Miaomiao Cai
RMBRec: Robust Multi-Behavior Recommendation towards Target Behaviors
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Multi-behavior recommendation faces a critical challenge in practice: auxiliary behaviors (e.g., clicks, carts) are often noisy, weakly correlated, or semantically misaligned with the target behavior (e.g., purchase), which leads to biased preference learning and suboptimal performance. While existing methods attempt to fuse these heterogeneous signals, they inherently lack a principled mechanism to ensure robustness against such behavioral inconsistency. In this work, we propose Robust Multi-Behavior Recommendation towards Target Behaviors (RMBRec), a robust multi-behavior recommendation framework grounded in an information-theoretic robustness principle. We interpret robustness as a joint process of maximizing predictive information while minimizing its variance across heterogeneous behavioral environments. Under this perspective, the Representation Robustness Module (RRM) enhances local semantic consistency by maximizing the mutual information between users' auxiliary and target representations, whereas the Optimization Robustness Module (ORM) enforces global stability by minimizing the variance of predictive risks across behaviors, which is an efficient approximation to invariant risk minimization. This local-global collaboration bridges representation purification and optimization invariance in a theoretically coherent way. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that RMBRec not only outperforms state-of-the-art methods in accuracy but also maintains remarkable stability under various noise perturbations. For reproducibility, our code is available at https://github.com/miaomiao-cai2/RMBRec/.
Mitigating Recommendation Biases via Group-Alignment and Global-Uniformity in Representation Learning
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Collaborative Filtering~(CF) plays a crucial role in modern recommender systems, leveraging historical user-item interactions to provide personalized suggestions. However, CF-based methods often encounter biases due to imbalances in training data. This phenomenon makes CF-based methods tend to prioritize recommending popular items and performing unsatisfactorily on inactive users. Existing works address this issue by rebalancing training samples, reranking recommendation results, or making the modeling process robust to the bias. Despite their effectiveness, these approaches can compromise accuracy or be sensitive to weighting strategies, making them challenging to train. In this paper, we deeply analyze the causes and effects of the biases and propose a framework to alleviate biases in recommendation from the perspective of representation distribution, namely Group-Alignment and Global-Uniformity Enhanced Representation Learning for Debiasing Recommendation (AURL). Specifically, we identify two significant problems in the representation distribution of users and items, namely group-discrepancy and global-collapse. These two problems directly lead to biases in the recommendation results. To this end, we propose two simple but effective regularizers in the representation space, respectively named group-alignment and global-uniformity. The goal of group-alignment is to bring the representation distribution of long-tail entities closer to that of popular entities, while global-uniformity aims to preserve the information of entities as much as possible by evenly distributing representations. Our method directly optimizes both the group-alignment and global-uniformity regularization terms to mitigate recommendation biases. Extensive experiments on three real datasets and various recommendation backbones verify the superiority of our proposed framework.
I$^3$-MRec: Invariant Learning with Information Bottleneck for Incomplete Modality Recommendation
Aug 06, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal recommender systems (MRS) improve recommendation performance by integrating diverse semantic information from multiple modalities. However, the assumption of the availability of all modalities rarely holds in practice due to missing images, incomplete descriptions, or inconsistent user content. These challenges significantly degrade the robustness and generalization capabilities of current models. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel method called \textbf{I$^3$-MRec}, which uses \textbf{I}nvariant learning with \textbf{I}nformation bottleneck principle for \textbf{I}ncomplete \textbf{M}odality \textbf{Rec}ommendation. To achieve robust performance in missing modality scenarios, I$^3$-MRec enforces two pivotal properties: (i) cross-modal preference invariance, which ensures consistent user preference modeling across varying modality environments, and (ii) compact yet effective modality representation, which filters out task-irrelevant modality information while maximally preserving essential features relevant to recommendation. By treating each modality as a distinct semantic environment, I$^3$-MRec employs invariant risk minimization (IRM) to learn modality-specific item representations. In parallel, a missing-aware fusion module grounded in the Information Bottleneck (IB) principle extracts compact and effective item embeddings by suppressing modality noise and preserving core user preference signals. Extensive experiments conducted on three real-world datasets demonstrate that I$^3$-MRec consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art MRS methods across various modality-missing scenarios, highlighting its effectiveness and robustness in practical applications. The code and processed datasets are released at https://github.com/HuilinChenJN/I3-MRec.
* ACM Multimedia 2025 Accepted
DSPO: Direct Semantic Preference Optimization for Real-World Image Super-Resolution
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models have improved Real-World Image Super-Resolution (Real-ISR), but existing methods lack human feedback integration, risking misalignment with human preference and may leading to artifacts, hallucinations and harmful content generation. To this end, we are the first to introduce human preference alignment into Real-ISR, a technique that has been successfully applied in Large Language Models and Text-to-Image tasks to effectively enhance the alignment of generated outputs with human preferences. Specifically, we introduce Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) into Real-ISR to achieve alignment, where DPO serves as a general alignment technique that directly learns from the human preference dataset. Nevertheless, unlike high-level tasks, the pixel-level reconstruction objectives of Real-ISR are difficult to reconcile with the image-level preferences of DPO, which can lead to the DPO being overly sensitive to local anomalies, leading to reduced generation quality. To resolve this dichotomy, we propose Direct Semantic Preference Optimization (DSPO) to align instance-level human preferences by incorporating semantic guidance, which is through two strategies: (a) semantic instance alignment strategy, implementing instance-level alignment to ensure fine-grained perceptual consistency, and (b) user description feedback strategy, mitigating hallucinations through semantic textual feedback on instance-level images. As a plug-and-play solution, DSPO proves highly effective in both one-step and multi-step SR frameworks.
Graph-Structured Driven Dual Adaptation for Mitigating Popularity Bias
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:Popularity bias challenges recommender systems by causing uneven recommendation performance and amplifying the Matthew effect. Limited user-item interactions confine unpopular items within embedding neighborhoods of few users, leading to representation collapse and reduced model generalization. Existing supervised alignment and reweighting methods mitigate this bias but have key limitations: (1) ignoring inherent variability across Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) layers, causing negative effects in deeper layers; (2) reliance on fixed hyperparameters to balance item popularity, restricting adaptability and increasing complexity. To address these issues, we propose the Graph-Structured Dual Adaptation Framework (GSDA). Our theoretical analysis identifies a crucial limitation of supervised alignment methods caused by over-smoothing in GCNs. As GCN layers deepen, popular and unpopular items increasingly lose distinctiveness, quantified by reduced conditional entropy. This diminished distinctiveness weakens supervised alignment effectiveness in mitigating popularity bias. Motivated by this, GSDA captures structural and distribution characteristics from the adjacency matrix through a dual adaptive strategy. First, a hierarchical adaptive alignment mechanism uses the adjacency matrix's Frobenius norm for layer-specific weight decay, countering conditional entropy reduction effects at deeper layers. Second, a distribution-aware dynamic contrast weighting strategy, guided by a real-time Gini coefficient, removes dependence on fixed hyperparameters, enabling adaptability to diverse data. Experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate GSDA significantly alleviates popularity bias and consistently outperforms state-of-the-art recommendation methods.
Autoregressive Image Generation Guided by Chains of Thought
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:In the field of autoregressive (AR) image generation, models based on the 'next-token prediction' paradigm of LLMs have shown comparable performance to diffusion models by reducing inductive biases. However, directly applying LLMs to complex image generation can struggle with reconstructing the structure and details of the image, impacting the accuracy and stability of generation. Additionally, the 'next-token prediction' paradigm in the AR model does not align with the contextual scanning and logical reasoning processes involved in human visual perception, limiting effective image generation. Chain-of-Thought (CoT), as a key reasoning capability of LLMs, utilizes reasoning prompts to guide the model, improving reasoning performance on complex natural language process (NLP) tasks, enhancing accuracy and stability of generation, and helping the model maintain contextual coherence and logical consistency, similar to human reasoning. Inspired by CoT from the field of NLP, we propose autoregressive Image Generation with Thoughtful Reasoning (IGTR) to enhance autoregressive image generation. IGTR adds reasoning prompts without modifying the model structure or raster generation order. Specifically, we design specialized image-related reasoning prompts for AR image generation to simulate the human reasoning process, which enhances contextual reasoning by allowing the model to first perceive overall distribution information before generating the image, and improve generation stability by increasing the inference steps. Compared to the AR method without prompts, our method shows outstanding performance and achieves an approximate improvement of 20%.
Popularity-Aware Alignment and Contrast for Mitigating Popularity Bias
May 31, 2024



Abstract:Collaborative Filtering (CF) typically suffers from the significant challenge of popularity bias due to the uneven distribution of items in real-world datasets. This bias leads to a significant accuracy gap between popular and unpopular items. It not only hinders accurate user preference understanding but also exacerbates the Matthew effect in recommendation systems. To alleviate popularity bias, existing efforts focus on emphasizing unpopular items or separating the correlation between item representations and their popularity. Despite the effectiveness, existing works still face two persistent challenges: (1) how to extract common supervision signals from popular items to improve the unpopular item representations, and (2) how to alleviate the representation separation caused by popularity bias. In this work, we conduct an empirical analysis of popularity bias and propose Popularity-Aware Alignment and Contrast (PAAC) to address two challenges. Specifically, we use the common supervisory signals modeled in popular item representations and propose a novel popularity-aware supervised alignment module to learn unpopular item representations. Additionally, we suggest re-weighting the contrastive learning loss to mitigate the representation separation from a popularity-centric perspective. Finally, we validate the effectiveness and rationale of PAAC in mitigating popularity bias through extensive experiments on three real-world datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/miaomiao-cai2/KDD2024-PAAC.
TrOMR:Transformer-Based Polyphonic Optical Music Recognition
Aug 18, 2023
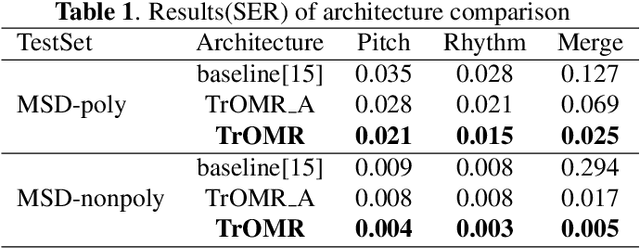
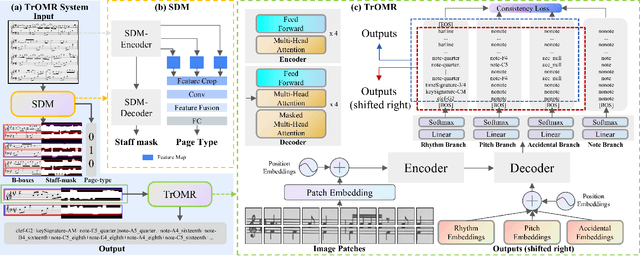
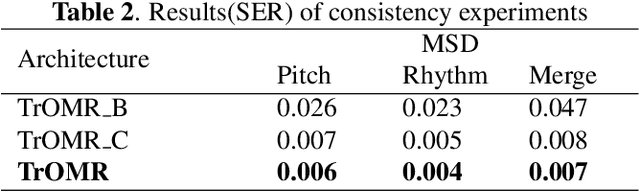
Abstract:Optical Music Recognition (OMR) is an important technology in music and has been researched for a long time. Previous approaches for OMR are usually based on CNN for image understanding and RNN for music symbol classification. In this paper, we propose a transformer-based approach with excellent global perceptual capability for end-to-end polyphonic OMR, called TrOMR. We also introduce a novel consistency loss function and a reasonable approach for data annotation to improve recognition accuracy for complex music scores. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TrOMR outperforms current OMR methods, especially in real-world scenarios. We also develop a TrOMR system and build a camera scene dataset for full-page music scores in real-world. The code and datasets will be made available for reproducibility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge