Bohan Hou
Axe: A Simple Unified Layout Abstraction for Machine Learning Compilers
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Scaling modern deep learning workloads demands coordinated placement of data and compute across device meshes, memory hierarchies, and heterogeneous accelerators. We present Axe Layout, a hardware-aware abstraction that maps logical tensor coordinates to a multi-axis physical space via named axes. Axe unifies tiling, sharding, replication, and offsets across inter-device distribution and on-device layouts, enabling collective primitives to be expressed consistently from device meshes to threads. Building on Axe, we design a multi-granularity, distribution-aware DSL and compiler that composes thread-local control with collective operators in a single kernel. Experiments show that our unified approach can bring performance close to hand-tuned kernels on across latest GPU devices and multi-device environments and accelerator backends.
Gecko: An Efficient Neural Architecture Inherently Processing Sequences with Arbitrary Lengths
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Designing a unified neural network to efficiently and inherently process sequential data with arbitrary lengths is a central and challenging problem in sequence modeling. The design choices in Transformer, including quadratic complexity and weak length extrapolation, have limited their ability to scale to long sequences. In this work, we propose Gecko, a neural architecture that inherits the design of Mega and Megalodon (exponential moving average with gated attention), and further introduces multiple technical components to improve its capability to capture long range dependencies, including timestep decay normalization, sliding chunk attention mechanism, and adaptive working memory. In a controlled pretraining comparison with Llama2 and Megalodon in the scale of 7 billion parameters and 2 trillion training tokens, Gecko achieves better efficiency and long-context scalability. Gecko reaches a training loss of 1.68, significantly outperforming Llama2-7B (1.75) and Megalodon-7B (1.70), and landing close to Llama2-13B (1.67). Notably, without relying on any context-extension techniques, Gecko exhibits inherent long-context processing and retrieval capabilities, stably handling sequences of up to 4 million tokens and retrieving information from contexts up to $4\times$ longer than its attention window. Code: https://github.com/XuezheMax/gecko-llm
Mirage Persistent Kernel: A Compiler and Runtime for Mega-Kernelizing Tensor Programs
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:We introduce Mirage Persistent Kernel (MPK), the first compiler and runtime system that automatically transforms multi-GPU model inference into a single high-performance megakernel. MPK introduces an SM-level graph representation that captures data dependencies at the granularity of individual streaming multiprocessors (SMs), enabling cross-operator software pipelining, fine-grained kernel overlap, and other previously infeasible GPU optimizations. The MPK compiler lowers tensor programs into highly optimized SM-level task graphs and generates optimized CUDA implementations for all tasks, while the MPK in-kernel parallel runtime executes these tasks within a single mega-kernel using decentralized scheduling across SMs. Together, these components provide end-to-end kernel fusion with minimal developer effort, while preserving the flexibility of existing programming models. Our evaluation shows that MPK significantly outperforms existing kernel-per-operator LLM serving systems by reducing end-to-end inference latency by up to 1.7x, pushing LLM inference performance close to hardware limits. MPK is publicly available at https://github.com/mirage-project/mirage.
ImgEdit: A Unified Image Editing Dataset and Benchmark
May 26, 2025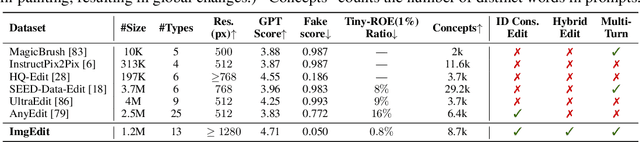
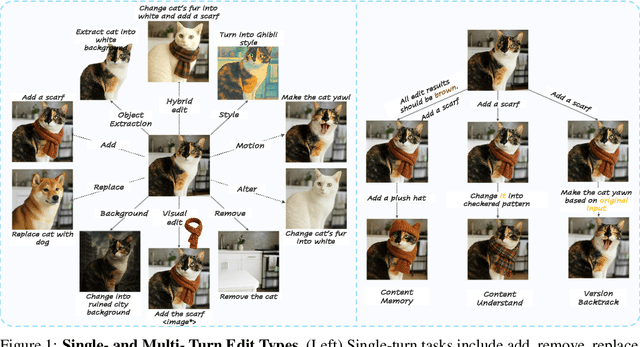
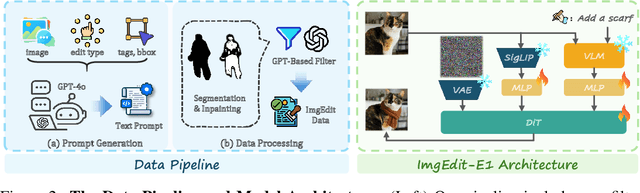

Abstract:Recent advancements in generative models have enabled high-fidelity text-to-image generation. However, open-source image-editing models still lag behind their proprietary counterparts, primarily due to limited high-quality data and insufficient benchmarks. To overcome these limitations, we introduce ImgEdit, a large-scale, high-quality image-editing dataset comprising 1.2 million carefully curated edit pairs, which contain both novel and complex single-turn edits, as well as challenging multi-turn tasks. To ensure the data quality, we employ a multi-stage pipeline that integrates a cutting-edge vision-language model, a detection model, a segmentation model, alongside task-specific in-painting procedures and strict post-processing. ImgEdit surpasses existing datasets in both task novelty and data quality. Using ImgEdit, we train ImgEdit-E1, an editing model using Vision Language Model to process the reference image and editing prompt, which outperforms existing open-source models on multiple tasks, highlighting the value of ImgEdit and model design. For comprehensive evaluation, we introduce ImgEdit-Bench, a benchmark designed to evaluate image editing performance in terms of instruction adherence, editing quality, and detail preservation. It includes a basic testsuite, a challenging single-turn suite, and a dedicated multi-turn suite. We evaluate both open-source and proprietary models, as well as ImgEdit-E1, providing deep analysis and actionable insights into the current behavior of image-editing models. The source data are publicly available on https://github.com/PKU-YuanGroup/ImgEdit.
Tilus: A Virtual Machine for Arbitrary Low-Precision GPGPU Computation in LLM Serving
Apr 25, 2025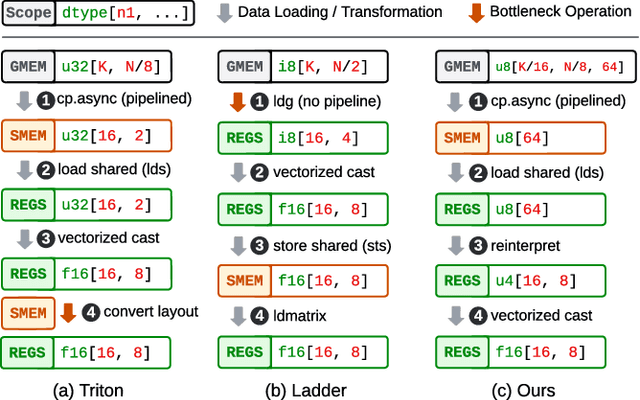
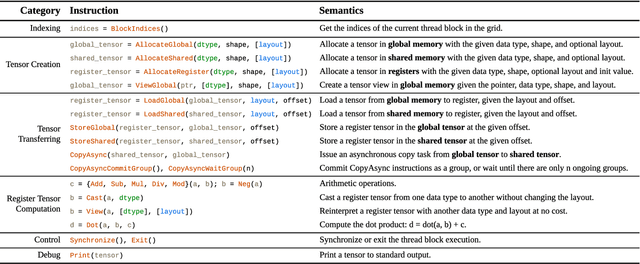
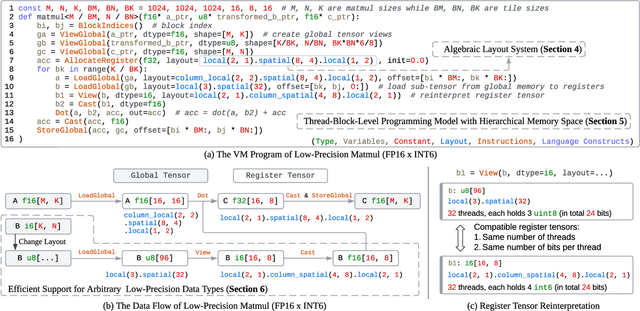
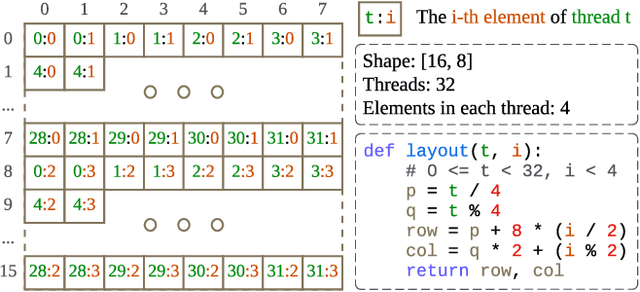
Abstract:Serving Large Language Models (LLMs) is critical for AI-powered applications but demands substantial computational resources, particularly in memory bandwidth and computational throughput. Low-precision computation has emerged as a key technique to improve efficiency while reducing resource consumption. Existing approaches for generating low-precision kernels are limited to weight bit widths that are powers of two and suffer from suboptimal performance due to high-level GPU programming abstractions. These abstractions restrict critical optimizations, such as fine-grained register management and optimized memory access patterns, which are essential for efficient low-precision computations. In this paper, we introduce a virtual machine (VM) designed for General-Purpose GPU (GPGPU) computing, enabling support for low-precision data types with arbitrary bit widths while maintaining GPU programmability. The proposed VM features a thread-block-level programming model, a hierarchical memory space, a novel algebraic layout system, and extensive support for diverse low-precision data types. VM programs are compiled into highly efficient GPU programs with automatic vectorization and instruction selection. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our VM efficiently supports a full spectrum of low-precision data types, and outperforms state-of-the-art low-precision kernels on their supported types. Compared to existing compilers like Triton and Ladder, as well as hand-optimized kernels such as QuantLLM and Marlin, our VM achieves performance improvements of 1.75x, 2.61x, 1.29x and 1.03x, respectively.
A Virtual Machine for Arbitrary Low-Precision GPGPU Computation in LLM Serving
Apr 17, 2025



Abstract:Serving Large Language Models (LLMs) is critical for AI-powered applications but demands substantial computational resources, particularly in memory bandwidth and computational throughput. Low-precision computation has emerged as a key technique to improve efficiency while reducing resource consumption. Existing approaches for generating low-precision kernels are limited to weight bit widths that are powers of two and suffer from suboptimal performance due to high-level GPU programming abstractions. These abstractions restrict critical optimizations, such as fine-grained register management and optimized memory access patterns, which are essential for efficient low-precision computations. In this paper, we introduce a virtual machine (VM) designed for General-Purpose GPU (GPGPU) computing, enabling support for low-precision data types with arbitrary bit widths while maintaining GPU programmability. The proposed VM features a thread-block-level programming model, a hierarchical memory space, a novel algebraic layout system, and extensive support for diverse low-precision data types. VM programs are compiled into highly efficient GPU programs with automatic vectorization and instruction selection. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our VM efficiently supports a full spectrum of low-precision data types, and outperforms state-of-the-art low-precision kernels on their supported types. Compared to existing compilers like Triton and Ladder, as well as hand-optimized kernels such as QuantLLM and Marlin, our VM achieves performance improvements of 1.75x, 2.61x, 1.29x and 1.03x, respectively.
A Comprehensive Survey on Composed Image Retrieval
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) is an emerging yet challenging task that allows users to search for target images using a multimodal query, comprising a reference image and a modification text specifying the user's desired changes to the reference image. Given its significant academic and practical value, CIR has become a rapidly growing area of interest in the computer vision and machine learning communities, particularly with the advances in deep learning. To the best of our knowledge, there is currently no comprehensive review of CIR to provide a timely overview of this field. Therefore, we synthesize insights from over 120 publications in top conferences and journals, including ACM TOIS, SIGIR, and CVPR In particular, we systematically categorize existing supervised CIR and zero-shot CIR models using a fine-grained taxonomy. For a comprehensive review, we also briefly discuss approaches for tasks closely related to CIR, such as attribute-based CIR and dialog-based CIR. Additionally, we summarize benchmark datasets for evaluation and analyze existing supervised and zero-shot CIR methods by comparing experimental results across multiple datasets. Furthermore, we present promising future directions in this field, offering practical insights for researchers interested in further exploration.
WebLLM: A High-Performance In-Browser LLM Inference Engine
Dec 20, 2024

Abstract:Advancements in large language models (LLMs) have unlocked remarkable capabilities. While deploying these models typically requires server-grade GPUs and cloud-based inference, the recent emergence of smaller open-source models and increasingly powerful consumer devices have made on-device deployment practical. The web browser as a platform for on-device deployment is universally accessible, provides a natural agentic environment, and conveniently abstracts out the different backends from diverse device vendors. To address this opportunity, we introduce WebLLM, an open-source JavaScript framework that enables high-performance LLM inference entirely within web browsers. WebLLM provides an OpenAI-style API for seamless integration into web applications, and leverages WebGPU for efficient local GPU acceleration and WebAssembly for performant CPU computation. With machine learning compilers MLC-LLM and Apache TVM, WebLLM leverages optimized WebGPU kernels, overcoming the absence of performant WebGPU kernel libraries. Evaluations show that WebLLM can retain up to 80% native performance on the same device, with room to further close the gap. WebLLM paves the way for universally accessible, privacy-preserving, personalized, and locally powered LLM applications in web browsers. The code is available at: https://github.com/mlc-ai/web-llm.
Pseudo-triplet Guided Few-shot Composed Image Retrieval
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) is a challenging task that aims to retrieve the target image based on a multimodal query, i.e., a reference image and its corresponding modification text. While previous supervised or zero-shot learning paradigms all fail to strike a good trade-off between time-consuming annotation cost and retrieval performance, recent researchers introduced the task of few-shot CIR (FS-CIR) and proposed a textual inversion-based network based on pretrained CLIP model to realize it. Despite its promising performance, the approach suffers from two key limitations: insufficient multimodal query composition training and indiscriminative training triplet selection. To address these two limitations, in this work, we propose a novel two-stage pseudo triplet guided few-shot CIR scheme, dubbed PTG-FSCIR. In the first stage, we employ a masked training strategy and advanced image caption generator to construct pseudo triplets from pure image data to enable the model to acquire primary knowledge related to multimodal query composition. In the second stage, based on active learning, we design a pseudo modification text-based query-target distance metric to evaluate the challenging score for each unlabeled sample. Meanwhile, we propose a robust top range-based random sampling strategy according to the 3-$\sigma$ rule in statistics, to sample the challenging samples for fine-tuning the pretrained model. Notably, our scheme is plug-and-play and compatible with any existing supervised CIR models. We tested our scheme across three backbones on three public datasets (i.e., FashionIQ, CIRR, and Birds-to-Words), achieving maximum improvements of 26.4%, 25.5% and 21.6% respectively, demonstrating our scheme's effectiveness.
Optimal Kernel Orchestration for Tensor Programs with Korch
Jun 13, 2024


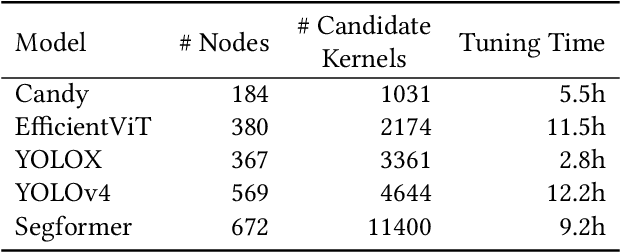
Abstract:Kernel orchestration is the task of mapping the computation defined in different operators of a deep neural network (DNN) to the execution of GPU kernels on modern hardware platforms. Prior approaches optimize kernel orchestration by greedily applying operator fusion, which fuses the computation of multiple operators into a single kernel, and miss a variety of optimization opportunities in kernel orchestration. This paper presents Korch, a tensor program optimizer that discovers optimal kernel orchestration strategies for tensor programs. Instead of directly fusing operators, Korch first applies operator fission to decompose tensor operators into a small set of basic tensor algebra primitives. This decomposition enables a diversity of fine-grained, inter-operator optimizations. Next, Korch optimizes kernel orchestration by formalizing it as a constrained optimization problem, leveraging an off-the-shelf binary linear programming solver to discover an optimal orchestration strategy, and generating an executable that can be directly deployed on modern GPU platforms. Evaluation on a variety of DNNs shows that Korch outperforms existing tensor program optimizers by up to 1.7x on V100 GPUs and up to 1.6x on A100 GPUs. Korch is publicly available at https://github.com/humuyan/Korch.
* Fix some typos in the ASPLOS version
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge