Feihu Che
ELDeR: Getting Efficient LLMs through Data-Driven Regularized Layer-wise Pruning
May 23, 2025Abstract:The deployment of Large language models (LLMs) in many fields is largely hindered by their high computational and memory costs. Recent studies suggest that LLMs exhibit sparsity, which can be used for pruning. Previous pruning methods typically follow a prune-then-finetune paradigm. Since the pruned parts still contain valuable information, statically removing them without updating the remaining parameters often results in irreversible performance degradation, requiring costly recovery fine-tuning (RFT) to maintain performance. To address this, we propose a novel paradigm: first apply regularization, then prune. Based on this paradigm, we propose ELDeR: Getting Efficient LLMs through Data-Driven Regularized Layer-wise Pruning. We multiply the output of each transformer layer by an initial weight, then we iteratively learn the weights of each transformer layer by using a small amount of data in a simple way. After that, we apply regularization to the difference between the output and input of the layers with smaller weights, forcing the information to be transferred to the remaining layers. Compared with direct pruning, ELDeR reduces the information loss caused by direct parameter removal, thus better preserving the model's language modeling ability. Experimental results show that ELDeR achieves superior performance compared with powerful layer-wise structured pruning methods, while greatly reducing RFT computational costs. Since ELDeR is a layer-wise pruning method, its end-to-end acceleration effect is obvious, making it a promising technique for efficient LLMs.
Boosting Multimodal Reasoning with MCTS-Automated Structured Thinking
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) exhibit impressive capabilities but still face challenges in complex visual reasoning. While recent efforts attempt to enhance MLLMs' reasoning by incorporating OpenAI o1-like structured thinking through explicit search structures or teacher-guided distillation, they often struggle to balance performance and efficiency. A critical limitation is their heavy reliance on extensive data and search spaces, resulting in low-efficiency implicit insight extraction and data utilization. To address this, we propose AStar, an Automated Structured thinking paradigm for multimodal reasoning via Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS). AStar automatically derives high-level cognitive reasoning patterns from limited data using MCTS-powered hierarchical structures. Building on these explicit patterns, we design a unified reasoning framework that seamlessly integrates models' internal reasoning capabilities and external reasoning guidelines, enabling efficient inference with minimal tree iterations. This novel paradigm strikes a compelling balance between performance and efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate AStar's effectiveness, achieving superior accuracy (54.0$\%$) on the MathVerse benchmark with a 7B backbone, surpassing GPT-4o (50.2$\%$) while maintaining substantial data and computational efficiency.
DReSS: Data-driven Regularized Structured Streamlining for Large Language Models
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved significant progress across various domains, but their increasing scale results in high computational and memory costs. Recent studies have revealed that LLMs exhibit sparsity, providing the potential to reduce model size through pruning techniques. However, existing pruning methods typically follow a prune-then-finetune paradigm. Since the pruned components still contain valuable information, their direct removal often leads to irreversible performance degradation, imposing a substantial computational burden to recover performance during finetuning. In this paper, we propose a novel paradigm that first applies regularization, then prunes, and finally finetunes. Based on this paradigm, we introduce DReSS, a simple and effective Data-driven Regularized Structured Streamlining method for LLMs. By leveraging a small amount of data to regularize the components to be pruned, DReSS explicitly transfers the important information to the remaining parts of the model in advance. Compared to direct pruning, this can reduce the information loss caused by parameter removal, thereby enhancing its language modeling capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that DReSS significantly outperforms existing pruning methods even under extreme pruning ratios, significantly reducing latency and increasing throughput.
Beyond Examples: High-level Automated Reasoning Paradigm in In-Context Learning via MCTS
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:In-context Learning (ICL) enables large language models (LLMs) to tackle downstream tasks through sophisticated prompting and high-quality demonstrations. However, this traditional ICL paradigm shows limitations when facing complex mathematical reasoning tasks, primarily due to its heavy dependence on example quality and the necessity for human intervention in challenging scenarios. To address these limitations, this paper presents HiAR-ICL, a \textbf{Hi}gh-level \textbf{A}utomated \textbf{R}easoning paradigm in \textbf{ICL} that shifts focus from specific examples to abstract thinking patterns, extending the conventional concept of context in ICL. HiAR-ICL introduces five atomic reasoning actions as fundamental components for constructing chain-structured patterns. Using Monte Carlo Tree Search, we explore reasoning paths and construct thought cards to guide subsequent inference. We then develop a cognitive complexity framework that dynamically matches problems with appropriate thought cards. Experimental results demonstrate HiAR-ICL's effectiveness, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy (79.6$\%$) on the MATH benchmark with Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct, surpassing GPT-4o (76.6$\%$) and Claude 3.5 (71.1$\%$).
Pandora's Box or Aladdin's Lamp: A Comprehensive Analysis Revealing the Role of RAG Noise in Large Language Models
Aug 24, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a crucial method for addressing hallucinations in large language models (LLMs). While recent research has extended RAG models to complex noisy scenarios, these explorations often confine themselves to limited noise types and presuppose that noise is inherently detrimental to LLMs, potentially deviating from real-world retrieval environments and restricting practical applicability. In this paper, we define seven distinct noise types from a linguistic perspective and establish a Noise RAG Benchmark (NoiserBench), a comprehensive evaluation framework encompassing multiple datasets and reasoning tasks. Through empirical evaluation of eight representative LLMs with diverse architectures and scales, we reveal that these noises can be further categorized into two practical groups: noise that is beneficial to LLMs (aka beneficial noise) and noise that is harmful to LLMs (aka harmful noise). While harmful noise generally impairs performance, beneficial noise may enhance several aspects of model capabilities and overall performance. Our analysis offers insights for developing more robust, adaptable RAG solutions and mitigating hallucinations across diverse retrieval scenarios.
Can large language models understand uncommon meanings of common words?
May 09, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT have shown significant advancements across diverse natural language understanding (NLU) tasks, including intelligent dialogue and autonomous agents. Yet, lacking widely acknowledged testing mechanisms, answering `whether LLMs are stochastic parrots or genuinely comprehend the world' remains unclear, fostering numerous studies and sparking heated debates. Prevailing research mainly focuses on surface-level NLU, neglecting fine-grained explorations. However, such explorations are crucial for understanding their unique comprehension mechanisms, aligning with human cognition, and finally enhancing LLMs' general NLU capacities. To address this gap, our study delves into LLMs' nuanced semantic comprehension capabilities, particularly regarding common words with uncommon meanings. The idea stems from foundational principles of human communication within psychology, which underscore accurate shared understandings of word semantics. Specifically, this paper presents the innovative construction of a Lexical Semantic Comprehension (LeSC) dataset with novel evaluation metrics, the first benchmark encompassing both fine-grained and cross-lingual dimensions. Introducing models of both open-source and closed-source, varied scales and architectures, our extensive empirical experiments demonstrate the inferior performance of existing models in this basic lexical-meaning understanding task. Notably, even the state-of-the-art LLMs GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 lag behind 16-year-old humans by 3.9% and 22.3%, respectively. Additionally, multiple advanced prompting techniques and retrieval-augmented generation are also introduced to help alleviate this trouble, yet limitations persist. By highlighting the above critical shortcomings, this research motivates further investigation and offers novel insights for developing more intelligent LLMs.
KS-LLM: Knowledge Selection of Large Language Models with Evidence Document for Question Answering
Apr 24, 2024
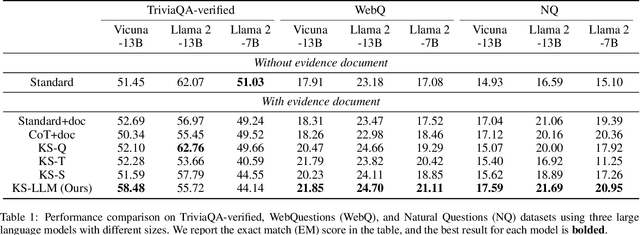
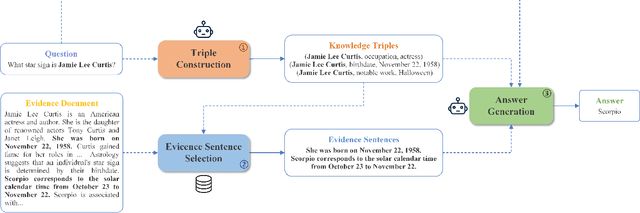
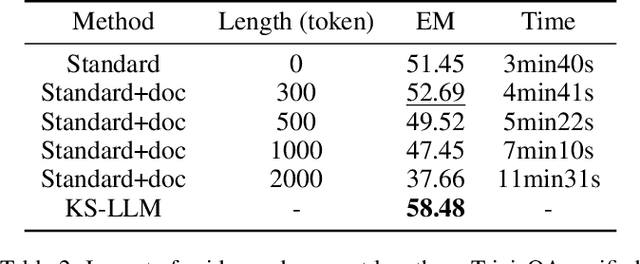
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) suffer from the hallucination problem and face significant challenges when applied to knowledge-intensive tasks. A promising approach is to leverage evidence documents as extra supporting knowledge, which can be obtained through retrieval or generation. However, existing methods directly leverage the entire contents of the evidence document, which may introduce noise information and impair the performance of large language models. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel Knowledge Selection of Large Language Models (KS-LLM) method, aiming to identify valuable information from evidence documents. The KS-LLM approach utilizes triples to effectively select knowledge snippets from evidence documents that are beneficial to answering questions. Specifically, we first generate triples based on the input question, then select the evidence sentences most similar to triples from the evidence document, and finally combine the evidence sentences and triples to assist large language models in generating answers. Experimental comparisons on several question answering datasets, such as TriviaQA, WebQ, and NQ, demonstrate that the proposed method surpasses the baselines and achieves the best results.
Adaptive Pseudo-Siamese Policy Network for Temporal Knowledge Prediction
Apr 26, 2022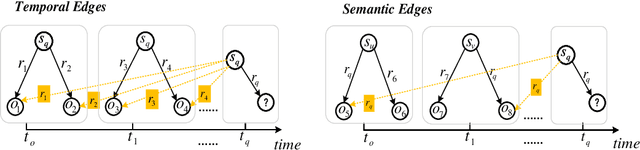
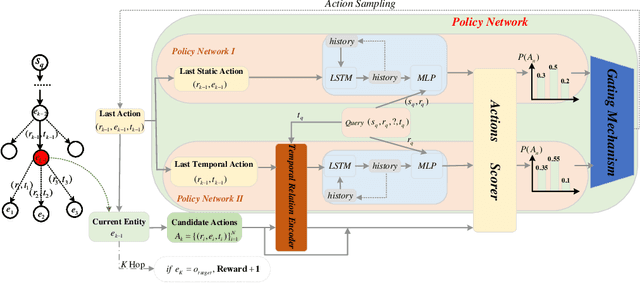
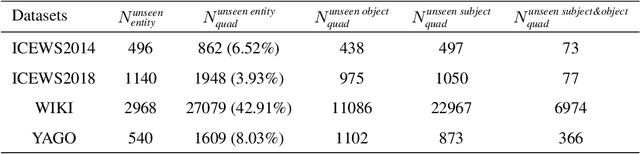
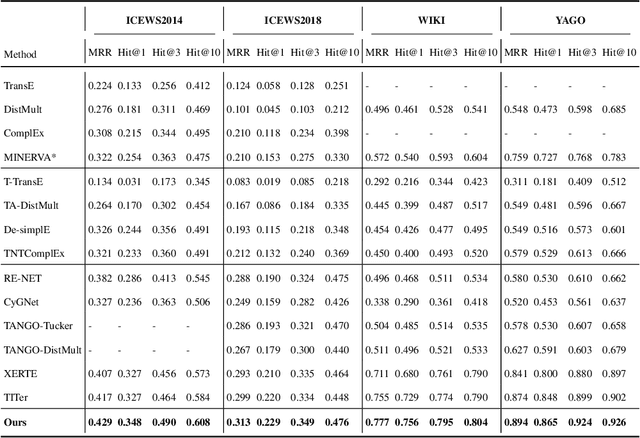
Abstract:Temporal knowledge prediction is a crucial task for the event early warning that has gained increasing attention in recent years, which aims to predict the future facts by using relevant historical facts on the temporal knowledge graphs. There are two main difficulties in this prediction task. First, from the historical facts point of view, how to model the evolutionary patterns of the facts to predict the query accurately. Second, from the query perspective, how to handle the two cases where the query contains seen and unseen entities in a unified framework. Driven by the two problems, we propose a novel adaptive pseudo-siamese policy network for temporal knowledge prediction based on reinforcement learning. Specifically, we design the policy network in our model as a pseudo-siamese policy network that consists of two sub-policy networks. In sub-policy network I, the agent searches for the answer for the query along the entity-relation paths to capture the static evolutionary patterns. And in sub-policy network II, the agent searches for the answer for the query along the relation-time paths to deal with unseen entities. Moreover, we develop a temporal relation encoder to capture the temporal evolutionary patterns. Finally, we design a gating mechanism to adaptively integrate the results of the two sub-policy networks to help the agent focus on the destination answer. To assess our model performance, we conduct link prediction on four benchmark datasets, the experimental results demonstrate that our method obtains considerable performance compared with existing methods.
MixKG: Mixing for harder negative samples in knowledge graph
Feb 19, 2022

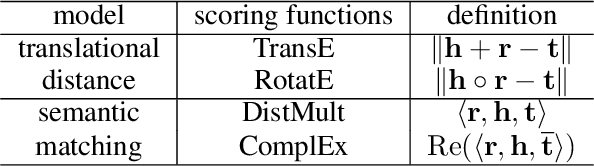
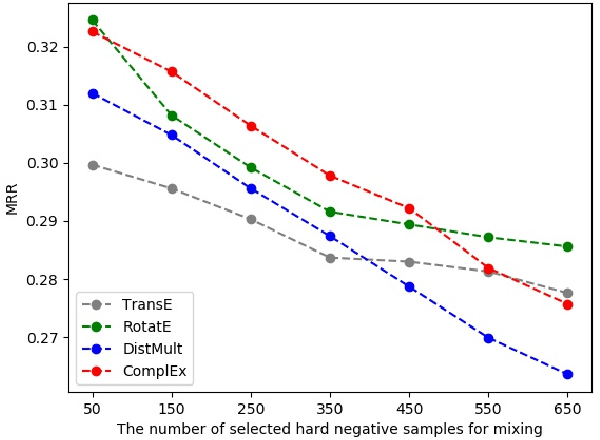
Abstract:Knowledge graph embedding~(KGE) aims to represent entities and relations into low-dimensional vectors for many real-world applications. The representations of entities and relations are learned via contrasting the positive and negative triplets. Thus, high-quality negative samples are extremely important in KGE. However, the present KGE models either rely on simple negative sampling methods, which makes it difficult to obtain informative negative triplets; or employ complex adversarial methods, which requires more training data and strategies. In addition, these methods can only construct negative triplets using the existing entities, which limits the potential to explore harder negative triplets. To address these issues, we adopt mixing operation in generating harder negative samples for knowledge graphs and introduce an inexpensive but effective method called MixKG. Technically, MixKG first proposes two kinds of criteria to filter hard negative triplets among the sampled negatives: based on scoring function and based on correct entity similarity. Then, MixKG synthesizes harder negative samples via the convex combinations of the paired selected hard negatives. Experiments on two public datasets and four classical KGE methods show MixKG is superior to previous negative sampling algorithms.
Knowledge graph enhanced recommender system
Dec 17, 2021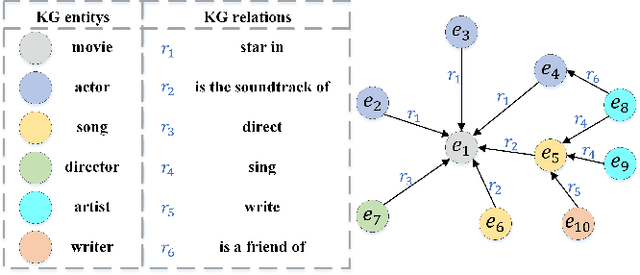
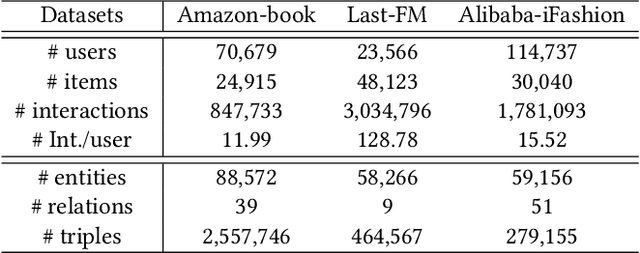
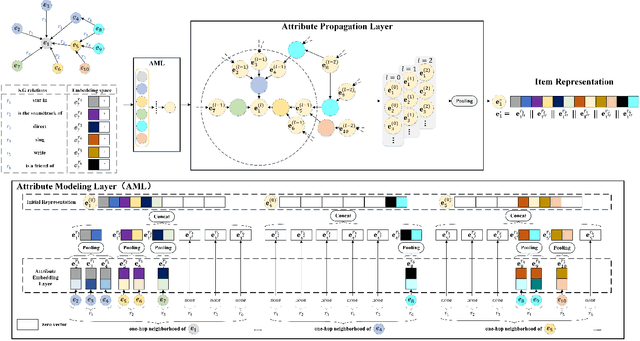
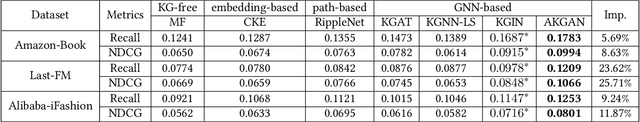
Abstract:Knowledge Graphs (KGs) have shown great success in recommendation. This is attributed to the rich attribute information contained in KG to improve item and user representations as side information. However, existing knowledge-aware methods leverage attribute information at a coarse-grained level both in item and user side. In this paper, we proposed a novel attentive knowledge graph attribute network(AKGAN) to learn item attributes and user interests via attribute information in KG. Technically, AKGAN adopts a heterogeneous graph neural network framework, which has a different design between the first layer and the latter layer. With one attribute placed in the corresponding range of element-wise positions, AKGAN employs a novel interest-aware attention network, which releases the limitation that the sum of attention weight is 1, to model the complexity and personality of user interests towards attributes. Experimental results on three benchmark datasets show the effectiveness and explainability of AKGAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge