Xiaowu Zhang
Unveiling the Impact of Multimodal Features on Chinese Spelling Correction: From Analysis to Design
Apr 10, 2025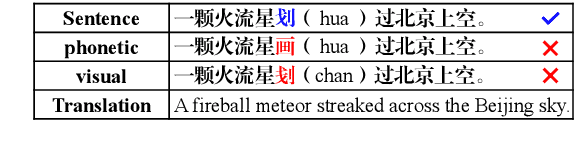
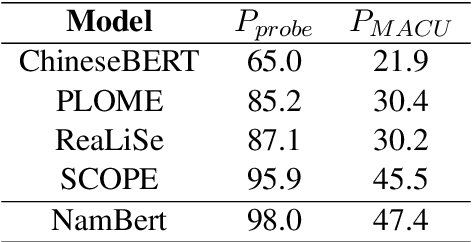
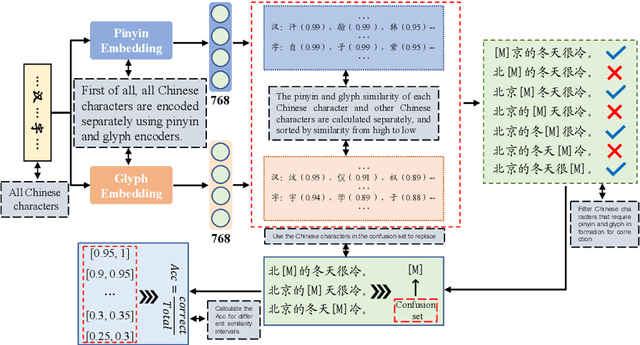
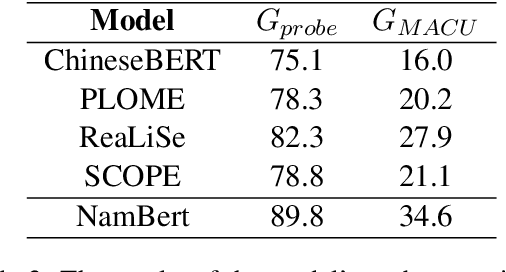
Abstract:The Chinese Spelling Correction (CSC) task focuses on detecting and correcting spelling errors in sentences. Current research primarily explores two approaches: traditional multimodal pre-trained models and large language models (LLMs). However, LLMs face limitations in CSC, particularly over-correction, making them suboptimal for this task. While existing studies have investigated the use of phonetic and graphemic information in multimodal CSC models, effectively leveraging these features to enhance correction performance remains a challenge. To address this, we propose the Multimodal Analysis for Character Usage (\textbf{MACU}) experiment, identifying potential improvements for multimodal correctison. Based on empirical findings, we introduce \textbf{NamBert}, a novel multimodal model for Chinese spelling correction. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate NamBert's superiority over SOTA methods. We also conduct a comprehensive comparison between NamBert and LLMs, systematically evaluating their strengths and limitations in CSC. Our code and model are available at https://github.com/iioSnail/NamBert.
Research on Domain-Specific Chinese Spelling Correction Method Based on Plugin Extension Modules
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:This paper proposes a Chinese spelling correction method based on plugin extension modules, aimed at addressing the limitations of existing models in handling domain-specific texts. Traditional Chinese spelling correction models are typically trained on general-domain datasets, resulting in poor performance when encountering specialized terminology in domain-specific texts. To address this issue, we design an extension module that learns the features of domain-specific terminology, thereby enhancing the model's correction capabilities within specific domains. This extension module can provide domain knowledge to the model without compromising its general spelling correction performance, thus improving its accuracy in specialized fields. Experimental results demonstrate that after integrating extension modules for medical, legal, and official document domains, the model's correction performance is significantly improved compared to the baseline model without any extension modules.
Does Correction Remain A Problem For Large Language Models?
Aug 14, 2023Abstract:As large language models, such as GPT, continue to advance the capabilities of natural language processing (NLP), the question arises: does the problem of correction still persist? This paper investigates the role of correction in the context of large language models by conducting two experiments. The first experiment focuses on correction as a standalone task, employing few-shot learning techniques with GPT-like models for error correction. The second experiment explores the notion of correction as a preparatory task for other NLP tasks, examining whether large language models can tolerate and perform adequately on texts containing certain levels of noise or errors. By addressing these experiments, we aim to shed light on the significance of correction in the era of large language models and its implications for various NLP applications.
XRoute Environment: A Novel Reinforcement Learning Environment for Routing
May 23, 2023Abstract:Routing is a crucial and time-consuming stage in modern design automation flow for advanced technology nodes. Great progress in the field of reinforcement learning makes it possible to use those approaches to improve the routing quality and efficiency. However, the scale of the routing problems solved by reinforcement learning-based methods in recent studies is too small for these methods to be used in commercial EDA tools. We introduce the XRoute Environment, a new reinforcement learning environment where agents are trained to select and route nets in an advanced, end-to-end routing framework. Novel algorithms and ideas can be quickly tested in a safe and reproducible manner in it. The resulting environment is challenging, easy to use, customize and add additional scenarios, and it is available under a permissive open-source license. In addition, it provides support for distributed deployment and multi-instance experiments. We propose two tasks for learning and build a full-chip test bed with routing benchmarks of various region sizes. We also pre-define several static routing regions with different pin density and number of nets for easier learning and testing. For net ordering task, we report baseline results for two widely used reinforcement learning algorithms (PPO and DQN) and one searching-based algorithm (TritonRoute). The XRoute Environment will be available at https://github.com/xplanlab/xroute_env.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge