KS-LLM: Knowledge Selection of Large Language Models with Evidence Document for Question Answering
Paper and Code
Apr 24, 2024
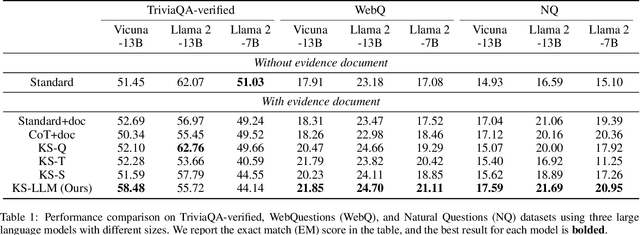
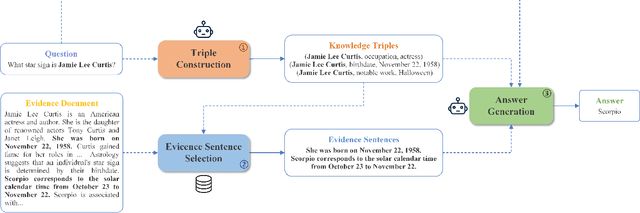
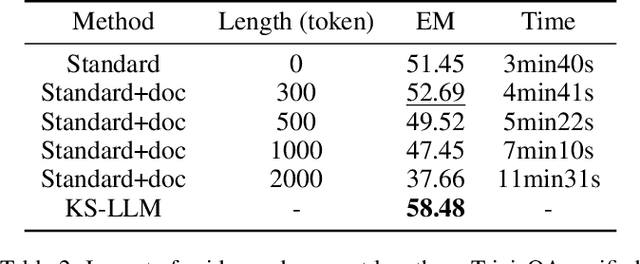
Large language models (LLMs) suffer from the hallucination problem and face significant challenges when applied to knowledge-intensive tasks. A promising approach is to leverage evidence documents as extra supporting knowledge, which can be obtained through retrieval or generation. However, existing methods directly leverage the entire contents of the evidence document, which may introduce noise information and impair the performance of large language models. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel Knowledge Selection of Large Language Models (KS-LLM) method, aiming to identify valuable information from evidence documents. The KS-LLM approach utilizes triples to effectively select knowledge snippets from evidence documents that are beneficial to answering questions. Specifically, we first generate triples based on the input question, then select the evidence sentences most similar to triples from the evidence document, and finally combine the evidence sentences and triples to assist large language models in generating answers. Experimental comparisons on several question answering datasets, such as TriviaQA, WebQ, and NQ, demonstrate that the proposed method surpasses the baselines and achieves the best results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge