Yuxuan Li
MiniCPM-SALA: Hybridizing Sparse and Linear Attention for Efficient Long-Context Modeling
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:The evolution of large language models (LLMs) towards applications with ultra-long contexts faces challenges posed by the high computational and memory costs of the Transformer architecture. While existing sparse and linear attention mechanisms attempt to mitigate these issues, they typically involve a trade-off between memory efficiency and model performance. This paper introduces MiniCPM-SALA, a 9B-parameter hybrid architecture that integrates the high-fidelity long-context modeling of sparse attention (InfLLM-V2) with the global efficiency of linear attention (Lightning Attention). By employing a layer selection algorithm to integrate these mechanisms in a 1:3 ratio and utilizing a hybrid positional encoding (HyPE), the model maintains efficiency and performance for long-context tasks. Furthermore, we introduce a cost-effective continual training framework that transforms pre-trained Transformer-based models into hybrid models, which reduces training costs by approximately 75% compared to training from scratch. Extensive experiments show that MiniCPM-SALA maintains general capabilities comparable to full-attention models while offering improved efficiency. On a single NVIDIA A6000D GPU, the model achieves up to 3.5x the inference speed of the full-attention model at the sequence length of 256K tokens and supports context lengths of up to 1M tokens, a scale where traditional full-attention 8B models fail because of memory constraints.
ARGOS: Automated Functional Safety Requirement Synthesis for Embodied AI via Attribute-Guided Combinatorial Reasoning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Ensuring functional safety is essential for the deployment of Embodied AI in complex open-world environments. However, traditional Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment (HARA) methods struggle to scale in this domain. While HARA relies on enumerating risks for finite and pre-defined function lists, Embodied AI operates on open-ended natural language instructions, creating a challenge of combinatorial interaction risks. Whereas Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as a promising solution to this scalability challenge, they often lack physical grounding, yielding semantically superficial and incoherent hazard descriptions. To overcome these limitations, we propose a new framework ARGOS (AttRibute-Guided cOmbinatorial reaSoning), which bridges the gap between open-ended user instructions and concrete physical attributes. By dynamically decomposing entities from instructions into these fine-grained properties, ARGOS grounds LLM reasoning in causal risk factors to generate physically plausible hazard scenarios. It then instantiates abstract safety standards, such as ISO 13482, into context-specific Functional Safety Requirements (FSRs) by integrating these scenarios with robot capabilities. Extensive experiments validate that ARGOS produces high-quality FSRs and outperforms baselines in identifying long-tail risks. Overall, this work paves the way for systematic and grounded functional safety requirement generation, a critical step toward the safe industrial deployment of Embodied AI.
Continual Policy Distillation from Distributed Reinforcement Learning Teachers
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Continual Reinforcement Learning (CRL) aims to develop lifelong learning agents to continuously acquire knowledge across diverse tasks while mitigating catastrophic forgetting. This requires efficiently managing the stability-plasticity dilemma and leveraging prior experience to rapidly generalize to novel tasks. While various enhancement strategies for both aspects have been proposed, achieving scalable performance by directly applying RL to sequential task streams remains challenging. In this paper, we propose a novel teacher-student framework that decouples CRL into two independent processes: training single-task teacher models through distributed RL and continually distilling them into a central generalist model. This design is motivated by the observation that RL excels at solving single tasks, while policy distillation -- a relatively stable supervised learning process -- is well aligned with large foundation models and multi-task learning. Moreover, a mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture and a replay-based approach are employed to enhance the plasticity and stability of the continual policy distillation process. Extensive experiments on the Meta-World benchmark demonstrate that our framework enables efficient continual RL, recovering over 85% of teacher performance while constraining task-wise forgetting to within 10%.
Context Structure Reshapes the Representational Geometry of Language Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been shown to organize the representations of input sequences into straighter neural trajectories in their deep layers, which has been hypothesized to facilitate next-token prediction via linear extrapolation. Language models can also adapt to diverse tasks and learn new structure in context, and recent work has shown that this in-context learning (ICL) can be reflected in representational changes. Here we bring these two lines of research together to explore whether representation straightening occurs \emph{within} a context during ICL. We measure representational straightening in Gemma 2 models across a diverse set of in-context tasks, and uncover a dichotomy in how LLMs' representations change in context. In continual prediction settings (e.g., natural language, grid world traversal tasks) we observe that increasing context increases the straightness of neural sequence trajectories, which is correlated with improvement in model prediction. Conversely, in structured prediction settings (e.g., few-shot tasks), straightening is inconsistent -- it is only present in phases of the task with explicit structure (e.g., repeating a template), but vanishes elsewhere. These results suggest that ICL is not a monolithic process. Instead, we propose that LLMs function like a Swiss Army knife: depending on task structure, the LLM dynamically selects between strategies, only some of which yield representational straightening.
Linear representations in language models can change dramatically over a conversation
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Language model representations often contain linear directions that correspond to high-level concepts. Here, we study the dynamics of these representations: how representations evolve along these dimensions within the context of (simulated) conversations. We find that linear representations can change dramatically over a conversation; for example, information that is represented as factual at the beginning of a conversation can be represented as non-factual at the end and vice versa. These changes are content-dependent; while representations of conversation-relevant information may change, generic information is generally preserved. These changes are robust even for dimensions that disentangle factuality from more superficial response patterns, and occur across different model families and layers of the model. These representation changes do not require on-policy conversations; even replaying a conversation script written by an entirely different model can produce similar changes. However, adaptation is much weaker from simply having a sci-fi story in context that is framed more explicitly as such. We also show that steering along a representational direction can have dramatically different effects at different points in a conversation. These results are consistent with the idea that representations may evolve in response to the model playing a particular role that is cued by a conversation. Our findings may pose challenges for interpretability and steering -- in particular, they imply that it may be misleading to use static interpretations of features or directions, or probes that assume a particular range of features consistently corresponds to a particular ground-truth value. However, these types of representational dynamics also point to exciting new research directions for understanding how models adapt to context.
Evaluating Feature Dependent Noise in Preference-based Reinforcement Learning
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Learning from Preferences in Reinforcement Learning (PbRL) has gained attention recently, as it serves as a natural fit for complicated tasks where the reward function is not easily available. However, preferences often come with uncertainty and noise if they are not from perfect teachers. Much prior literature aimed to detect noise, but with limited types of noise and most being uniformly distributed with no connection to observations. In this work, we formalize the notion of targeted feature-dependent noise and propose several variants like trajectory feature noise, trajectory similarity noise, uncertainty-aware noise, and Language Model noise. We evaluate feature-dependent noise, where noise is correlated with certain features in complex continuous control tasks from DMControl and Meta-world. Our experiments show that in some feature-dependent noise settings, the state-of-the-art noise-robust PbRL method's learning performance is significantly deteriorated, while PbRL method with no explicit denoising can surprisingly outperform noise-robust PbRL in majority settings. We also find language model's noise exhibits similar characteristics to feature-dependent noise, thereby simulating realistic humans and call for further study in learning with feature-dependent noise robustly.
JOGS: Joint Optimization of Pose Estimation and 3D Gaussian Splatting
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Traditional novel view synthesis methods heavily rely on external camera pose estimation tools such as COLMAP, which often introduce computational bottlenecks and propagate errors. To address these challenges, we propose a unified framework that jointly optimizes 3D Gaussian points and camera poses without requiring pre-calibrated inputs. Our approach iteratively refines 3D Gaussian parameters and updates camera poses through a novel co-optimization strategy, ensuring simultaneous improvements in scene reconstruction fidelity and pose accuracy. The key innovation lies in decoupling the joint optimization into two interleaved phases: first, updating 3D Gaussian parameters via differentiable rendering with fixed poses, and second, refining camera poses using a customized 3D optical flow algorithm that incorporates geometric and photometric constraints. This formulation progressively reduces projection errors, particularly in challenging scenarios with large viewpoint variations and sparse feature distributions, where traditional methods struggle. Extensive evaluations on multiple datasets demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing COLMAP-free techniques in reconstruction quality, and also surpasses the standard COLMAP-based baseline in general.
Latent learning: episodic memory complements parametric learning by enabling flexible reuse of experiences
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:When do machine learning systems fail to generalize, and what mechanisms could improve their generalization? Here, we draw inspiration from cognitive science to argue that one weakness of machine learning systems is their failure to exhibit latent learning -- learning information that is not relevant to the task at hand, but that might be useful in a future task. We show how this perspective links failures ranging from the reversal curse in language modeling to new findings on agent-based navigation. We then highlight how cognitive science points to episodic memory as a potential part of the solution to these issues. Correspondingly, we show that a system with an oracle retrieval mechanism can use learning experiences more flexibly to generalize better across many of these challenges. We also identify some of the essential components for effectively using retrieval, including the importance of within-example in-context learning for acquiring the ability to use information across retrieved examples. In summary, our results illustrate one possible contributor to the relative data inefficiency of current machine learning systems compared to natural intelligence, and help to understand how retrieval methods can complement parametric learning to improve generalization.
Representation biases: will we achieve complete understanding by analyzing representations?
Jul 29, 2025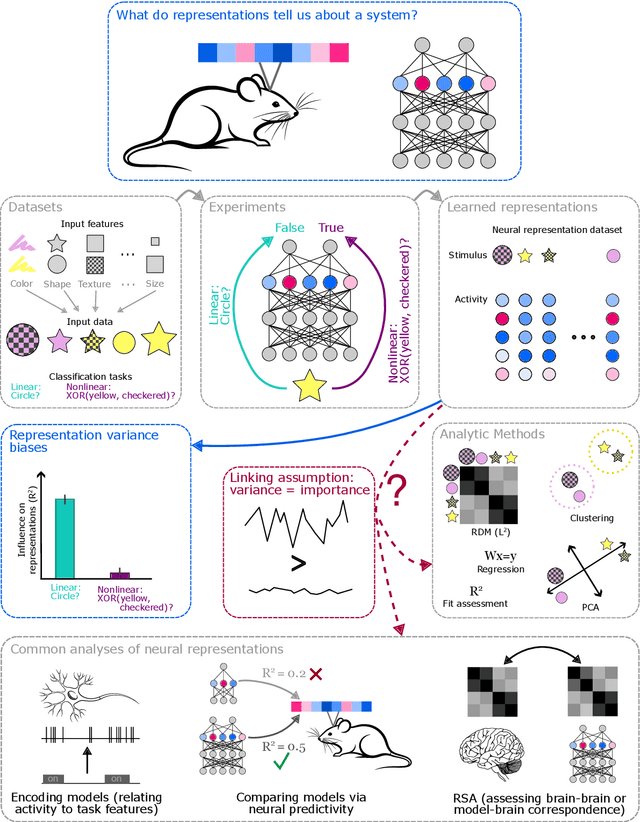
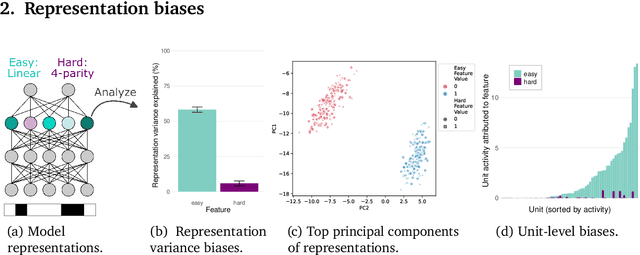
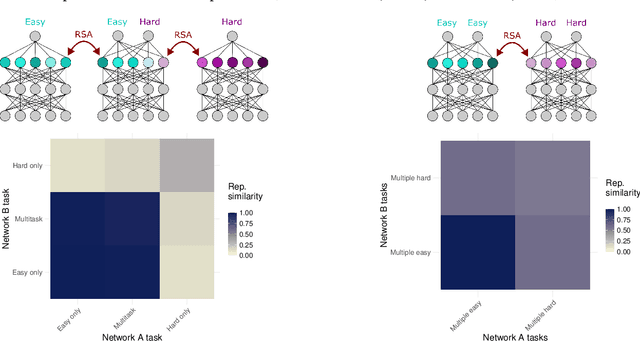
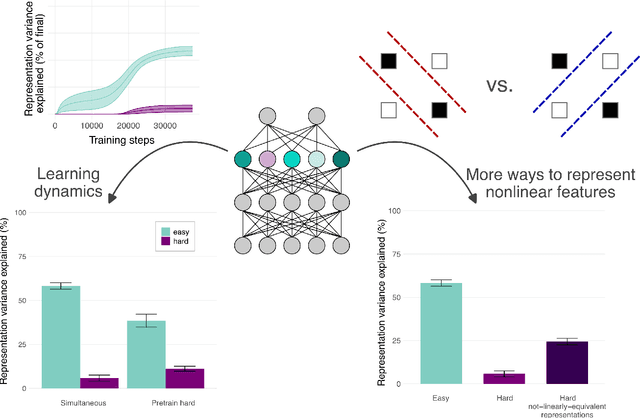
Abstract:A common approach in neuroscience is to study neural representations as a means to understand a system -- increasingly, by relating the neural representations to the internal representations learned by computational models. However, a recent work in machine learning (Lampinen, 2024) shows that learned feature representations may be biased to over-represent certain features, and represent others more weakly and less-consistently. For example, simple (linear) features may be more strongly and more consistently represented than complex (highly nonlinear) features. These biases could pose challenges for achieving full understanding of a system through representational analysis. In this perspective, we illustrate these challenges -- showing how feature representation biases can lead to strongly biased inferences from common analyses like PCA, regression, and RSA. We also present homomorphic encryption as a simple case study of the potential for strong dissociation between patterns of representation and computation. We discuss the implications of these results for representational comparisons between systems, and for neuroscience more generally.
MiniCPM4: Ultra-Efficient LLMs on End Devices
Jun 09, 2025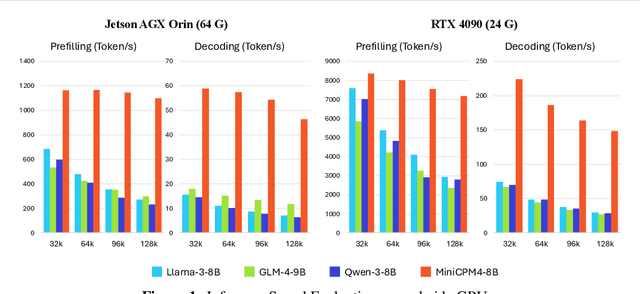

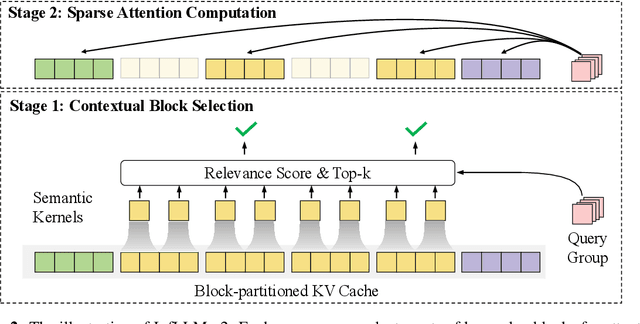
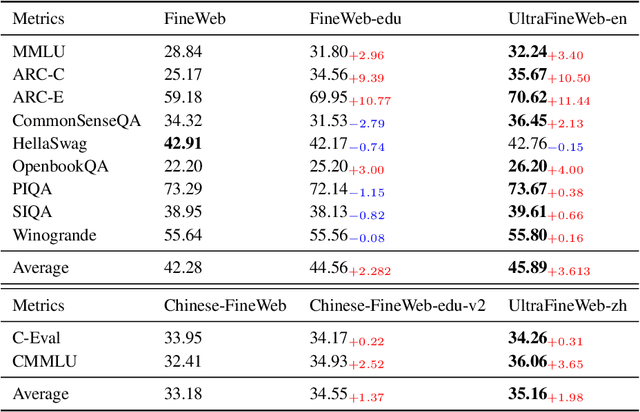
Abstract:This paper introduces MiniCPM4, a highly efficient large language model (LLM) designed explicitly for end-side devices. We achieve this efficiency through systematic innovation in four key dimensions: model architecture, training data, training algorithms, and inference systems. Specifically, in terms of model architecture, we propose InfLLM v2, a trainable sparse attention mechanism that accelerates both prefilling and decoding phases for long-context processing. Regarding training data, we propose UltraClean, an efficient and accurate pre-training data filtering and generation strategy, and UltraChat v2, a comprehensive supervised fine-tuning dataset. These datasets enable satisfactory model performance to be achieved using just 8 trillion training tokens. Regarding training algorithms, we propose ModelTunnel v2 for efficient pre-training strategy search, and improve existing post-training methods by introducing chunk-wise rollout for load-balanced reinforcement learning and data-efficient tenary LLM, BitCPM. Regarding inference systems, we propose CPM.cu that integrates sparse attention, model quantization, and speculative sampling to achieve efficient prefilling and decoding. To meet diverse on-device requirements, MiniCPM4 is available in two versions, with 0.5B and 8B parameters, respectively. Sufficient evaluation results show that MiniCPM4 outperforms open-source models of similar size across multiple benchmarks, highlighting both its efficiency and effectiveness. Notably, MiniCPM4-8B demonstrates significant speed improvements over Qwen3-8B when processing long sequences. Through further adaptation, MiniCPM4 successfully powers diverse applications, including trustworthy survey generation and tool use with model context protocol, clearly showcasing its broad usability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge