrated that the Lantern can significantly improve the performance of current vanilla models by up to 1.23% and 1.80%.
UniAutoML: A Human-Centered Framework for Unified Discriminative and Generative AutoML with Large Language Models
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) has simplified complex ML processes such as data pre-processing, model selection, and hyper-parameter searching. However, traditional AutoML frameworks focus solely on discriminative tasks, often falling short in tackling AutoML for generative models. Additionally, these frameworks lack interpretability and user engagement during the training process, primarily due to the absence of human-centered design. It leads to a lack of transparency in final decision-making and limited user control, potentially reducing trust and adoption of AutoML methods. To address these limitations, we introduce UniAutoML, a human-centered AutoML framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to unify AutoML for both discriminative (e.g., Transformers and CNNs for classification or regression tasks) and generative tasks (e.g., fine-tuning diffusion models or LLMs). The human-centered design of UniAutoML innovatively features a conversational user interface (CUI) that facilitates natural language interactions, providing users with real-time guidance, feedback, and progress updates for better interpretability. This design enhances transparency and user control throughout the AutoML training process, allowing users to seamlessly break down or modify the model being trained. To mitigate potential risks associated with LLM generated content, UniAutoML incorporates a safety guardline that filters inputs and censors outputs. We evaluated UniAutoML's performance and usability through experiments on eight diverse datasets and user studies involving 25 participants, demonstrating that UniAutoML not only enhances performance but also improves user control and trust. Our human-centered design bridges the gap between AutoML capabilities and user understanding, making ML more accessible to a broader audience.
3DFacePolicy: Speech-Driven 3D Facial Animation with Diffusion Policy
Sep 17, 2024Abstract:Audio-driven 3D facial animation has made immersive progress both in research and application developments. The newest approaches focus on Transformer-based methods and diffusion-based methods, however, there is still gap in the vividness and emotional expression between the generated animation and real human face. To tackle this limitation, we propose 3DFacePolicy, a diffusion policy model for 3D facial animation prediction. This method generates variable and realistic human facial movements by predicting the 3D vertex trajectory on the 3D facial template with diffusion policy instead of facial generation for every frame. It takes audio and vertex states as observations to predict the vertex trajectory and imitate real human facial expressions, which keeps the continuous and natural flow of human emotions. The experiments show that our approach is effective in variable and dynamic facial motion synthesizing.
MicroEmo: Time-Sensitive Multimodal Emotion Recognition with Micro-Expression Dynamics in Video Dialogues
Jul 24, 2024Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated remarkable multimodal emotion recognition capabilities, integrating multimodal cues from visual, acoustic, and linguistic contexts in the video to recognize human emotional states. However, existing methods ignore capturing local facial features of temporal dynamics of micro-expressions and do not leverage the contextual dependencies of the utterance-aware temporal segments in the video, thereby limiting their expected effectiveness to a certain extent. In this work, we propose MicroEmo, a time-sensitive MLLM aimed at directing attention to the local facial micro-expression dynamics and the contextual dependencies of utterance-aware video clips. Our model incorporates two key architectural contributions: (1) a global-local attention visual encoder that integrates global frame-level timestamp-bound image features with local facial features of temporal dynamics of micro-expressions; (2) an utterance-aware video Q-Former that captures multi-scale and contextual dependencies by generating visual token sequences for each utterance segment and for the entire video then combining them. Preliminary qualitative experiments demonstrate that in a new Explainable Multimodal Emotion Recognition (EMER) task that exploits multi-modal and multi-faceted clues to predict emotions in an open-vocabulary (OV) manner, MicroEmo demonstrates its effectiveness compared with the latest methods.
Panoptic-based Object Style-Align for Image-to-Image Translation
Dec 03, 2021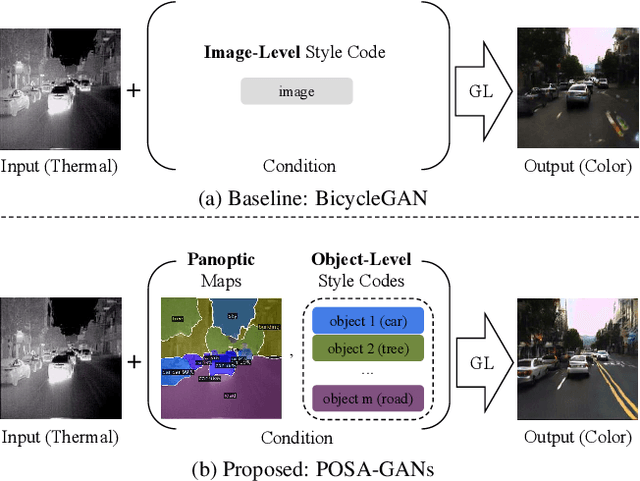
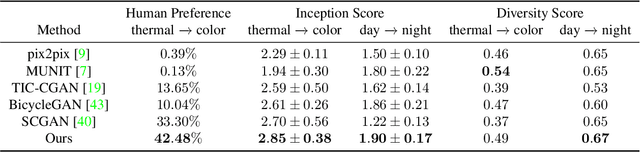
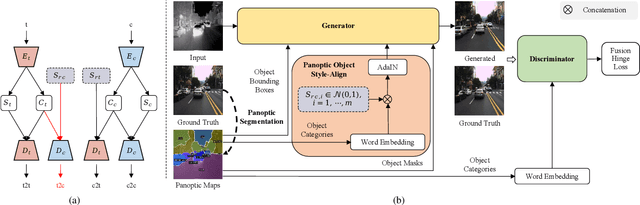
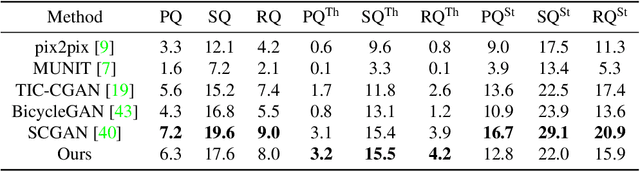
Abstract:Despite remarkable recent progress in image translation, the complex scene with multiple discrepant objects remains a challenging problem. Because the translated images have low fidelity and tiny objects in fewer details and obtain unsatisfactory performance in object recognition. Without the thorough object perception (i.e., bounding boxes, categories, and masks) of the image as prior knowledge, the style transformation of each object will be difficult to track in the image translation process. We propose panoptic-based object style-align generative adversarial networks (POSA-GANs) for image-to-image translation together with a compact panoptic segmentation dataset. The panoptic segmentation model is utilized to extract panoptic-level perception (i.e., overlap-removed foreground object instances and background semantic regions in the image). This is utilized to guide the alignment between the object content codes of the input domain image and object style codes sampled from the style space of the target domain. The style-aligned object representations are further transformed to obtain precise boundaries layout for higher fidelity object generation. The proposed method was systematically compared with different competing methods and obtained significant improvement on both image quality and object recognition performance for translated images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge