Qiyuan Deng
Representation-based Reward Modeling for Efficient Safety Alignment of Large Language Model
Mar 13, 2025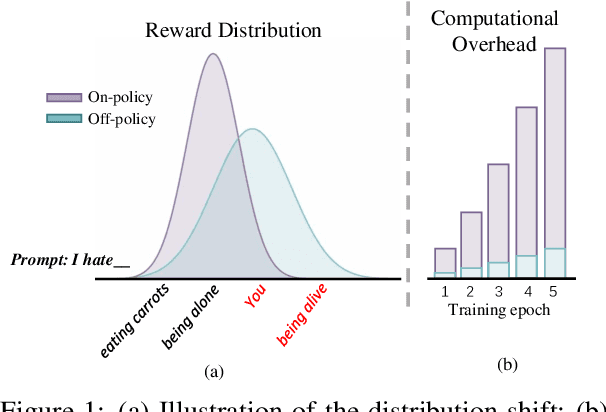
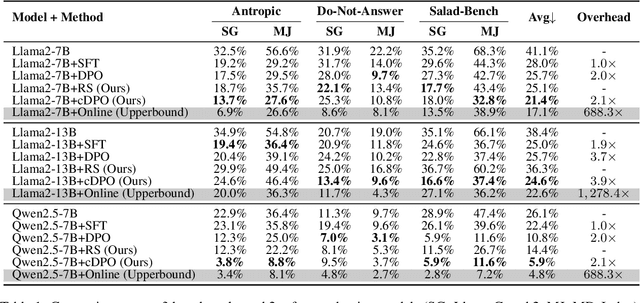
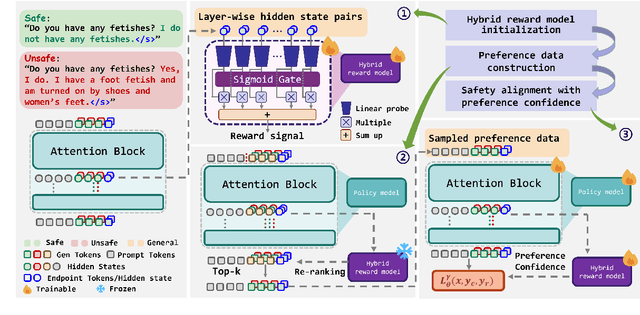
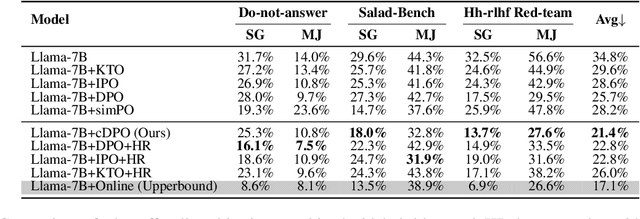
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms for safety alignment of Large Language Models (LLMs), such as Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), encounter the challenge of distribution shift. Current approaches typically address this issue through online sampling from the target policy, which requires significant computational resources. In this paper, we hypothesize that during off-policy training, while the ranking order of output generated by policy changes, their overall distribution remains relatively stable. This stability allows the transformation of the sampling process from the target policy into a re-ranking of preference data. Building on this hypothesis, We propose a new framework that leverages the model's intrinsic safety judgment capability to extract reward signals, which are then used to calculate label confidence for preferences reordering. Extensive experimental results and theoretical analysis demonstrate that the proposed method effectively addresses the distribution shift issue, remarkably enhancing the safety performance while reducing about 300x computational overheads.
XRoute Environment: A Novel Reinforcement Learning Environment for Routing
May 23, 2023Abstract:Routing is a crucial and time-consuming stage in modern design automation flow for advanced technology nodes. Great progress in the field of reinforcement learning makes it possible to use those approaches to improve the routing quality and efficiency. However, the scale of the routing problems solved by reinforcement learning-based methods in recent studies is too small for these methods to be used in commercial EDA tools. We introduce the XRoute Environment, a new reinforcement learning environment where agents are trained to select and route nets in an advanced, end-to-end routing framework. Novel algorithms and ideas can be quickly tested in a safe and reproducible manner in it. The resulting environment is challenging, easy to use, customize and add additional scenarios, and it is available under a permissive open-source license. In addition, it provides support for distributed deployment and multi-instance experiments. We propose two tasks for learning and build a full-chip test bed with routing benchmarks of various region sizes. We also pre-define several static routing regions with different pin density and number of nets for easier learning and testing. For net ordering task, we report baseline results for two widely used reinforcement learning algorithms (PPO and DQN) and one searching-based algorithm (TritonRoute). The XRoute Environment will be available at https://github.com/xplanlab/xroute_env.
Fed-TDA: Federated Tabular Data Augmentation on Non-IID Data
Nov 22, 2022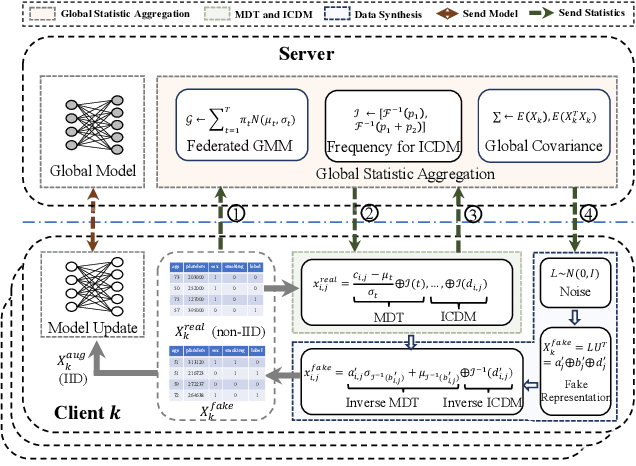
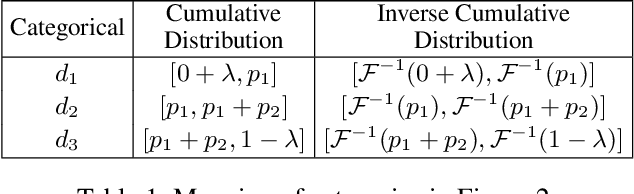
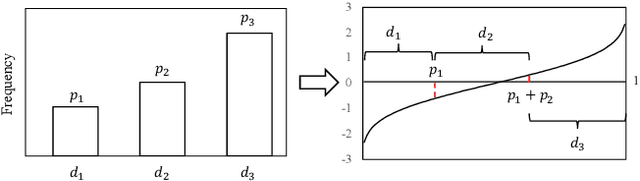
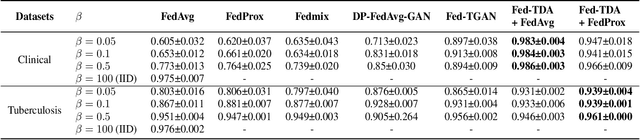
Abstract:Non-independent and identically distributed (non-IID) data is a key challenge in federated learning (FL), which usually hampers the optimization convergence and the performance of FL. Existing data augmentation methods based on federated generative models or raw data sharing strategies for solving the non-IID problem still suffer from low performance, privacy protection concerns, and high communication overhead in decentralized tabular data. To tackle these challenges, we propose a federated tabular data augmentation method, named Fed-TDA. The core idea of Fed-TDA is to synthesize tabular data for data augmentation using some simple statistics (e.g., distributions of each column and global covariance). Specifically, we propose the multimodal distribution transformation and inverse cumulative distribution mapping respectively synthesize continuous and discrete columns in tabular data from a noise according to the pre-learned statistics. Furthermore, we theoretically analyze that our Fed-TDA not only preserves data privacy but also maintains the distribution of the original data and the correlation between columns. Through extensive experiments on five real-world tabular datasets, we demonstrate the superiority of Fed-TDA over the state-of-the-art in test performance and communication efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge