Yunxiao Wang
TIME: Temporal-sensitive Multi-dimensional Instruction Tuning and Benchmarking for Video-LLMs
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Video large language models have achieved remarkable performance in tasks such as video question answering, however, their temporal understanding remains suboptimal. To address this limitation, we curate a dedicated instruction fine-tuning dataset that focuses on enhancing temporal comprehension across five key dimensions. In order to reduce reliance on costly temporal annotations, we introduce a multi-task prompt fine-tuning approach that seamlessly integrates temporal-sensitive tasks into existing instruction datasets without requiring additional annotations. Furthermore, we develop a novel benchmark for temporal-sensitive video understanding that not only fills the gaps in dimension coverage left by existing benchmarks but also rigorously filters out potential shortcuts, ensuring a more accurate evaluation. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach significantly enhances the temporal understanding of video-LLMs while avoiding reliance on shortcuts.
Exo2Ego: Exocentric Knowledge Guided MLLM for Egocentric Video Understanding
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:AI personal assistants, deployed through robots or wearables, require embodied understanding to collaborate effectively with humans. Current Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) primarily focus on third-person (exocentric) vision, overlooking the unique aspects of first-person (egocentric) videos. Additionally, high acquisition costs limit data size, impairing MLLM performance. To address these challenges, we propose learning the mapping between exocentric and egocentric domains, leveraging the extensive exocentric knowledge within existing MLLMs to enhance egocentric video understanding. To this end, we introduce Ego-ExoClip, a pre-training dataset comprising 1.1M synchronized ego-exo clip-text pairs derived from Ego-Exo4D. Our approach features a progressive training pipeline with three stages: Teacher Self-Preparation, Teacher-Student Guidance, and Student Self-Practice. Additionally, we propose an instruction-tuning data EgoIT from multiple sources to strengthen the model's instruction-following capabilities, along with the EgoBench benchmark comprising eight different tasks for thorough evaluation. Extensive experiments across diverse egocentric tasks reveal that existing MLLMs perform inadequately in egocentric video understanding, while our model significantly outperforms these leading models.
TabDeco: A Comprehensive Contrastive Framework for Decoupled Representations in Tabular Data
Nov 17, 2024



Abstract:Representation learning is a fundamental aspect of modern artificial intelligence, driving substantial improvements across diverse applications. While selfsupervised contrastive learning has led to significant advancements in fields like computer vision and natural language processing, its adaptation to tabular data presents unique challenges. Traditional approaches often prioritize optimizing model architecture and loss functions but may overlook the crucial task of constructing meaningful positive and negative sample pairs from various perspectives like feature interactions, instance-level patterns and batch-specific contexts. To address these challenges, we introduce TabDeco, a novel method that leverages attention-based encoding strategies across both rows and columns and employs contrastive learning framework to effectively disentangle feature representations at multiple levels, including features, instances and data batches. With the innovative feature decoupling hierarchies, TabDeco consistently surpasses existing deep learning methods and leading gradient boosting algorithms, including XG-Boost, CatBoost, and LightGBM, across various benchmark tasks, underscoring its effectiveness in advancing tabular data representation learning.
Towards Large-scale Masked Face Recognition
Oct 25, 2023



Abstract:During the COVID-19 coronavirus epidemic, almost everyone is wearing masks, which poses a huge challenge for deep learning-based face recognition algorithms. In this paper, we will present our \textbf{championship} solutions in ICCV MFR WebFace260M and InsightFace unconstrained tracks. We will focus on four challenges in large-scale masked face recognition, i.e., super-large scale training, data noise handling, masked and non-masked face recognition accuracy balancing, and how to design inference-friendly model architecture. We hope that the discussion on these four aspects can guide future research towards more robust masked face recognition systems.
MISSRec: Pre-training and Transferring Multi-modal Interest-aware Sequence Representation for Recommendation
Aug 22, 2023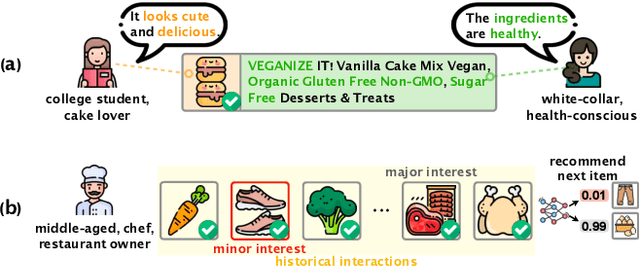

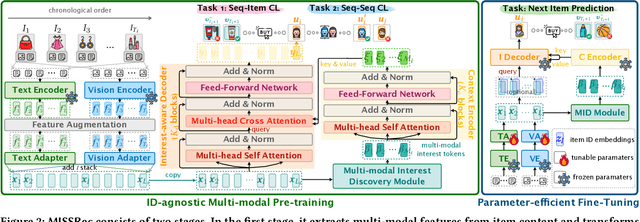

Abstract:The goal of sequential recommendation (SR) is to predict a user's potential interested items based on her/his historical interaction sequences. Most existing sequential recommenders are developed based on ID features, which, despite their widespread use, often underperform with sparse IDs and struggle with the cold-start problem. Besides, inconsistent ID mappings hinder the model's transferability, isolating similar recommendation domains that could have been co-optimized. This paper aims to address these issues by exploring the potential of multi-modal information in learning robust and generalizable sequence representations. We propose MISSRec, a multi-modal pre-training and transfer learning framework for SR. On the user side, we design a Transformer-based encoder-decoder model, where the contextual encoder learns to capture the sequence-level multi-modal synergy while a novel interest-aware decoder is developed to grasp item-modality-interest relations for better sequence representation. On the candidate item side, we adopt a dynamic fusion module to produce user-adaptive item representation, providing more precise matching between users and items. We pre-train the model with contrastive learning objectives and fine-tune it in an efficient manner. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and flexibility of MISSRec, promising an practical solution for real-world recommendation scenarios.
A Survey on Video Moment Localization
Jun 13, 2023Abstract:Video moment localization, also known as video moment retrieval, aiming to search a target segment within a video described by a given natural language query. Beyond the task of temporal action localization whereby the target actions are pre-defined, video moment retrieval can query arbitrary complex activities. In this survey paper, we aim to present a comprehensive review of existing video moment localization techniques, including supervised, weakly supervised, and unsupervised ones. We also review the datasets available for video moment localization and group results of related work. In addition, we discuss promising future directions for this field, in particular large-scale datasets and interpretable video moment localization models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge