Richang Hong
Controllable Value Alignment in Large Language Models through Neuron-Level Editing
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:Aligning large language models (LLMs) with human values has become increasingly important as their influence on human behavior and decision-making expands. However, existing steering-based alignment methods suffer from limited controllability: steering a target value often unintentionally activates other, non-target values. To characterize this limitation, we introduce value leakage, a diagnostic notion that captures the unintended activation of non-target values during value steering, along with a normalized leakage metric grounded in Schwartz's value theory. In light of this analysis, we propose NeVA, a neuron-level editing framework for controllable value alignment in LLMs. NeVA identifies sparse, value-relevant neurons and performs inference-time activation editing, enabling fine-grained control without parameter updates or retraining. Experiments show that NeVA achieves stronger target value alignment while incurring smaller performance degradation on general capability. Moreover, NeVA significantly reduces the average leakage, with residual effects largely confined to semantically related value classes. Overall, NeVA offers a more controllable and interpretable mechanism for value alignment.
Revisiting Robustness for LLM Safety Alignment via Selective Geometry Control
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:Safety alignment of large language models remains brittle under domain shift and noisy preference supervision. Most existing robust alignment methods focus on uncertainty in alignment data, while overlooking optimization-induced fragility in preference-based objectives. In this work, we revisit robustness for LLM safety alignment from an optimization geometry perspective, and argue that robustness failures cannot be addressed by data-centric methods alone. We propose ShaPO, a geometry-aware preference optimization framework that enforces worst-case alignment objectives via selective geometry control over alignment-critical parameter subspace. By avoiding uniform geometry constraints, ShaPO mitigates the over-regularization that can harm robustness under distribution shift. We instantiate ShaPO at two levels: token-level ShaPO stabilizes likelihood-based surrogate optimization, while reward-level ShaPO enforces reward-consistent optimization under noisy supervision. Across diverse safety benchmarks and noisy preference settings, ShaPO consistently improves safety robustness over popular preference optimization methods. Moreover, ShaPO composes cleanly with data-robust objectives, yielding additional gains and empirically supporting the proposed optimization-geometry perspective.
Selective Mixup for Debiasing Question Selection in Computerized Adaptive Testing
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Computerized Adaptive Testing (CAT) is a widely used technology for evaluating learners' proficiency in online education platforms. By leveraging prior estimates of proficiency to select questions and updating the estimates iteratively based on responses, CAT enables personalized learner modeling and has attracted substantial attention. Despite this progress, most existing works focus primarily on improving diagnostic accuracy, while overlooking the selection bias inherent in the adaptive process. Selection Bias arises because the question selection is strongly influenced by the estimated proficiency, such as assigning easier questions to learners with lower proficiency and harder ones to learners with higher proficiency. Since the selection depends on prior estimation, this bias propagates into the diagnosis model, which is further amplified during iterative updates, leading to misalignment and biased predictions. Moreover, the imbalanced nature of learners' historical interactions often exacerbates the bias in diagnosis models. To address this issue, we propose a debiasing framework consisting of two key modules: Cross-Attribute Examinee Retrieval and Selective Mixup-based Regularization. First, we retrieve balanced examinees with relatively even distributions of correct and incorrect responses and use them as neutral references for biased examinees. Then, mixup is applied between each biased examinee and its matched balanced counterpart under label consistency. This augmentation enriches the diversity of bias-conflicting samples and smooths selection boundaries. Finally, extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets with multiple advanced diagnosis models demonstrate that our method substantially improves both the generalization ability and fairness of question selection in CAT.
Bridging the Gap Between Bayesian Deep Learning and Ensemble Weather Forecasts
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Weather forecasting is fundamentally challenged by the chaotic nature of the atmosphere, necessitating probabilistic approaches to quantify uncertainty. While traditional ensemble prediction (EPS) addresses this through computationally intensive simulations, recent advances in Bayesian Deep Learning (BDL) offer a promising but often disconnected alternative. We bridge these paradigms through a unified hybrid Bayesian Deep Learning framework for ensemble weather forecasting that explicitly decomposes predictive uncertainty into epistemic and aleatoric components, learned via variational inference and a physics-informed stochastic perturbation scheme modeling flow-dependent atmospheric dynamics, respectively. We further establish a unified theoretical framework that rigorously connects BDL and EPS, providing formal theorems that decompose total predictive uncertainty into epistemic and aleatoric components under the hybrid BDL framework. We validate our framework on the large-scale 40-year ERA5 reanalysis dataset (1979-2019) with 0.25° spatial resolution. Experimental results show that our method not only improves forecast accuracy and yields better-calibrated uncertainty quantification but also achieves superior computational efficiency compared to state-of-the-art probabilistic diffusion models. We commit to making our code open-source upon acceptance of this paper.
MGCA-Net: Multi-Grained Category-Aware Network for Open-Vocabulary Temporal Action Localization
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Open-Vocabulary Temporal Action Localization (OV-TAL) aims to recognize and localize instances of any desired action categories in videos without explicitly curating training data for all categories. Existing methods mostly recognize action categories at a single granularity, which degrades the recognition accuracy of both base and novel action categories. To address these issues, we propose a Multi-Grained Category-Aware Network (MGCA-Net) comprising a localizer, an action presence predictor, a conventional classifier, and a coarse-to-fine classifier. Specifically, the localizer localizes category-agnostic action proposals. For these action proposals, the action presence predictor estimates the probability that they belong to an action instance. At the same time, the conventional classifier predicts the probability of each action proposal over base action categories at the snippet granularity. Novel action categories are recognized by the coarse-to-fine classifier, which first identifies action presence at the video granularity. Finally, it assigns each action proposal to one category from the coarse categories at the proposal granularity. Through coarse-to-fine category awareness for novel actions and the conventional classifier's awareness of base actions, multi-grained category awareness is achieved, effectively enhancing localization performance. Comprehensive evaluations on the THUMOS'14 and ActivityNet-1.3 benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance. Furthermore, our MGCA-Net achieves state-of-the-art results under the Zero-Shot Temporal Action Localization setting.
Debate over Mixed-knowledge: A Robust Multi-Agent Framework for Incomplete Knowledge Graph Question Answering
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Knowledge Graph Question Answering (KGQA) aims to improve factual accuracy by leveraging structured knowledge. However, real-world Knowledge Graphs (KGs) are often incomplete, leading to the problem of Incomplete KGQA (IKGQA). A common solution is to incorporate external data to fill knowledge gaps, but existing methods lack the capacity to adaptively and contextually fuse multiple sources, failing to fully exploit their complementary strengths. To this end, we propose Debate over Mixed-knowledge (DoM), a novel framework that enables dynamic integration of structured and unstructured knowledge for IKGQA. Built upon the Multi-Agent Debate paradigm, DoM assigns specialized agents to perform inference over knowledge graphs and external texts separately, and coordinates their outputs through iterative interaction. It decomposes the input question into sub-questions, retrieves evidence via dual agents (KG and Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG), and employs a judge agent to evaluate and aggregate intermediate answers. This collaboration exploits knowledge complementarity and enhances robustness to KG incompleteness. In addition, existing IKGQA datasets simulate incompleteness by randomly removing triples, failing to capture the irregular and unpredictable nature of real-world knowledge incompleteness. To address this, we introduce a new dataset, Incomplete Knowledge Graph WebQuestions, constructed by leveraging real-world knowledge updates. These updates reflect knowledge beyond the static scope of KGs, yielding a more realistic and challenging benchmark. Through extensive experiments, we show that DoM consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines.
Mamba-driven multi-perspective structural understanding for molecular ground-state conformation prediction
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:A comprehensive understanding of molecular structures is important for the prediction of molecular ground-state conformation involving property information. Meanwhile, state space model (e.g., Mamba) has recently emerged as a promising mechanism for long sequence modeling and has achieved remarkable results in various language and vision tasks. However, towards molecular ground-state conformation prediction, exploiting Mamba to understand molecular structure is underexplored. To this end, we strive to design a generic and efficient framework with Mamba to capture critical components. In general, molecular structure could be considered to consist of three elements, i.e., atom types, atom positions, and connections between atoms. Thus, considering the three elements, an approach of Mamba-driven multi-perspective structural understanding (MPSU-Mamba) is proposed to localize molecular ground-state conformation. Particularly, for complex and diverse molecules, three different kinds of dedicated scanning strategies are explored to construct a comprehensive perception of corresponding molecular structures. And a bright-channel guided mechanism is defined to discriminate the critical conformation-related atom information. Experimental results on QM9 and Molecule3D datasets indicate that MPSU-Mamba significantly outperforms existing methods. Furthermore, we observe that for the case of few training samples, MPSU-Mamba still achieves superior performance, demonstrating that our method is indeed beneficial for understanding molecular structures.
A Survey on Generative Recommendation: Data, Model, and Tasks
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Recommender systems serve as foundational infrastructure in modern information ecosystems, helping users navigate digital content and discover items aligned with their preferences. At their core, recommender systems address a fundamental problem: matching users with items. Over the past decades, the field has experienced successive paradigm shifts, from collaborative filtering and matrix factorization in the machine learning era to neural architectures in the deep learning era. Recently, the emergence of generative models, especially large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models, have sparked a new paradigm: generative recommendation, which reconceptualizes recommendation as a generation task rather than discriminative scoring. This survey provides a comprehensive examination through a unified tripartite framework spanning data, model, and task dimensions. Rather than simply categorizing works, we systematically decompose approaches into operational stages-data augmentation and unification, model alignment and training, task formulation and execution. At the data level, generative models enable knowledge-infused augmentation and agent-based simulation while unifying heterogeneous signals. At the model level, we taxonomize LLM-based methods, large recommendation models, and diffusion approaches, analyzing their alignment mechanisms and innovations. At the task level, we illuminate new capabilities including conversational interaction, explainable reasoning, and personalized content generation. We identify five key advantages: world knowledge integration, natural language understanding, reasoning capabilities, scaling laws, and creative generation. We critically examine challenges in benchmark design, model robustness, and deployment efficiency, while charting a roadmap toward intelligent recommendation assistants that fundamentally reshape human-information interaction.
Disentangling Foreground and Background for vision-Language Navigation via Online Augmentation
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Following language instructions, vision-language navigation (VLN) agents are tasked with navigating unseen environments. While augmenting multifaceted visual representations has propelled advancements in VLN, the significance of foreground and background in visual observations remains underexplored. Intuitively, foreground regions provide semantic cues, whereas the background encompasses spatial connectivity information. Inspired on this insight, we propose a Consensus-driven Online Feature Augmentation strategy (COFA) with alternative foreground and background features to facilitate the navigable generalization. Specifically, we first leverage semantically-enhanced landmark identification to disentangle foreground and background as candidate augmented features. Subsequently, a consensus-driven online augmentation strategy encourages the agent to consolidate two-stage voting results on feature preferences according to diverse instructions and navigational locations. Experiments on REVERIE and R2R demonstrate that our online foreground-background augmentation boosts the generalization of baseline and attains state-of-the-art performance.
Generalizable Engagement Estimation in Conversation via Domain Prompting and Parallel Attention
Aug 20, 2025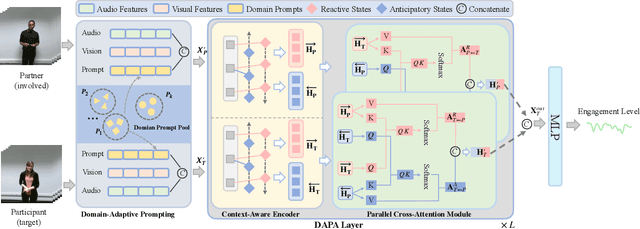
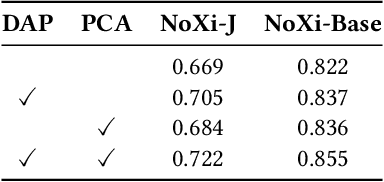
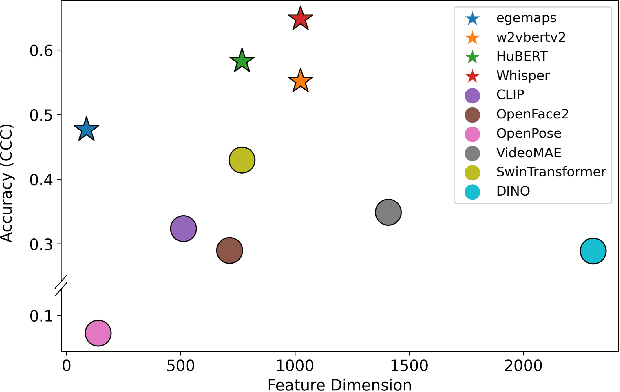
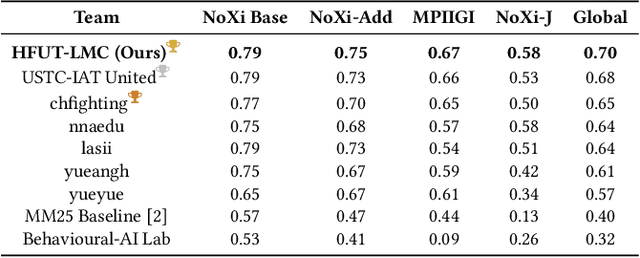
Abstract:Accurate engagement estimation is essential for adaptive human-computer interaction systems, yet robust deployment is hindered by poor generalizability across diverse domains and challenges in modeling complex interaction dynamics.To tackle these issues, we propose DAPA (Domain-Adaptive Parallel Attention), a novel framework for generalizable conversational engagement modeling. DAPA introduces a Domain Prompting mechanism by prepending learnable domain-specific vectors to the input, explicitly conditioning the model on the data's origin to facilitate domain-aware adaptation while preserving generalizable engagement representations. To capture interactional synchrony, the framework also incorporates a Parallel Cross-Attention module that explicitly aligns reactive (forward BiLSTM) and anticipatory (backward BiLSTM) states between participants.Extensive experiments demonstrate that DAPA establishes a new state-of-the-art performance on several cross-cultural and cross-linguistic benchmarks, notably achieving an absolute improvement of 0.45 in Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC) over a strong baseline on the NoXi-J test set. The superiority of our method was also confirmed by winning the first place in the Multi-Domain Engagement Estimation Challenge at MultiMediate'25.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge