Jianhua Tao
Exploring Knowledge Purification in Multi-Teacher Knowledge Distillation for LLMs
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Knowledge distillation has emerged as a pivotal technique for transferring knowledge from stronger large language models (LLMs) to smaller, more efficient models. However, traditional distillation approaches face challenges related to knowledge conflicts and high resource demands, particularly when leveraging multiple teacher models. In this paper, we introduce the concept of \textbf{Knowledge Purification}, which consolidates the rationales from multiple teacher LLMs into a single rationale, thereby mitigating conflicts and enhancing efficiency. To investigate the effectiveness of knowledge purification, we further propose five purification methods from various perspectives. Our experiments demonstrate that these methods not only improve the performance of the distilled model but also effectively alleviate knowledge conflicts. Moreover, router-based methods exhibit robust generalization capabilities, underscoring the potential of innovative purification techniques in optimizing multi-teacher distillation and facilitating the practical deployment of powerful yet lightweight models.
Edit Content, Preserve Acoustics: Imperceptible Text-Based Speech Editing via Self-Consistency Rewards
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Imperceptible text-based speech editing allows users to modify spoken content by altering the transcript. It demands that modified segments fuse seamlessly with the surrounding context. Prevalent methods operating in the acoustic space suffer from inherent content-style entanglement, leading to generation instability and boundary artifacts. In this paper, we propose a novel framework grounded in the principle of "Edit Content, Preserve Acoustics". Our approach relies on two core components: (1) Structural Foundations, which decouples editing into a stable semantic space while delegating acoustic reconstruction to a Flow Matching decoder; and (2) Perceptual Alignment, which employs a novel Self-Consistency Rewards Group Relative Policy Optimization. By leveraging a pre-trained Text-to-Speech model as an implicit critic -- complemented by strict intelligibility and duration constraints -- we effectively align the edited semantic token sequence with the original context. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art autoregressive and non-autoregressive baselines, achieving superior intelligibility, robustness, and perceptual quality.
Spark: Strategic Policy-Aware Exploration via Dynamic Branching for Long-Horizon Agentic Learning
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning has empowered large language models to act as intelligent agents, yet training them for long-horizon tasks remains challenging due to the scarcity of high-quality trajectories, especially under limited resources. Existing methods typically scale up rollout sizes and indiscriminately allocate computational resources among intermediate steps. Such attempts inherently waste substantial computation budget on trivial steps while failing to guarantee sample quality. To address this, we propose \textbf{Spark} (\textbf{S}trategic \textbf{P}olicy-\textbf{A}ware explo\textbf{R}ation via \textbf{K}ey-state dynamic branching), a novel framework that selectively branches at critical decision states for resource-efficient exploration. Our key insight is to activate adaptive branching exploration at critical decision points to probe promising trajectories, thereby achieving precise resource allocation that prioritizes sampling quality over blind coverage. This design leverages the agent's intrinsic decision-making signals to reduce dependence on human priors, enabling the agent to autonomously expand exploration and achieve stronger generalization. Experiments across diverse tasks (e.g., embodied planning), demonstrate that \textsc{Spark} achieves superior success rates with significantly fewer training samples, exhibiting robust generalization even in unseen scenarios.
Atlas: Orchestrating Heterogeneous Models and Tools for Multi-Domain Complex Reasoning
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:The integration of large language models (LLMs) with external tools has significantly expanded the capabilities of AI agents. However, as the diversity of both LLMs and tools increases, selecting the optimal model-tool combination becomes a high-dimensional optimization challenge. Existing approaches often rely on a single model or fixed tool-calling logic, failing to exploit the performance variations across heterogeneous model-tool pairs. In this paper, we present ATLAS (Adaptive Tool-LLM Alignment and Synergistic Invocation), a dual-path framework for dynamic tool usage in cross-domain complex reasoning. ATLAS operates via a dual-path approach: (1) \textbf{training-free cluster-based routing} that exploits empirical priors for domain-specific alignment, and (2) \textbf{RL-based multi-step routing} that explores autonomous trajectories for out-of-distribution generalization. Extensive experiments across 15 benchmarks demonstrate that our method outperforms closed-source models like GPT-4o, surpassing existing routing methods on both in-distribution (+10.1%) and out-of-distribution (+13.1%) tasks. Furthermore, our framework shows significant gains in visual reasoning by orchestrating specialized multi-modal tools.
OV-InstructTTS: Towards Open-Vocabulary Instruct Text-to-Speech
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Instruct Text-to-Speech (InstructTTS) leverages natural language descriptions as style prompts to guide speech synthesis. However, existing InstructTTS methods mainly rely on a direct combination of audio-related labels or their diverse rephrasings, making it difficult to handle flexible, high-level instructions. Such rigid control is insufficient for users such as content creators who wish to steer generation with descriptive instructions. To address these constraints, we introduce OV-InstructTTS, a new paradigm for open-vocabulary InstructTTS. We propose a comprehensive solution comprising a newly curated dataset, OV-Speech, and a novel reasoning-driven framework. The OV-Speech dataset pairs speech with open-vocabulary instructions, each augmented with a reasoning process that connects high-level instructions to acoustic features. The reasoning-driven framework infers emotional, acoustic, and paralinguistic information from open-vocabulary instructions before synthesizing speech. Evaluations show that this reasoning-driven approach significantly improves instruction-following fidelity and speech expressiveness. We believe this work can inspire the next user-friendly InstructTTS systems with stronger generalization and real-world applicability. The dataset and demos are publicly available on our project page.
RadialRouter: Structured Representation for Efficient and Robust Large Language Models Routing
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs) have led to the emergence of routing techniques, which aim to efficiently select the optimal LLM from diverse candidates to tackle specific tasks, optimizing performance while reducing costs. Current LLM routing methods are limited in effectiveness due to insufficient exploration of the intrinsic connection between user queries and the characteristics of LLMs. To address this issue, in this paper, we present RadialRouter, a novel framework for LLM routing which employs a lightweight Transformer-based backbone with a radial structure named RadialFormer to articulate the query-LLMs relationship. The optimal LLM selection is performed based on the final states of RadialFormer. The pipeline is further refined by an objective function that combines Kullback-Leibler divergence with the query-query contrastive loss to enhance robustness. Experimental results on RouterBench show that RadialRouter significantly outperforms existing routing methods by 9.2\% and 5.8\% in the Balance and Cost First scenarios, respectively. Additionally, its adaptability toward different performance-cost trade-offs and the dynamic LLM pool demonstrates practical application potential.
ELDeR: Getting Efficient LLMs through Data-Driven Regularized Layer-wise Pruning
May 23, 2025Abstract:The deployment of Large language models (LLMs) in many fields is largely hindered by their high computational and memory costs. Recent studies suggest that LLMs exhibit sparsity, which can be used for pruning. Previous pruning methods typically follow a prune-then-finetune paradigm. Since the pruned parts still contain valuable information, statically removing them without updating the remaining parameters often results in irreversible performance degradation, requiring costly recovery fine-tuning (RFT) to maintain performance. To address this, we propose a novel paradigm: first apply regularization, then prune. Based on this paradigm, we propose ELDeR: Getting Efficient LLMs through Data-Driven Regularized Layer-wise Pruning. We multiply the output of each transformer layer by an initial weight, then we iteratively learn the weights of each transformer layer by using a small amount of data in a simple way. After that, we apply regularization to the difference between the output and input of the layers with smaller weights, forcing the information to be transferred to the remaining layers. Compared with direct pruning, ELDeR reduces the information loss caused by direct parameter removal, thus better preserving the model's language modeling ability. Experimental results show that ELDeR achieves superior performance compared with powerful layer-wise structured pruning methods, while greatly reducing RFT computational costs. Since ELDeR is a layer-wise pruning method, its end-to-end acceleration effect is obvious, making it a promising technique for efficient LLMs.
Thought-Augmented Policy Optimization: Bridging External Guidance and Internal Capabilities
May 21, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as an effective method for training reasoning models. However, existing RL approaches typically bias the model's output distribution toward reward-maximizing paths without introducing external knowledge. This limits their exploration capacity and results in a narrower reasoning capability boundary compared to base models. To address this limitation, we propose TAPO (Thought-Augmented Policy Optimization), a novel framework that augments RL by incorporating external high-level guidance ("thought patterns"). By adaptively integrating structured thoughts during training, TAPO effectively balances model-internal exploration and external guidance exploitation. Extensive experiments show that our approach significantly outperforms GRPO by 99% on AIME, 41% on AMC, and 17% on Minerva Math. Notably, these high-level thought patterns, abstracted from only 500 prior samples, generalize effectively across various tasks and models. This highlights TAPO's potential for broader applications across multiple tasks and domains. Our further analysis reveals that introducing external guidance produces powerful reasoning models with superior explainability of inference behavior and enhanced output readability.
$\mathcal{A}LLM4ADD$: Unlocking the Capabilities of Audio Large Language Models for Audio Deepfake Detection
May 16, 2025
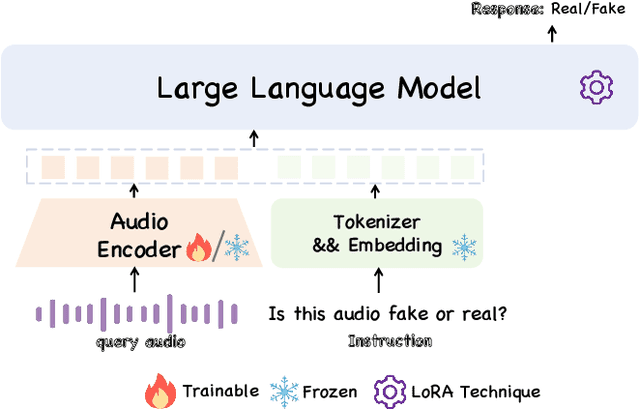
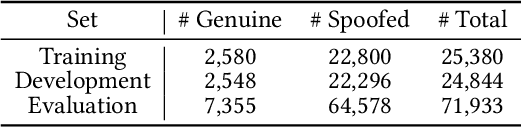
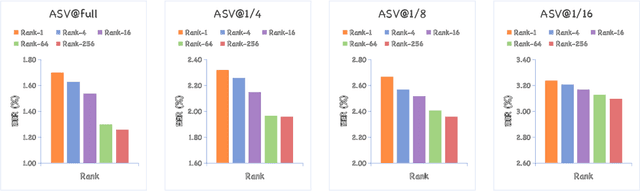
Abstract:Audio deepfake detection (ADD) has grown increasingly important due to the rise of high-fidelity audio generative models and their potential for misuse. Given that audio large language models (ALLMs) have made significant progress in various audio processing tasks, a heuristic question arises: Can ALLMs be leveraged to solve ADD?. In this paper, we first conduct a comprehensive zero-shot evaluation of ALLMs on ADD, revealing their ineffectiveness in detecting fake audio. To enhance their performance, we propose $\mathcal{A}LLM4ADD$, an ALLM-driven framework for ADD. Specifically, we reformulate ADD task as an audio question answering problem, prompting the model with the question: "Is this audio fake or real?". We then perform supervised fine-tuning to enable the ALLM to assess the authenticity of query audio. Extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate that our ALLM-based method can achieve superior performance in fake audio detection, particularly in data-scarce scenarios. As a pioneering study, we anticipate that this work will inspire the research community to leverage ALLMs to develop more effective ADD systems.
ImViD: Immersive Volumetric Videos for Enhanced VR Engagement
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:User engagement is greatly enhanced by fully immersive multi-modal experiences that combine visual and auditory stimuli. Consequently, the next frontier in VR/AR technologies lies in immersive volumetric videos with complete scene capture, large 6-DoF interaction space, multi-modal feedback, and high resolution & frame-rate contents. To stimulate the reconstruction of immersive volumetric videos, we introduce ImViD, a multi-view, multi-modal dataset featuring complete space-oriented data capture and various indoor/outdoor scenarios. Our capture rig supports multi-view video-audio capture while on the move, a capability absent in existing datasets, significantly enhancing the completeness, flexibility, and efficiency of data capture. The captured multi-view videos (with synchronized audios) are in 5K resolution at 60FPS, lasting from 1-5 minutes, and include rich foreground-background elements, and complex dynamics. We benchmark existing methods using our dataset and establish a base pipeline for constructing immersive volumetric videos from multi-view audiovisual inputs for 6-DoF multi-modal immersive VR experiences. The benchmark and the reconstruction and interaction results demonstrate the effectiveness of our dataset and baseline method, which we believe will stimulate future research on immersive volumetric video production.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge