Liqiang Nie
StructAlign: Structured Cross-Modal Alignment for Continual Text-to-Video Retrieval
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Continual Text-to-Video Retrieval (CTVR) is a challenging multimodal continual learning setting, where models must incrementally learn new semantic categories while maintaining accurate text-video alignment for previously learned ones, thus making it particularly prone to catastrophic forgetting. A key challenge in CTVR is feature drift, which manifests in two forms: intra-modal feature drift caused by continual learning within each modality, and non-cooperative feature drift across modalities that leads to modality misalignment. To mitigate these issues, we propose StructAlign, a structured cross-modal alignment method for CTVR. First, StructAlign introduces a simplex Equiangular Tight Frame (ETF) geometry as a unified geometric prior to mitigate modality misalignment. Building upon this geometric prior, we design a cross-modal ETF alignment loss that aligns text and video features with category-level ETF prototypes, encouraging the learned representations to form an approximate simplex ETF geometry. In addition, to suppress intra-modal feature drift, we design a Cross-modal Relation Preserving loss, which leverages complementary modalities to preserve cross-modal similarity relations, providing stable relational supervision for feature updates. By jointly addressing non-cooperative feature drift across modalities and intra-modal feature drift, StructAlign effectively alleviates catastrophic forgetting in CTVR. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art continual retrieval approaches.
AR-Omni: A Unified Autoregressive Model for Any-to-Any Generation
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Real-world perception and interaction are inherently multimodal, encompassing not only language but also vision and speech, which motivates the development of "Omni" MLLMs that support both multimodal inputs and multimodal outputs. While a sequence of omni MLLMs has emerged, most existing systems still rely on additional expert components to achieve multimodal generation, limiting the simplicity of unified training and inference. Autoregressive (AR) modeling, with a single token stream, a single next-token objective, and a single decoder, is an elegant and scalable foundation in the text domain. Motivated by this, we present AR-Omni, a unified any-to-any model in the autoregressive paradigm without any expert decoders. AR-Omni supports autoregressive text and image generation, as well as streaming speech generation, all under a single Transformer decoder. We further address three practical issues in unified AR modeling: modality imbalance via task-aware loss reweighting, visual fidelity via a lightweight token-level perceptual alignment loss for image tokens, and stability-creativity trade-offs via a finite-state decoding mechanism. Empirically, AR-Omni achieves strong quality across three modalities while remaining real-time, achieving a 0.88 real-time factor for speech generation.
Omni-R1: Towards the Unified Generative Paradigm for Multimodal Reasoning
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are making significant progress in multimodal reasoning. Early approaches focus on pure text-based reasoning. More recent studies have incorporated multimodal information into the reasoning steps; however, they often follow a single task-specific reasoning pattern, which limits their generalizability across various multimodal tasks. In fact, there are numerous multimodal tasks requiring diverse reasoning skills, such as zooming in on a specific region or marking an object within an image. To address this, we propose unified generative multimodal reasoning, which unifies diverse multimodal reasoning skills by generating intermediate images during the reasoning process. We instantiate this paradigm with Omni-R1, a two-stage SFT+RL framework featuring perception alignment loss and perception reward, thereby enabling functional image generation. Additionally, we introduce Omni-R1-Zero, which eliminates the need for multimodal annotations by bootstrapping step-wise visualizations from text-only reasoning data. Empirical results show that Omni-R1 achieves unified generative reasoning across a wide range of multimodal tasks, and Omni-R1-Zero can match or even surpass Omni-R1 on average, suggesting a promising direction for generative multimodal reasoning.
PersonalAlign: Hierarchical Implicit Intent Alignment for Personalized GUI Agent with Long-Term User-Centric Records
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:While GUI agents have shown strong performance under explicit and completion instructions, real-world deployment requires aligning with users' more complex implicit intents. In this work, we highlight Hierarchical Implicit Intent Alignment for Personalized GUI Agent (PersonalAlign), a new agent task that requires agents to leverage long-term user records as persistent context to resolve omitted preferences in vague instructions and anticipate latent routines by user state for proactive assistance. To facilitate this study, we introduce AndroidIntent, a benchmark designed to evaluate agents' ability in resolving vague instructions and providing proactive suggestions through reasoning over long-term user records. We annotated 775 user-specific preferences and 215 routines from 20k long-term records across different users for evaluation. Furthermore, we introduce Hierarchical Intent Memory Agent (HIM-Agent), which maintains a continuously updating personal memory and hierarchically organizes user preferences and routines for personalization. Finally, we evaluate a range of GUI agents on AndroidIntent, including GPT-5, Qwen3-VL, and UI-TARS, further results show that HIM-Agent significantly improves both execution and proactive performance by 15.7% and 7.3%.
SemanticVLA: Semantic-Aligned Sparsification and Enhancement for Efficient Robotic Manipulation
Nov 13, 2025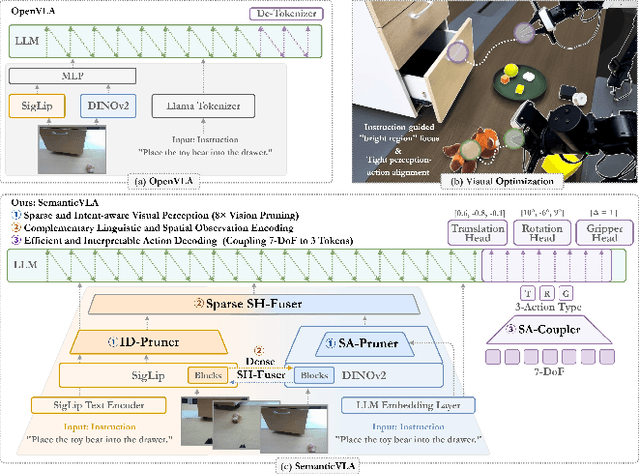
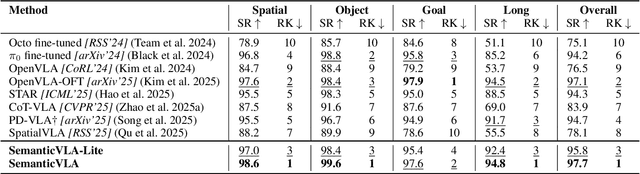
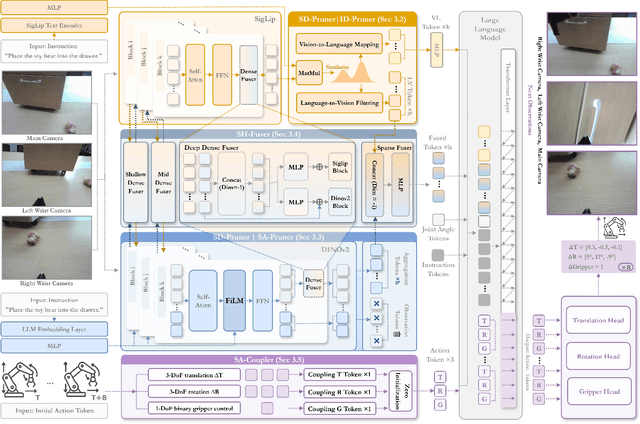
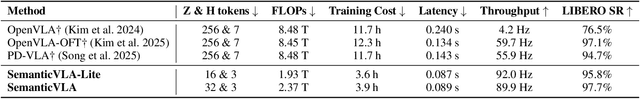
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have advanced in robotic manipulation, yet practical deployment remains hindered by two key limitations: 1) perceptual redundancy, where irrelevant visual inputs are processed inefficiently, and 2) superficial instruction-vision alignment, which hampers semantic grounding of actions. In this paper, we propose SemanticVLA, a novel VLA framework that performs Semantic-Aligned Sparsification and Enhancement for Efficient Robotic Manipulation. Specifically: 1) To sparsify redundant perception while preserving semantic alignment, Semantic-guided Dual Visual Pruner (SD-Pruner) performs: Instruction-driven Pruner (ID-Pruner) extracts global action cues and local semantic anchors in SigLIP; Spatial-aggregation Pruner (SA-Pruner) compacts geometry-rich features into task-adaptive tokens in DINOv2. 2) To exploit sparsified features and integrate semantics with spatial geometry, Semantic-complementary Hierarchical Fuser (SH-Fuser) fuses dense patches and sparse tokens across SigLIP and DINOv2 for coherent representation. 3) To enhance the transformation from perception to action, Semantic-conditioned Action Coupler (SA-Coupler) replaces the conventional observation-to-DoF approach, yielding more efficient and interpretable behavior modeling for manipulation tasks. Extensive experiments on simulation and real-world tasks show that SemanticVLA sets a new SOTA in both performance and efficiency. SemanticVLA surpasses OpenVLA on LIBERO benchmark by 21.1% in success rate, while reducing training cost and inference latency by 3.0-fold and 2.7-fold.SemanticVLA is open-sourced and publicly available at https://github.com/JiuTian-VL/SemanticVLA
A Polynomial-time Algorithm for Online Sparse Linear Regression with Improved Regret Bound under Weaker Conditions
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we study the problem of online sparse linear regression (OSLR) where the algorithms are restricted to accessing only $k$ out of $d$ attributes per instance for prediction, which was proved to be NP-hard. Previous work gave polynomial-time algorithms assuming the data matrix satisfies the linear independence of features, the compatibility condition, or the restricted isometry property. We introduce a new polynomial-time algorithm, which significantly improves previous regret bounds (Ito et al., 2017) under the compatibility condition that is weaker than the other two assumptions. The improvements benefit from a tighter convergence rate of the $\ell_1$-norm error of our estimators. Our algorithm leverages the well-studied Dantzig Selector, but importantly with several novel techniques, including an algorithm-dependent sampling scheme for estimating the covariance matrix, an adaptive parameter tuning scheme, and a batching online Newton step with careful initializations. We also give novel and non-trivial analyses, including an induction method for analyzing the $\ell_1$-norm error, careful analyses on the covariance of non-independent random variables, and a decomposition on the regret. We further extend our algorithm to OSLR with additional observations where the algorithms can observe additional $k_0$ attributes after each prediction, and improve previous regret bounds (Kale et al., 2017; Ito et al., 2017).
Open Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Factual Image Generation
Oct 26, 2025



Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have achieved remarkable progress in generating photorealistic and prompt-aligned images, but they often produce outputs that contradict verifiable knowledge, especially when prompts involve fine-grained attributes or time-sensitive events. Conventional retrieval-augmented approaches attempt to address this issue by introducing external information, yet they are fundamentally incapable of grounding generation in accurate and evolving knowledge due to their reliance on static sources and shallow evidence integration. To bridge this gap, we introduce ORIG, an agentic open multimodal retrieval-augmented framework for Factual Image Generation (FIG), a new task that requires both visual realism and factual grounding. ORIG iteratively retrieves and filters multimodal evidence from the web and incrementally integrates the refined knowledge into enriched prompts to guide generation. To support systematic evaluation, we build FIG-Eval, a benchmark spanning ten categories across perceptual, compositional, and temporal dimensions. Experiments demonstrate that ORIG substantially improves factual consistency and overall image quality over strong baselines, highlighting the potential of open multimodal retrieval for factual image generation.
Reasoning in the Dark: Interleaved Vision-Text Reasoning in Latent Space
Oct 14, 2025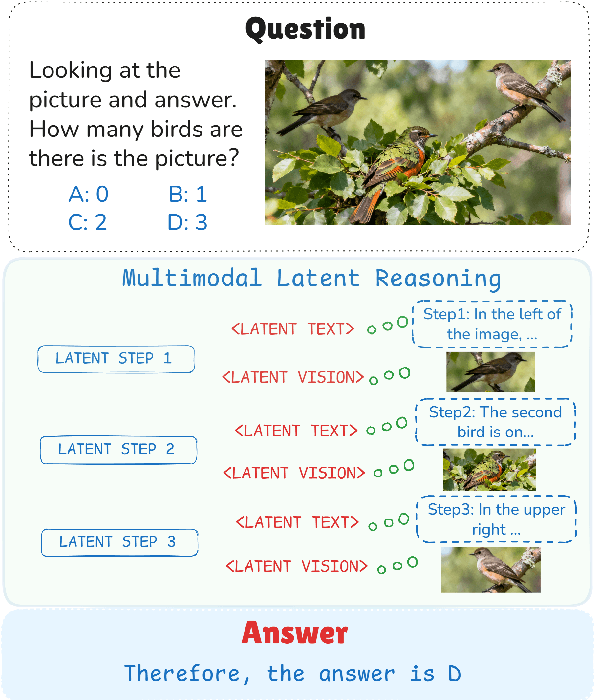
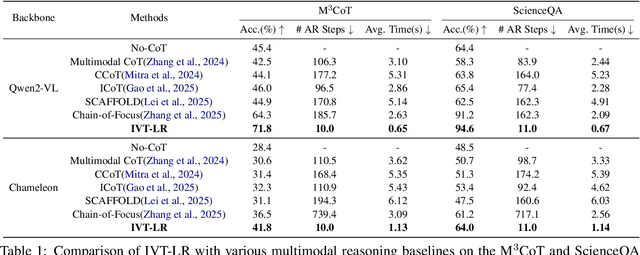
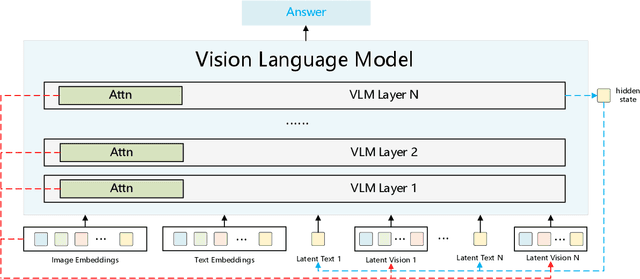
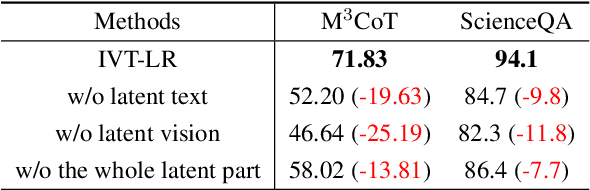
Abstract:Multimodal reasoning aims to enhance the capabilities of MLLMs by incorporating intermediate reasoning steps before reaching the final answer. It has evolved from text-only reasoning to the integration of visual information, enabling the thought process to be conveyed through both images and text. Despite its effectiveness, current multimodal reasoning methods depend on explicit reasoning steps that require labor-intensive vision-text annotations and inherently introduce significant inference latency. To address these issues, we introduce multimodal latent reasoning with the advantages of multimodal representation, reduced annotation, and inference efficiency. To facilicate it, we propose Interleaved Vision-Text Latent Reasoning (IVT-LR), which injects both visual and textual information in the reasoning process within the latent space. Specifically, IVT-LR represents each reasoning step by combining two implicit parts: latent text (the hidden states from the previous step) and latent vision (a set of selected image embeddings). We further introduce a progressive multi-stage training strategy to enable MLLMs to perform the above multimodal latent reasoning steps. Experiments on M3CoT and ScienceQA demonstrate that our IVT-LR method achieves an average performance increase of 5.45% in accuracy, while simultaneously achieving a speed increase of over 5 times compared to existing approaches. Code available at https://github.com/FYYDCC/IVT-LR.
Parallel Test-Time Scaling for Latent Reasoning Models
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Parallel test-time scaling (TTS) is a pivotal approach for enhancing large language models (LLMs), typically by sampling multiple token-based chains-of-thought in parallel and aggregating outcomes through voting or search. Recent advances in latent reasoning, where intermediate reasoning unfolds in continuous vector spaces, offer a more efficient alternative to explicit Chain-of-Thought, yet whether such latent models can similarly benefit from parallel TTS remains open, mainly due to the absence of sampling mechanisms in continuous space, and the lack of probabilistic signals for advanced trajectory aggregation. \ This work enables parallel TTS for latent reasoning models by addressing the above issues. For sampling, we introduce two uncertainty-inspired stochastic strategies: Monte Carlo Dropout and Additive Gaussian Noise. For aggregation, we design a Latent Reward Model (LatentRM) trained with step-wise contrastive objective to score and guide latent reasoning. Extensive experiments and visualization analyses show that both sampling strategies scale effectively with compute and exhibit distinct exploration dynamics, while LatentRM enables effective trajectory selection. Together, our explorations open a new direction for scalable inference in continuous spaces. Code released at https://github.com/YRYangang/LatentTTS.
IntentionVLA: Generalizable and Efficient Embodied Intention Reasoning for Human-Robot Interaction
Oct 09, 2025



Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models leverage pretrained vision-language models (VLMs) to couple perception with robotic control, offering a promising path toward general-purpose embodied intelligence. However, current SOTA VLAs are primarily pretrained on multimodal tasks with limited relevance to embodied scenarios, and then finetuned to map explicit instructions to actions. Consequently, due to the lack of reasoning-intensive pretraining and reasoning-guided manipulation, these models are unable to perform implicit human intention reasoning required for complex, real-world interactions. To overcome these limitations, we propose \textbf{IntentionVLA}, a VLA framework with a curriculum training paradigm and an efficient inference mechanism. Our proposed method first leverages carefully designed reasoning data that combine intention inference, spatial grounding, and compact embodied reasoning, endowing the model with both reasoning and perception capabilities. In the following finetuning stage, IntentionVLA employs the compact reasoning outputs as contextual guidance for action generation, enabling fast inference under indirect instructions. Experimental results show that IntentionVLA substantially outperforms $\pi_0$, achieving 18\% higher success rates with direct instructions and 28\% higher than ECoT under intention instructions. On out-of-distribution intention tasks, IntentionVLA achieves over twice the success rate of all baselines, and further enables zero-shot human-robot interaction with 40\% success rate. These results highlight IntentionVLA as a promising paradigm for next-generation human-robot interaction (HRI) systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge