Haotian Xu
CityCube: Benchmarking Cross-view Spatial Reasoning on Vision-Language Models in Urban Environments
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Cross-view spatial reasoning is essential for embodied AI, underpinning spatial understanding, mental simulation and planning in complex environments. Existing benchmarks primarily emphasize indoor or street settings, overlooking the unique challenges of open-ended urban spaces characterized by rich semantics, complex geometries, and view variations. To address this, we introduce CityCube, a systematic benchmark designed to probe cross-view reasoning capabilities of current VLMs in urban settings. CityCube integrates four viewpoint dynamics to mimic camera movements and spans a wide spectrum of perspectives from multiple platforms, e.g., vehicles, drones and satellites. For a comprehensive assessment, it features 5,022 meticulously annotated multi-view QA pairs categorized into five cognitive dimensions and three spatial relation expressions. A comprehensive evaluation of 33 VLMs reveals a significant performance disparity with humans: even large-scale models struggle to exceed 54.1% accuracy, remaining 34.2% below human performance. By contrast, small-scale fine-tuned VLMs achieve over 60.0% accuracy, highlighting the necessity of our benchmark. Further analyses indicate the task correlations and fundamental cognitive disparity between VLMs and human-like reasoning.
Adversarial Robustness in Zero-Shot Learning:An Empirical Study on Class and Concept-Level Vulnerabilities
Dec 21, 2025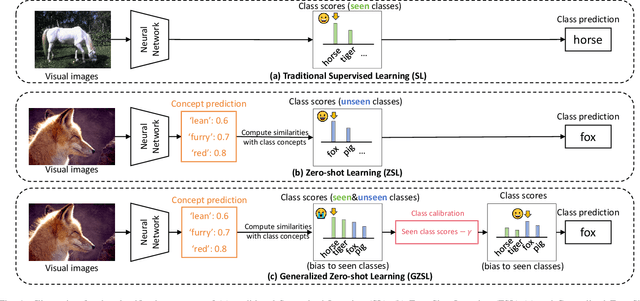

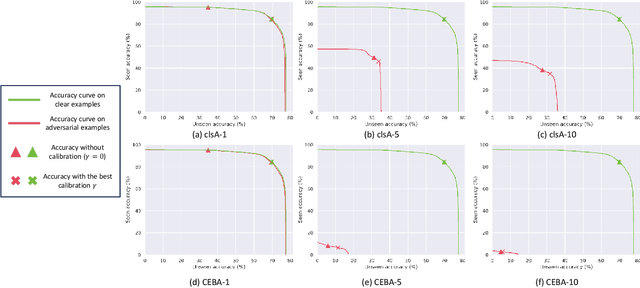
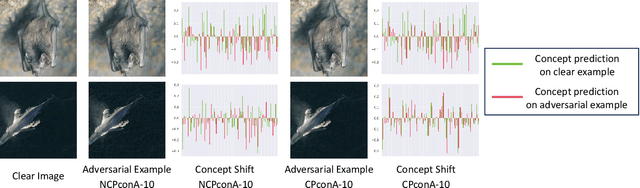
Abstract:Zero-shot Learning (ZSL) aims to enable image classifiers to recognize images from unseen classes that were not included during training. Unlike traditional supervised classification, ZSL typically relies on learning a mapping from visual features to predefined, human-understandable class concepts. While ZSL models promise to improve generalization and interpretability, their robustness under systematic input perturbations remain unclear. In this study, we present an empirical analysis about the robustness of existing ZSL methods at both classlevel and concept-level. Specifically, we successfully disrupted their class prediction by the well-known non-target class attack (clsA). However, in the Generalized Zero-shot Learning (GZSL) setting, we observe that the success of clsA is only at the original best-calibrated point. After the attack, the optimal bestcalibration point shifts, and ZSL models maintain relatively strong performance at other calibration points, indicating that clsA results in a spurious attack success in the GZSL. To address this, we propose the Class-Bias Enhanced Attack (CBEA), which completely eliminates GZSL accuracy across all calibrated points by enhancing the gap between seen and unseen class probabilities.Next, at concept-level attack, we introduce two novel attack modes: Class-Preserving Concept Attack (CPconA) and NonClass-Preserving Concept Attack (NCPconA). Our extensive experiments evaluate three typical ZSL models across various architectures from the past three years and reveal that ZSL models are vulnerable not only to the traditional class attack but also to concept-based attacks. These attacks allow malicious actors to easily manipulate class predictions by erasing or introducing concepts. Our findings highlight a significant performance gap between existing approaches, emphasizing the need for improved adversarial robustness in current ZSL models.
Resting Neurons, Active Insights: Improving Input Sparsification for Large Language Models
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) achieve state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of applications, but their massive scale poses significant challenges for both efficiency and interpretability. Structural pruning, which reduces model size by removing redundant computational units such as neurons, has been widely explored as a solution, and this study devotes to input sparsification, an increasingly popular technique that improves efficiency by selectively activating only a subset of entry values for each input. However, existing approaches focus primarily on computational savings, often overlooking the representational consequences of sparsification and leaving a noticeable performance gap compared to full models. In this work, we first reinterpret input sparsification as a form of dynamic structural pruning. Motivated by the spontaneous baseline firing rates observed in biological neurons, we introduce a small set of trainable spontaneous neurons that act as compensatory units to stabilize activations in sparsified LLMs. Experiments demonstrate that these auxiliary neurons substantially reduce the sparsification-induced performance gap while generalizing effectively across tasks.
IterResearch: Rethinking Long-Horizon Agents via Markovian State Reconstruction
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in deep-research agents have shown promise for autonomous knowledge construction through dynamic reasoning over external sources. However, existing approaches rely on a mono-contextual paradigm that accumulates all information in a single, expanding context window, leading to context suffocation and noise contamination that limit their effectiveness on long-horizon tasks. We introduce IterResearch, a novel iterative deep-research paradigm that reformulates long-horizon research as a Markov Decision Process with strategic workspace reconstruction. By maintaining an evolving report as memory and periodically synthesizing insights, our approach preserves consistent reasoning capacity across arbitrary exploration depths. We further develop Efficiency-Aware Policy Optimization (EAPO), a reinforcement learning framework that incentivizes efficient exploration through geometric reward discounting and enables stable distributed training via adaptive downsampling. Extensive experiments demonstrate that IterResearch achieves substantial improvements over existing open-source agents with average +14.5pp across six benchmarks and narrows the gap with frontier proprietary systems. Remarkably, our paradigm exhibits unprecedented interaction scaling, extending to 2048 interactions with dramatic performance gains (from 3.5\% to 42.5\%), and serves as an effective prompting strategy, improving frontier models by up to 19.2pp over ReAct on long-horizon tasks. These findings position IterResearch as a versatile solution for long-horizon reasoning, effective both as a trained agent and as a prompting paradigm for frontier models.
Search Self-play: Pushing the Frontier of Agent Capability without Supervision
Oct 21, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has become the mainstream technique for training LLM agents. However, RLVR highly depends on well-crafted task queries and corresponding ground-truth answers to provide accurate rewards, which requires massive human efforts and hinders the RL scaling processes, especially under agentic scenarios. Although a few recent works explore task synthesis methods, the difficulty of generated agentic tasks can hardly be controlled to provide effective RL training advantages. To achieve agentic RLVR with higher scalability, we explore self-play training for deep search agents, in which the learning LLM utilizes multi-turn search engine calling and acts simultaneously as both a task proposer and a problem solver. The task proposer aims to generate deep search queries with well-defined ground-truth answers and increasing task difficulty. The problem solver tries to handle the generated search queries and output the correct answer predictions. To ensure that each generated search query has accurate ground truth, we collect all the searching results from the proposer's trajectory as external knowledge, then conduct retrieval-augmentation generation (RAG) to test whether the proposed query can be correctly answered with all necessary search documents provided. In this search self-play (SSP) game, the proposer and the solver co-evolve their agent capabilities through both competition and cooperation. With substantial experimental results, we find that SSP can significantly improve search agents' performance uniformly on various benchmarks without any supervision under both from-scratch and continuous RL training setups. The code is at https://github.com/Alibaba-Quark/SSP.
LiteLong: Resource-Efficient Long-Context Data Synthesis for LLMs
Sep 19, 2025
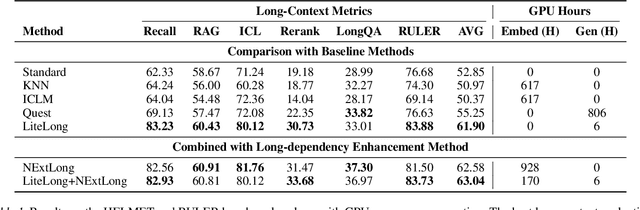


Abstract:High-quality long-context data is essential for training large language models (LLMs) capable of processing extensive documents, yet existing synthesis approaches using relevance-based aggregation face challenges of computational efficiency. We present LiteLong, a resource-efficient method for synthesizing long-context data through structured topic organization and multi-agent debate. Our approach leverages the BISAC book classification system to provide a comprehensive hierarchical topic organization, and then employs a debate mechanism with multiple LLMs to generate diverse, high-quality topics within this structure. For each topic, we use lightweight BM25 retrieval to obtain relevant documents and concatenate them into 128K-token training samples. Experiments on HELMET and Ruler benchmarks demonstrate that LiteLong achieves competitive long-context performance and can seamlessly integrate with other long-dependency enhancement methods. LiteLong makes high-quality long-context data synthesis more accessible by reducing both computational and data engineering costs, facilitating further research in long-context language training.
Graph Concept Bottleneck Models
Aug 19, 2025Abstract:Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) provide explicit interpretations for deep neural networks through concepts and allow intervention with concepts to adjust final predictions. Existing CBMs assume concepts are conditionally independent given labels and isolated from each other, ignoring the hidden relationships among concepts. However, the set of concepts in CBMs often has an intrinsic structure where concepts are generally correlated: changing one concept will inherently impact its related concepts. To mitigate this limitation, we propose GraphCBMs: a new variant of CBM that facilitates concept relationships by constructing latent concept graphs, which can be combined with CBMs to enhance model performance while retaining their interpretability. Our experiment results on real-world image classification tasks demonstrate Graph CBMs offer the following benefits: (1) superior in image classification tasks while providing more concept structure information for interpretability; (2) able to utilize latent concept graphs for more effective interventions; and (3) robust in performance across different training and architecture settings.
MedKGent: A Large Language Model Agent Framework for Constructing Temporally Evolving Medical Knowledge Graph
Aug 17, 2025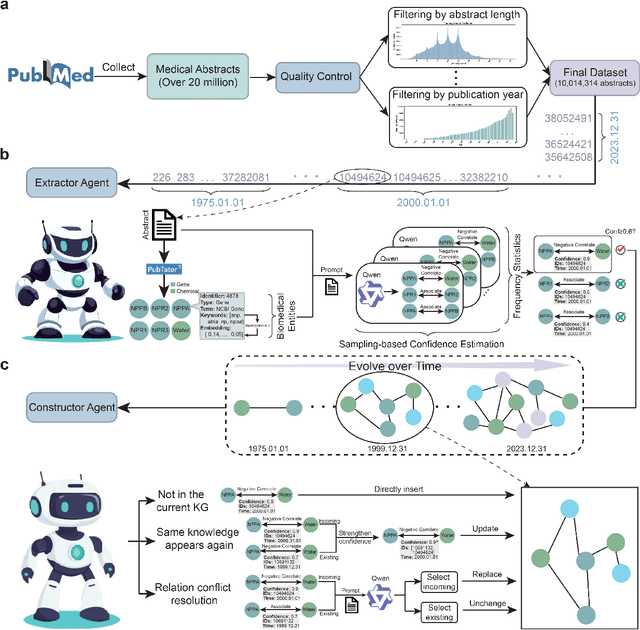
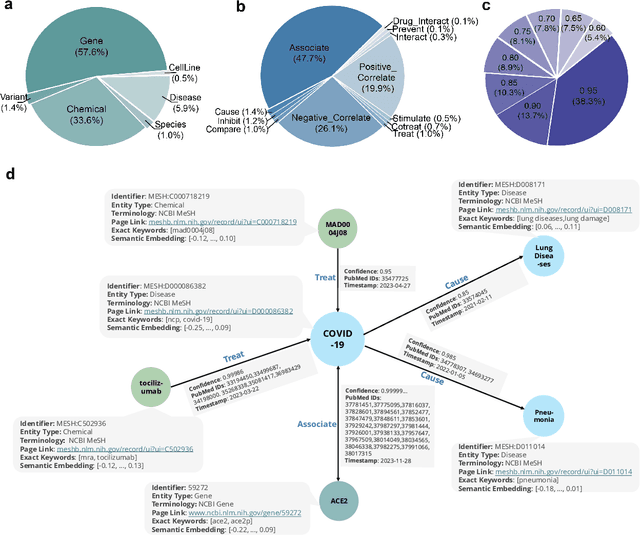
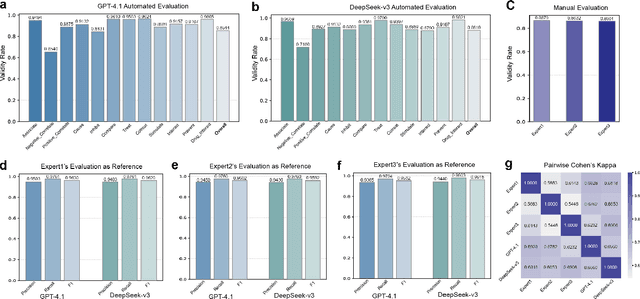
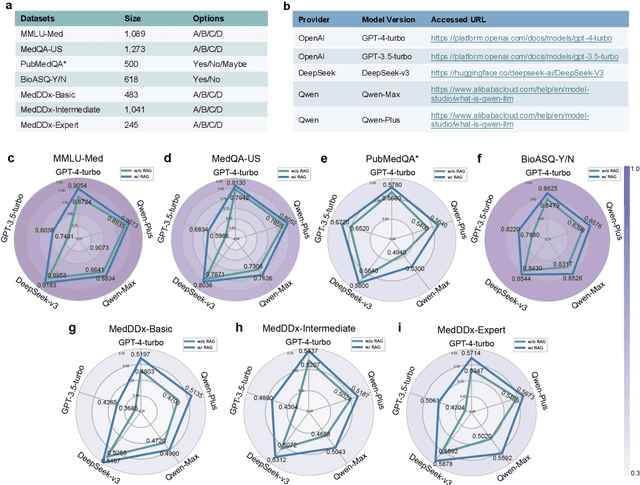
Abstract:The rapid expansion of medical literature presents growing challenges for structuring and integrating domain knowledge at scale. Knowledge Graphs (KGs) offer a promising solution by enabling efficient retrieval, automated reasoning, and knowledge discovery. However, current KG construction methods often rely on supervised pipelines with limited generalizability or naively aggregate outputs from Large Language Models (LLMs), treating biomedical corpora as static and ignoring the temporal dynamics and contextual uncertainty of evolving knowledge. To address these limitations, we introduce MedKGent, a LLM agent framework for constructing temporally evolving medical KGs. Leveraging over 10 million PubMed abstracts published between 1975 and 2023, we simulate the emergence of biomedical knowledge via a fine-grained daily time series. MedKGent incrementally builds the KG in a day-by-day manner using two specialized agents powered by the Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct model. The Extractor Agent identifies knowledge triples and assigns confidence scores via sampling-based estimation, which are used to filter low-confidence extractions and inform downstream processing. The Constructor Agent incrementally integrates the retained triples into a temporally evolving graph, guided by confidence scores and timestamps to reinforce recurring knowledge and resolve conflicts. The resulting KG contains 156,275 entities and 2,971,384 relational triples. Quality assessments by two SOTA LLMs and three domain experts demonstrate an accuracy approaching 90\%, with strong inter-rater agreement. To evaluate downstream utility, we conduct RAG across seven medical question answering benchmarks using five leading LLMs, consistently observing significant improvements over non-augmented baselines. Case studies further demonstrate the KG's value in literature-based drug repurposing via confidence-aware causal inference.
Omni-DPO: A Dual-Perspective Paradigm for Dynamic Preference Learning of LLMs
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has become a cornerstone of reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) due to its simplicity and efficiency. However, existing DPO-based approaches typically treat all preference pairs uniformly, ignoring critical variations in their inherent quality and learning utility, leading to suboptimal data utilization and performance. To address this challenge, we propose Omni-DPO, a dual-perspective optimization framework that jointly accounts for (1) the inherent quality of each preference pair and (2) the model's evolving performance on those pairs. By adaptively weighting samples according to both data quality and the model's learning dynamics during training, Omni-DPO enables more effective training data utilization and achieves better performance. Experimental results on various models and benchmarks demonstrate the superiority and generalization capabilities of Omni-DPO. On textual understanding tasks, Gemma-2-9b-it finetuned with Omni-DPO beats the leading LLM, Claude 3 Opus, by a significant margin of 6.7 points on the Arena-Hard benchmark. On mathematical reasoning tasks, Omni-DPO consistently outperforms the baseline methods across all benchmarks, providing strong empirical evidence for the effectiveness and robustness of our approach. Code and models will be available at https://github.com/pspdada/Omni-DPO.
Agent RL Scaling Law: Agent RL with Spontaneous Code Execution for Mathematical Problem Solving
May 14, 2025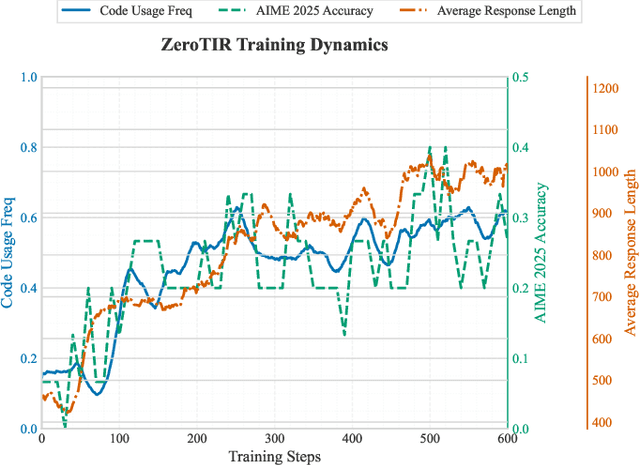
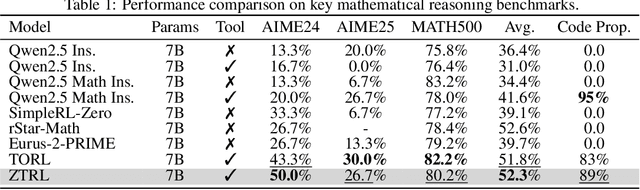

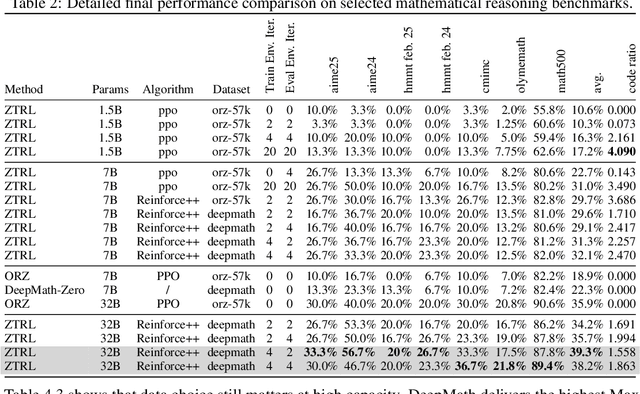
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle with mathematical reasoning tasks requiring precise, verifiable computation. While Reinforcement Learning (RL) from outcome-based rewards enhances text-based reasoning, understanding how agents autonomously learn to leverage external tools like code execution remains crucial. We investigate RL from outcome-based rewards for Tool-Integrated Reasoning, ZeroTIR, training base LLMs to spontaneously generate and execute Python code for mathematical problems without supervised tool-use examples. Our central contribution is we demonstrate that as RL training progresses, key metrics scale predictably. Specifically, we observe strong positive correlations where increased training steps lead to increases in the spontaneous code execution frequency, the average response length, and, critically, the final task accuracy. This suggests a quantifiable relationship between computational effort invested in training and the emergence of effective, tool-augmented reasoning strategies. We implement a robust framework featuring a decoupled code execution environment and validate our findings across standard RL algorithms and frameworks. Experiments show ZeroTIR significantly surpasses non-tool ZeroRL baselines on challenging math benchmarks. Our findings provide a foundational understanding of how autonomous tool use is acquired and scales within Agent RL, offering a reproducible benchmark for future studies. Code is released at \href{https://github.com/yyht/openrlhf_async_pipline}{https://github.com/yyht/openrlhf\_async\_pipline}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge