Siyuan Liu
Institute of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System, School of Earth and Space Sciences, Peking University
EMemBench: Interactive Benchmarking of Episodic Memory for VLM Agents
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:We introduce EMemBench, a programmatic benchmark for evaluating long-term memory of agents through interactive games. Rather than using a fixed set of questions, EMemBench generates questions from each agent's own trajectory, covering both text and visual game environments. Each template computes verifiable ground truth from underlying game signals, with controlled answerability and balanced coverage over memory skills: single/multi-hop recall, induction, temporal, spatial, logical, and adversarial. We evaluate memory agents with strong LMs/VLMs as backbones, using in-context prompting as baselines. Across 15 text games and multiple visual seeds, results are far from saturated: induction and spatial reasoning are persistent bottlenecks, especially in visual setting. Persistent memory yields clear gains for open backbones on text games, but improvements are less consistent for VLM agents, suggesting that visually grounded episodic memory remains an open challenge. A human study further confirms the difficulty of EMemBench.
What Do LLM Agents Know About Their World? Task2Quiz: A Paradigm for Studying Environment Understanding
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Large language model (LLM) agents have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in complex decision-making and tool-use tasks, yet their ability to generalize across varying environments remains a under-examined concern. Current evaluation paradigms predominantly rely on trajectory-based metrics that measure task success, while failing to assess whether agents possess a grounded, transferable model of the environment. To address this gap, we propose Task-to-Quiz (T2Q), a deterministic and automated evaluation paradigm designed to decouple task execution from world-state understanding. We instantiate this paradigm in T2QBench, a suite comprising 30 environments and 1,967 grounded QA pairs across multiple difficulty levels. Our extensive experiments reveal that task success is often a poor proxy for environment understanding, and that current memory machanism can not effectively help agents acquire a grounded model of the environment. These findings identify proactive exploration and fine-grained state representation as primary bottlenecks, offering a robust foundation for developing more generalizable autonomous agents.
SimRPD: Optimizing Recruitment Proactive Dialogue Agents through Simulator-Based Data Evaluation and Selection
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Task-oriented proactive dialogue agents play a pivotal role in recruitment, particularly for steering conversations towards specific business outcomes, such as acquiring social-media contacts for private-channel conversion. Although supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning have proven effective for training such agents, their performance is heavily constrained by the scarcity of high-quality, goal-oriented domain-specific training data. To address this challenge, we propose SimRPD, a three-stage framework for training recruitment proactive dialogue agents. First, we develop a high-fidelity user simulator to synthesize large-scale conversational data through multi-turn online dialogue. Then we introduce a multi-dimensional evaluation framework based on Chain-of-Intention (CoI) to comprehensively assess the simulator and effectively select high-quality data, incorporating both global-level and instance-level metrics. Finally, we train the recruitment proactive dialogue agent on the selected dataset. Experiments in a real-world recruitment scenario demonstrate that SimRPD outperforms existing simulator-based data selection strategies, highlighting its practical value for industrial deployment and its potential applicability to other business-oriented dialogue scenarios.
SoulX-FlashTalk: Real-Time Infinite Streaming of Audio-Driven Avatars via Self-Correcting Bidirectional Distillation
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Deploying massive diffusion models for real-time, infinite-duration, audio-driven avatar generation presents a significant engineering challenge, primarily due to the conflict between computational load and strict latency constraints. Existing approaches often compromise visual fidelity by enforcing strictly unidirectional attention mechanisms or reducing model capacity. To address this problem, we introduce \textbf{SoulX-FlashTalk}, a 14B-parameter framework optimized for high-fidelity real-time streaming. Diverging from conventional unidirectional paradigms, we use a \textbf{Self-correcting Bidirectional Distillation} strategy that retains bidirectional attention within video chunks. This design preserves critical spatiotemporal correlations, significantly enhancing motion coherence and visual detail. To ensure stability during infinite generation, we incorporate a \textbf{Multi-step Retrospective Self-Correction Mechanism}, enabling the model to autonomously recover from accumulated errors and preventing collapse. Furthermore, we engineered a full-stack inference acceleration suite incorporating hybrid sequence parallelism, Parallel VAE, and kernel-level optimizations. Extensive evaluations confirm that SoulX-FlashTalk is the first 14B-scale system to achieve a \textbf{sub-second start-up latency (0.87s)} while reaching a real-time throughput of \textbf{32 FPS}, setting a new standard for high-fidelity interactive digital human synthesis.
SoulX-LiveTalk: Real-Time Infinite Streaming of Audio-Driven Avatars via Self-Correcting Bidirectional Distillation
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Deploying massive diffusion models for real-time, infinite-duration, audio-driven avatar generation presents a significant engineering challenge, primarily due to the conflict between computational load and strict latency constraints. Existing approaches often compromise visual fidelity by enforcing strictly unidirectional attention mechanisms or reducing model capacity. To address this problem, we introduce \textbf{SoulX-LiveTalk}, a 14B-parameter framework optimized for high-fidelity real-time streaming. Diverging from conventional unidirectional paradigms, we use a \textbf{Self-correcting Bidirectional Distillation} strategy that retains bidirectional attention within video chunks. This design preserves critical spatiotemporal correlations, significantly enhancing motion coherence and visual detail. To ensure stability during infinite generation, we incorporate a \textbf{Multi-step Retrospective Self-Correction Mechanism}, enabling the model to autonomously recover from accumulated errors and preventing collapse. Furthermore, we engineered a full-stack inference acceleration suite incorporating hybrid sequence parallelism, Parallel VAE, and kernel-level optimizations. Extensive evaluations confirm that SoulX-LiveTalk is the first 14B-scale system to achieve a \textbf{sub-second start-up latency (0.87s)} while reaching a real-time throughput of \textbf{32 FPS}, setting a new standard for high-fidelity interactive digital human synthesis.
RAP: Real-time Audio-driven Portrait Animation with Video Diffusion Transformer
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Audio-driven portrait animation aims to synthesize realistic and natural talking head videos from an input audio signal and a single reference image. While existing methods achieve high-quality results by leveraging high-dimensional intermediate representations and explicitly modeling motion dynamics, their computational complexity renders them unsuitable for real-time deployment. Real-time inference imposes stringent latency and memory constraints, often necessitating the use of highly compressed latent representations. However, operating in such compact spaces hinders the preservation of fine-grained spatiotemporal details, thereby complicating audio-visual synchronization RAP (Real-time Audio-driven Portrait animation), a unified framework for generating high-quality talking portraits under real-time constraints. Specifically, RAP introduces a hybrid attention mechanism for fine-grained audio control, and a static-dynamic training-inference paradigm that avoids explicit motion supervision. Through these techniques, RAP achieves precise audio-driven control, mitigates long-term temporal drift, and maintains high visual fidelity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RAP achieves state-of-the-art performance while operating under real-time constraints.
Marrying Autoregressive Transformer and Diffusion with Multi-Reference Autoregression
Jun 11, 2025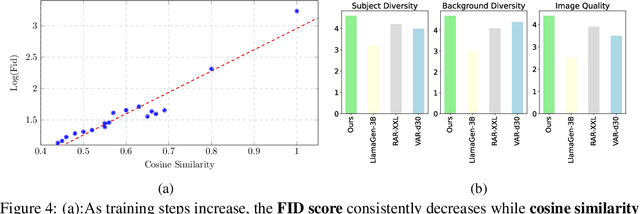

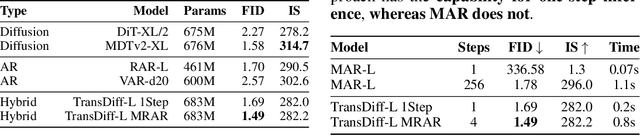
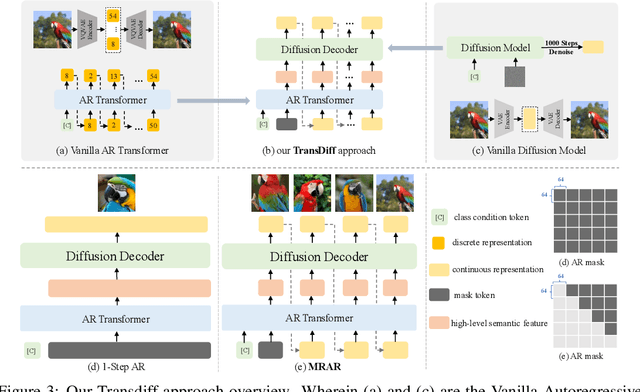
Abstract:We introduce TransDiff, the first image generation model that marries Autoregressive (AR) Transformer with diffusion models. In this joint modeling framework, TransDiff encodes labels and images into high-level semantic features and employs a diffusion model to estimate the distribution of image samples. On the ImageNet 256x256 benchmark, TransDiff significantly outperforms other image generation models based on standalone AR Transformer or diffusion models. Specifically, TransDiff achieves a Fr\'echet Inception Distance (FID) of 1.61 and an Inception Score (IS) of 293.4, and further provides x2 faster inference latency compared to state-of-the-art methods based on AR Transformer and x112 faster inference compared to diffusion-only models. Furthermore, building on the TransDiff model, we introduce a novel image generation paradigm called Multi-Reference Autoregression (MRAR), which performs autoregressive generation by predicting the next image. MRAR enables the model to reference multiple previously generated images, thereby facilitating the learning of more diverse representations and improving the quality of generated images in subsequent iterations. By applying MRAR, the performance of TransDiff is improved, with the FID reduced from 1.61 to 1.42. We expect TransDiff to open up a new frontier in the field of image generation.
Infi-Med: Low-Resource Medical MLLMs with Robust Reasoning Evaluation
May 29, 2025
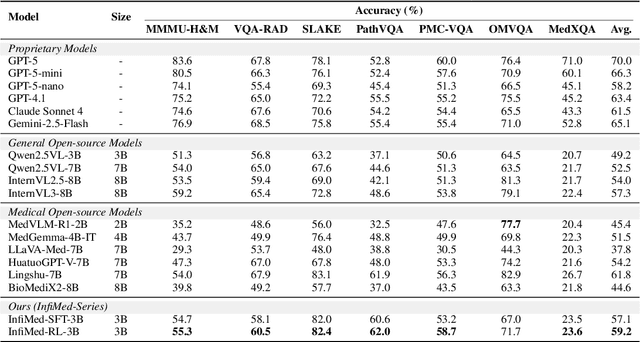
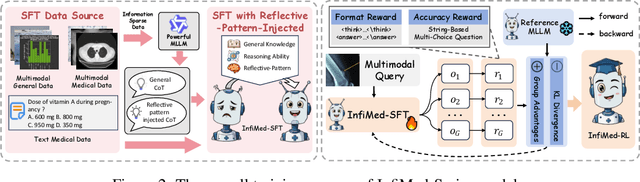
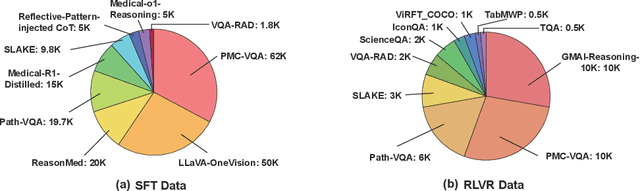
Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated promising prospects in healthcare, particularly for addressing complex medical tasks, supporting multidisciplinary treatment (MDT), and enabling personalized precision medicine. However, their practical deployment faces critical challenges in resource efficiency, diagnostic accuracy, clinical considerations, and ethical privacy. To address these limitations, we propose Infi-Med, a comprehensive framework for medical MLLMs that introduces three key innovations: (1) a resource-efficient approach through curating and constructing high-quality supervised fine-tuning (SFT) datasets with minimal sample requirements, with a forward-looking design that extends to both pretraining and posttraining phases; (2) enhanced multimodal reasoning capabilities for cross-modal integration and clinical task understanding; and (3) a systematic evaluation system that assesses model performance across medical modalities and task types. Our experiments demonstrate that Infi-Med achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in general medical reasoning while maintaining rapid adaptability to clinical scenarios. The framework establishes a solid foundation for deploying MLLMs in real-world healthcare settings by balancing model effectiveness with operational constraints.
ELDeR: Getting Efficient LLMs through Data-Driven Regularized Layer-wise Pruning
May 23, 2025Abstract:The deployment of Large language models (LLMs) in many fields is largely hindered by their high computational and memory costs. Recent studies suggest that LLMs exhibit sparsity, which can be used for pruning. Previous pruning methods typically follow a prune-then-finetune paradigm. Since the pruned parts still contain valuable information, statically removing them without updating the remaining parameters often results in irreversible performance degradation, requiring costly recovery fine-tuning (RFT) to maintain performance. To address this, we propose a novel paradigm: first apply regularization, then prune. Based on this paradigm, we propose ELDeR: Getting Efficient LLMs through Data-Driven Regularized Layer-wise Pruning. We multiply the output of each transformer layer by an initial weight, then we iteratively learn the weights of each transformer layer by using a small amount of data in a simple way. After that, we apply regularization to the difference between the output and input of the layers with smaller weights, forcing the information to be transferred to the remaining layers. Compared with direct pruning, ELDeR reduces the information loss caused by direct parameter removal, thus better preserving the model's language modeling ability. Experimental results show that ELDeR achieves superior performance compared with powerful layer-wise structured pruning methods, while greatly reducing RFT computational costs. Since ELDeR is a layer-wise pruning method, its end-to-end acceleration effect is obvious, making it a promising technique for efficient LLMs.
UTTG_ A Universal Teleoperation Approach via Online Trajectory Generation
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Teleoperation is crucial for hazardous environment operations and serves as a key tool for collecting expert demonstrations in robot learning. However, existing methods face robotic hardware dependency and control frequency mismatches between teleoperation devices and robotic platforms. Our approach automatically extracts kinematic parameters from unified robot description format (URDF) files, and enables pluggable deployment across diverse robots through uniform interfaces. The proposed interpolation algorithm bridges the frequency gap between low-rate human inputs and high-frequency robotic control commands through online continuous trajectory generation, \n{while requiring no access to the closed, bottom-level control loop}. To enhance trajectory smoothness, we introduce a minimum-stretch spline that optimizes the motion quality. The system further provides precision and rapid modes to accommodate different task requirements. Experiments across various robotic platforms including dual-arm ones demonstrate generality and smooth operation performance of our methods. The code is developed in C++ with python interface, and available at https://github.com/IRMV-Manipulation-Group/UTTG.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge