Ao Sun
State Rank Dynamics in Linear Attention LLMs
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Linear Attention Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a compelling recurrent formulation that compresses context into a fixed-size state matrix, enabling constant-time inference. However, the internal dynamics of this compressed state remain largely opaque. In this work, we present a comprehensive study on the runtime state dynamics of state-of-the-art Linear Attention models. We uncover a fundamental phenomenon termed State Rank Stratification, characterized by a distinct spectral bifurcation among linear attention heads: while one group maintains an effective rank oscillating near zero, the other exhibits rapid growth that converges to an upper bound. Extensive experiments across diverse inference contexts reveal that these dynamics remain strikingly consistent, indicating that the identity of a head,whether low-rank or high-rank,is an intrinsic structural property acquired during pre-training, rather than a transient state dependent on the input data. Furthermore, our diagnostic probes reveal a surprising functional divergence: low-rank heads are indispensable for model reasoning, whereas high-rank heads exhibit significant redundancy. Leveraging this insight, we propose Joint Rank-Norm Pruning, a zero-shot strategy that achieves a 38.9\% reduction in KV-cache overhead while largely maintaining model accuracy.
Spava: Accelerating Long-Video Understanding via Sequence-Parallelism-aware Approximate Attention
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:The efficiency of long-video inference remains a critical bottleneck, mainly due to the dense computation in the prefill stage of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs). Existing methods either compress visual embeddings or apply sparse attention on a single GPU, yielding limited acceleration or degraded performance and restricting LMMs from handling longer, more complex videos. To overcome these issues, we propose Spava, a sequence-parallel framework with optimized attention that accelerates long-video inference across multiple GPUs. By distributing approximate attention, Spava reduces computation and increases parallelism, enabling efficient processing of more visual embeddings without compression and thereby improving task performance. System-level optimizations, such as load balancing and fused forward passes, further unleash the potential of Spava, delivering speedups of 12.72x, 1.70x, and 1.18x over FlashAttn, ZigZagRing, and APB, without notable performance loss. Code available at https://github.com/thunlp/APB
CuMA: Aligning LLMs with Sparse Cultural Values via Demographic-Aware Mixture of Adapters
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) serve a global audience, alignment must transition from enforcing universal consensus to respecting cultural pluralism. We demonstrate that dense models, when forced to fit conflicting value distributions, suffer from \textbf{Mean Collapse}, converging to a generic average that fails to represent diverse groups. We attribute this to \textbf{Cultural Sparsity}, where gradient interference prevents dense parameters from spanning distinct cultural modes. To resolve this, we propose \textbf{\textsc{CuMA}} (\textbf{Cu}ltural \textbf{M}ixture of \textbf{A}dapters), a framework that frames alignment as a \textbf{conditional capacity separation} problem. By incorporating demographic-aware routing, \textsc{CuMA} internalizes a \textit{Latent Cultural Topology} to explicitly disentangle conflicting gradients into specialized expert subspaces. Extensive evaluations on WorldValuesBench, Community Alignment, and PRISM demonstrate that \textsc{CuMA} achieves state-of-the-art performance, significantly outperforming both dense baselines and semantic-only MoEs. Crucially, our analysis confirms that \textsc{CuMA} effectively mitigates mean collapse, preserving cultural diversity. Our code is available at https://github.com/Throll/CuMA.
ViDove: A Translation Agent System with Multimodal Context and Memory-Augmented Reasoning
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:LLM-based translation agents have achieved highly human-like translation results and are capable of handling longer and more complex contexts with greater efficiency. However, they are typically limited to text-only inputs. In this paper, we introduce ViDove, a translation agent system designed for multimodal input. Inspired by the workflow of human translators, ViDove leverages visual and contextual background information to enhance the translation process. Additionally, we integrate a multimodal memory system and long-short term memory modules enriched with domain-specific knowledge, enabling the agent to perform more accurately and adaptively in real-world scenarios. As a result, ViDove achieves significantly higher translation quality in both subtitle generation and general translation tasks, with a 28% improvement in BLEU scores and a 15% improvement in SubER compared to previous state-of-the-art baselines. Moreover, we introduce DoveBench, a new benchmark for long-form automatic video subtitling and translation, featuring 17 hours of high-quality, human-annotated data. Our code is available here: https://github.com/pigeonai-org/ViDove
LLM-Powered CPI Prediction Inference with Online Text Time Series
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Forecasting the Consumer Price Index (CPI) is an important yet challenging task in economics, where most existing approaches rely on low-frequency, survey-based data. With the recent advances of large language models (LLMs), there is growing potential to leverage high-frequency online text data for improved CPI prediction, an area still largely unexplored. This paper proposes LLM-CPI, an LLM-based approach for CPI prediction inference incorporating online text time series. We collect a large set of high-frequency online texts from a popularly used Chinese social network site and employ LLMs such as ChatGPT and the trained BERT models to construct continuous inflation labels for posts that are related to inflation. Online text embeddings are extracted via LDA and BERT. We develop a joint time series framework that combines monthly CPI data with LLM-generated daily CPI surrogates. The monthly model employs an ARX structure combining observed CPI data with text embeddings and macroeconomic variables, while the daily model uses a VARX structure built on LLM-generated CPI surrogates and text embeddings. We establish the asymptotic properties of the method and provide two forms of constructed prediction intervals. The finite-sample performance and practical advantages of LLM-CPI are demonstrated through both simulation and real data examples.
MiniCPM4: Ultra-Efficient LLMs on End Devices
Jun 09, 2025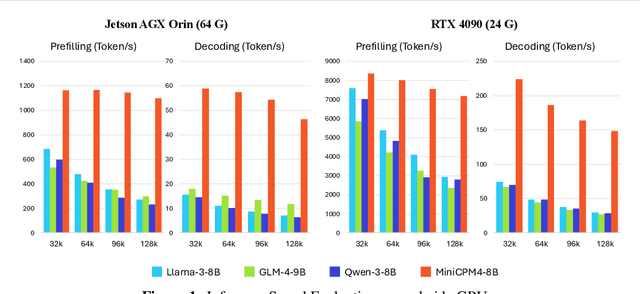

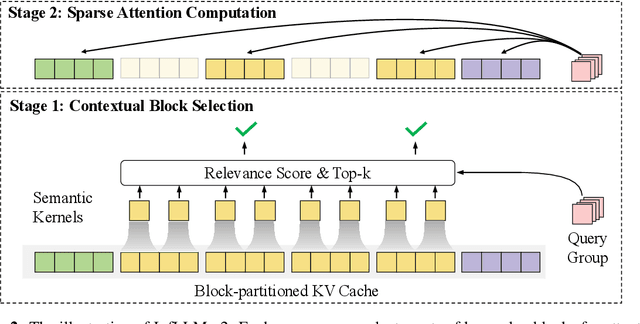
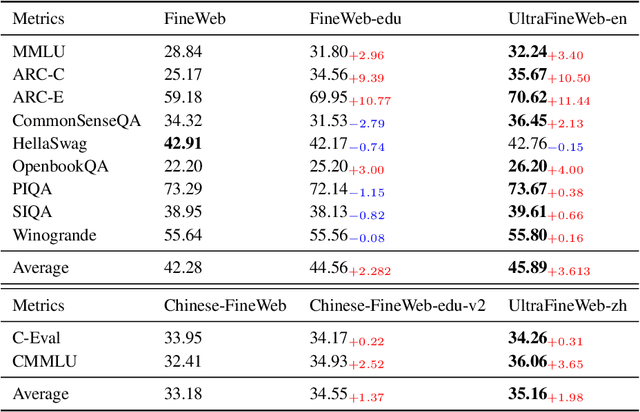
Abstract:This paper introduces MiniCPM4, a highly efficient large language model (LLM) designed explicitly for end-side devices. We achieve this efficiency through systematic innovation in four key dimensions: model architecture, training data, training algorithms, and inference systems. Specifically, in terms of model architecture, we propose InfLLM v2, a trainable sparse attention mechanism that accelerates both prefilling and decoding phases for long-context processing. Regarding training data, we propose UltraClean, an efficient and accurate pre-training data filtering and generation strategy, and UltraChat v2, a comprehensive supervised fine-tuning dataset. These datasets enable satisfactory model performance to be achieved using just 8 trillion training tokens. Regarding training algorithms, we propose ModelTunnel v2 for efficient pre-training strategy search, and improve existing post-training methods by introducing chunk-wise rollout for load-balanced reinforcement learning and data-efficient tenary LLM, BitCPM. Regarding inference systems, we propose CPM.cu that integrates sparse attention, model quantization, and speculative sampling to achieve efficient prefilling and decoding. To meet diverse on-device requirements, MiniCPM4 is available in two versions, with 0.5B and 8B parameters, respectively. Sufficient evaluation results show that MiniCPM4 outperforms open-source models of similar size across multiple benchmarks, highlighting both its efficiency and effectiveness. Notably, MiniCPM4-8B demonstrates significant speed improvements over Qwen3-8B when processing long sequences. Through further adaptation, MiniCPM4 successfully powers diverse applications, including trustworthy survey generation and tool use with model context protocol, clearly showcasing its broad usability.
FR-Spec: Accelerating Large-Vocabulary Language Models via Frequency-Ranked Speculative Sampling
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Speculative sampling has emerged as an important technique for accelerating the auto-regressive generation process of large language models (LLMs) by utilizing a draft-then-verify mechanism to produce multiple tokens per forward pass. While state-of-the-art speculative sampling methods use only a single layer and a language modeling (LM) head as the draft model to achieve impressive layer compression, their efficiency gains are substantially reduced for large-vocabulary LLMs, such as Llama-3-8B with a vocabulary of 128k tokens. To address this, we present FR-Spec, a frequency-ranked speculative sampling framework that optimizes draft candidate selection through vocabulary space compression. By constraining the draft search to a frequency-prioritized token subset, our method reduces LM Head computation overhead by 75% while ensuring the equivalence of the final output distribution. Experiments across multiple datasets demonstrate an average of 1.12$\times$ speedup over the state-of-the-art speculative sampling method EAGLE-2.
NavigateDiff: Visual Predictors are Zero-Shot Navigation Assistants
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Navigating unfamiliar environments presents significant challenges for household robots, requiring the ability to recognize and reason about novel decoration and layout. Existing reinforcement learning methods cannot be directly transferred to new environments, as they typically rely on extensive mapping and exploration, leading to time-consuming and inefficient. To address these challenges, we try to transfer the logical knowledge and the generalization ability of pre-trained foundation models to zero-shot navigation. By integrating a large vision-language model with a diffusion network, our approach named \mname ~constructs a visual predictor that continuously predicts the agent's potential observations in the next step which can assist robots generate robust actions. Furthermore, to adapt the temporal property of navigation, we introduce temporal historical information to ensure that the predicted image is aligned with the navigation scene. We then carefully designed an information fusion framework that embeds the predicted future frames as guidance into goal-reaching policy to solve downstream image navigation tasks. This approach enhances navigation control and generalization across both simulated and real-world environments. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate the robustness and versatility of our method, showcasing its potential to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of robotic navigation in diverse settings.
CHAIR-Classifier of Hallucination as Improver
Jan 05, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents a supervised method for detecting hallucinations in large language models. By analyzing token scores (logitis) across layers of the LLaMA model, we derive a small set, aiming to reduce overfitting, of features-including maximum, minimum, mean, standard deviation, and slope. We use logistic regression for classification and validate the model on the TruthfulQA and MMLU datasets. The results demonstrate significant performance gains, especially in zero-shot scenarios, highlighting the effectiveness and potential for generalization.
SDI-Net: Toward Sufficient Dual-View Interaction for Low-light Stereo Image Enhancement
Aug 20, 2024



Abstract:Currently, most low-light image enhancement methods only consider information from a single view, neglecting the correlation between cross-view information. Therefore, the enhancement results produced by these methods are often unsatisfactory. In this context, there have been efforts to develop methods specifically for low-light stereo image enhancement. These methods take into account the cross-view disparities and enable interaction between the left and right views, leading to improved performance. However, these methods still do not fully exploit the interaction between left and right view information. To address this issue, we propose a model called Toward Sufficient Dual-View Interaction for Low-light Stereo Image Enhancement (SDI-Net). The backbone structure of SDI-Net is two encoder-decoder pairs, which are used to learn the mapping function from low-light images to normal-light images. Among the encoders and the decoders, we design a module named Cross-View Sufficient Interaction Module (CSIM), aiming to fully exploit the correlations between the binocular views via the attention mechanism. The quantitative and visual results on public datasets validate the superiority of our method over other related methods. Ablation studies also demonstrate the effectiveness of the key elements in our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge