Guanjie Wang
Allocentric Perceiver: Disentangling Allocentric Reasoning from Egocentric Visual Priors via Frame Instantiation
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:With the rising need for spatially grounded tasks such as Vision-Language Navigation/Action, allocentric perception capabilities in Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are receiving growing focus. However, VLMs remain brittle on allocentric spatial queries that require explicit perspective shifts, where the answer depends on reasoning in a target-centric frame rather than the observed camera view. Thus, we introduce Allocentric Perceiver, a training-free strategy that recovers metric 3D states from one or more images with off-the-shelf geometric experts, and then instantiates a query-conditioned allocentric reference frame aligned with the instruction's semantic intent. By deterministically transforming reconstructed geometry into the target frame and prompting the backbone VLM with structured, geometry-grounded representations, Allocentric Perceriver offloads mental rotation from implicit reasoning to explicit computation. We evaluate Allocentric Perciver across multiple backbone families on spatial reasoning benchmarks, observing consistent and substantial gains ($\sim$10%) on allocentric tasks while maintaining strong egocentric performance, and surpassing both spatial-perception-finetuned models and state-of-the-art open-source and proprietary models.
Axe: A Simple Unified Layout Abstraction for Machine Learning Compilers
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Scaling modern deep learning workloads demands coordinated placement of data and compute across device meshes, memory hierarchies, and heterogeneous accelerators. We present Axe Layout, a hardware-aware abstraction that maps logical tensor coordinates to a multi-axis physical space via named axes. Axe unifies tiling, sharding, replication, and offsets across inter-device distribution and on-device layouts, enabling collective primitives to be expressed consistently from device meshes to threads. Building on Axe, we design a multi-granularity, distribution-aware DSL and compiler that composes thread-local control with collective operators in a single kernel. Experiments show that our unified approach can bring performance close to hand-tuned kernels on across latest GPU devices and multi-device environments and accelerator backends.
XGrammar 2: Dynamic and Efficient Structured Generation Engine for Agentic LLMs
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Modern LLM agents are required to handle increasingly complex structured generation tasks, such as tool calling and conditional structured generation. These tasks are significantly more dynamic than predefined structures, posing new challenges to the current structured generation engines. In this paper, we propose XGrammar 2, a highly optimized structured generation engine for agentic LLMs. XGrammar 2 accelerates the mask generation for these dynamic structured generation tasks through a new dynamic dispatching semantics: TagDispatch. We further introduce a just-in-time (JIT) compilation method to reduce compilation time and a cross-grammar caching mechanism to leverage the common sub-structures across different grammars. Additionally, we extend the previous PDA-based mask generation algorithm to the Earley-parser-based one and design a repetition compression algorithm to handle repetition structures in grammars. Evaluation results show that XGrammar 2 can achieve more than 6x speedup over the existing structured generation engines. Integrated with an LLM inference engine, XGrammar 2 can handle dynamic structured generation tasks with near-zero overhead.
FreeText: Training-Free Text Rendering in Diffusion Transformers via Attention Localization and Spectral Glyph Injection
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Large-scale text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models excel at open-domain synthesis but still struggle with precise text rendering, especially for multi-line layouts, dense typography, and long-tailed scripts such as Chinese. Prior solutions typically require costly retraining or rigid external layout constraints, which can degrade aesthetics and limit flexibility. We propose \textbf{FreeText}, a training-free, plug-and-play framework that improves text rendering by exploiting intrinsic mechanisms of \emph{Diffusion Transformer (DiT)} models. \textbf{FreeText} decomposes the problem into \emph{where to write} and \emph{what to write}. For \emph{where to write}, we localize writing regions by reading token-wise spatial attribution from endogenous image-to-text attention, using sink-like tokens as stable spatial anchors and topology-aware refinement to produce high-confidence masks. For \emph{what to write}, we introduce Spectral-Modulated Glyph Injection (SGMI), which injects a noise-aligned glyph prior with frequency-domain band-pass modulation to strengthen glyph structure and suppress semantic leakage (rendering the concept instead of the word). Extensive experiments on Qwen-Image, FLUX.1-dev, and SD3 variants across longText-Benchmark, CVTG, and our CLT-Bench show consistent gains in text readability while largely preserving semantic alignment and aesthetic quality, with modest inference overhead.
AuthSig: Safeguarding Scanned Signatures Against Unauthorized Reuse in Paperless Workflows
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:With the deepening trend of paperless workflows, signatures as a means of identity authentication are gradually shifting from traditional ink-on-paper to electronic formats.Despite the availability of dynamic pressure-sensitive and PKI-based digital signatures, static scanned signatures remain prevalent in practice due to their convenience. However, these static images, having almost lost their authentication attributes, cannot be reliably verified and are vulnerable to malicious copying and reuse. To address these issues, we propose AuthSig, a novel static electronic signature framework based on generative models and watermark, which binds authentication information to the signature image. Leveraging the human visual system's insensitivity to subtle style variations, AuthSig finely modulates style embeddings during generation to implicitly encode watermark bits-enforcing a One Signature, One Use policy.To overcome the scarcity of handwritten signature data and the limitations of traditional augmentation methods, we introduce a keypoint-driven data augmentation strategy that effectively enhances style diversity to support robust watermark embedding. Experimental results show that AuthSig achieves over 98% extraction accuracy under both digital-domain distortions and signature-specific degradations, and remains effective even in print-scan scenarios.
Autoregressive Image Generation Guided by Chains of Thought
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:In the field of autoregressive (AR) image generation, models based on the 'next-token prediction' paradigm of LLMs have shown comparable performance to diffusion models by reducing inductive biases. However, directly applying LLMs to complex image generation can struggle with reconstructing the structure and details of the image, impacting the accuracy and stability of generation. Additionally, the 'next-token prediction' paradigm in the AR model does not align with the contextual scanning and logical reasoning processes involved in human visual perception, limiting effective image generation. Chain-of-Thought (CoT), as a key reasoning capability of LLMs, utilizes reasoning prompts to guide the model, improving reasoning performance on complex natural language process (NLP) tasks, enhancing accuracy and stability of generation, and helping the model maintain contextual coherence and logical consistency, similar to human reasoning. Inspired by CoT from the field of NLP, we propose autoregressive Image Generation with Thoughtful Reasoning (IGTR) to enhance autoregressive image generation. IGTR adds reasoning prompts without modifying the model structure or raster generation order. Specifically, we design specialized image-related reasoning prompts for AR image generation to simulate the human reasoning process, which enhances contextual reasoning by allowing the model to first perceive overall distribution information before generating the image, and improve generation stability by increasing the inference steps. Compared to the AR method without prompts, our method shows outstanding performance and achieves an approximate improvement of 20%.
HeadText: Exploring Hands-free Text Entry using Head Gestures by Motion Sensing on a Smart Earpiece
May 23, 2022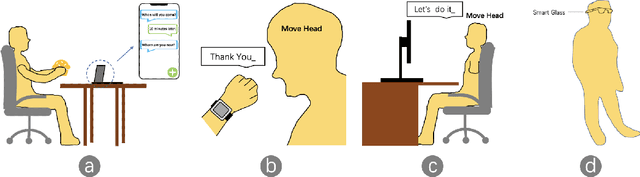
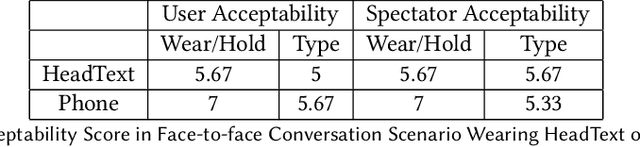
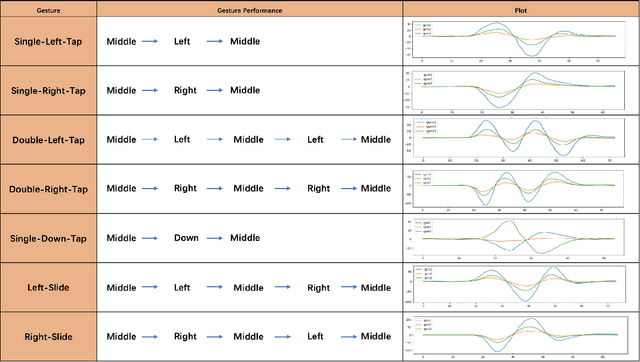
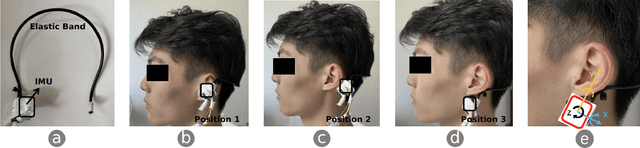
Abstract:We present HeadText, a hands-free technique on a smart earpiece for text entry by motion sensing. Users input text utilizing only 7 head gestures for key selection, word selection, word commitment and word cancelling tasks. Head gesture recognition is supported by motion sensing on a smart earpiece to capture head moving signals and machine learning algorithms (K-Nearest-Neighbor (KNN) with a Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) distance measurement). A 10-participant user study proved that HeadText could recognize 7 head gestures at an accuracy of 94.29%. After that, the second user study presented that HeadText could achieve a maximum accuracy of 10.65 WPM and an average accuracy of 9.84 WPM for text entry. Finally, we demonstrate potential applications of HeadText in hands-free scenarios for (a). text entry of people with motor impairments, (b). private text entry, and (c). socially acceptable text entry.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge