Yinchuan Li
PhysToolBench: Benchmarking Physical Tool Understanding for MLLMs
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:The ability to use, understand, and create tools is a hallmark of human intelligence, enabling sophisticated interaction with the physical world. For any general-purpose intelligent agent to achieve true versatility, it must also master these fundamental skills. While modern Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) leverage their extensive common knowledge for high-level planning in embodied AI and in downstream Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, the extent of their true understanding of physical tools remains unquantified. To bridge this gap, we present PhysToolBench, the first benchmark dedicated to evaluating the comprehension of physical tools by MLLMs. Our benchmark is structured as a Visual Question Answering (VQA) dataset comprising over 1,000 image-text pairs. It assesses capabilities across three distinct difficulty levels: (1) Tool Recognition: Requiring the recognition of a tool's primary function. (2) Tool Understanding: Testing the ability to grasp the underlying principles of a tool's operation. (3) Tool Creation: Challenging the model to fashion a new tool from surrounding objects when conventional options are unavailable. Our comprehensive evaluation of 32 MLLMs-spanning proprietary, open-source, specialized embodied, and backbones in VLAs-reveals a significant deficiency in tool understanding. Furthermore, we provide an in-depth analysis and propose preliminary solutions. Code and dataset are publicly available.
Mirage-1: Augmenting and Updating GUI Agent with Hierarchical Multimodal Skills
Jun 12, 2025



Abstract:Recent efforts to leverage the Multi-modal Large Language Model (MLLM) as GUI agents have yielded promising outcomes. However, these agents still struggle with long-horizon tasks in online environments, primarily due to insufficient knowledge and the inherent gap between offline and online domains. In this paper, inspired by how humans generalize knowledge in open-ended environments, we propose a Hierarchical Multimodal Skills (HMS) module to tackle the issue of insufficient knowledge. It progressively abstracts trajectories into execution skills, core skills, and ultimately meta-skills, providing a hierarchical knowledge structure for long-horizon task planning. To bridge the domain gap, we propose the Skill-Augmented Monte Carlo Tree Search (SA-MCTS) algorithm, which efficiently leverages skills acquired in offline environments to reduce the action search space during online tree exploration. Building on HMS, we propose Mirage-1, a multimodal, cross-platform, plug-and-play GUI agent. To validate the performance of Mirage-1 in real-world long-horizon scenarios, we constructed a new benchmark, AndroidLH. Experimental results show that Mirage-1 outperforms previous agents by 32\%, 19\%, 15\%, and 79\% on AndroidWorld, MobileMiniWob++, Mind2Web-Live, and AndroidLH, respectively. Project page: https://cybertronagent.github.io/Mirage-1.github.io/
STAR: Learning Diverse Robot Skill Abstractions through Rotation-Augmented Vector Quantization
Jun 04, 2025



Abstract:Transforming complex actions into discrete skill abstractions has demonstrated strong potential for robotic manipulation. Existing approaches mainly leverage latent variable models, e.g., VQ-VAE, to learn skill abstractions through learned vectors (codebooks), while they suffer from codebook collapse and modeling the causal relationship between learned skills. To address these limitations, we present \textbf{S}kill \textbf{T}raining with \textbf{A}ugmented \textbf{R}otation (\textbf{STAR}), a framework that advances both skill learning and composition to complete complex behaviors. Specifically, to prevent codebook collapse, we devise rotation-augmented residual skill quantization (RaRSQ). It encodes relative angles between encoder outputs into the gradient flow by rotation-based gradient mechanism. Points within the same skill code are forced to be either pushed apart or pulled closer together depending on gradient directions. Further, to capture the causal relationship between skills, we present causal skill transformer (CST) which explicitly models dependencies between skill representations through an autoregressive mechanism for coherent action generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of STAR on both LIBERO benchmark and realworld tasks, with around 12\% improvement over the baselines.
* Accepted by ICML 2025 Spotlight
Proximalized Preference Optimization for Diverse Feedback Types: A Decomposed Perspective on DPO
May 29, 2025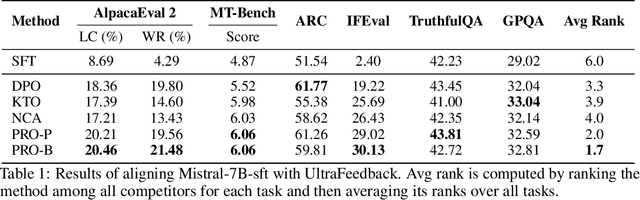


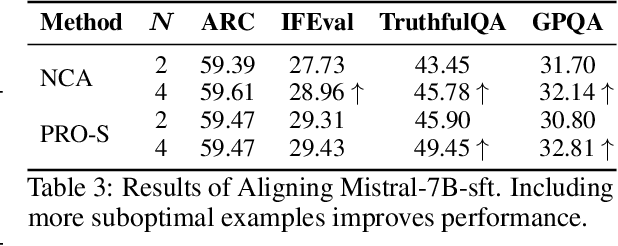
Abstract:Direct alignment methods typically optimize large language models (LLMs) by contrasting the likelihoods of preferred versus dispreferred responses. While effective in steering LLMs to match relative preference, these methods are frequently noted for decreasing the absolute likelihoods of example responses. As a result, aligned models tend to generate outputs that deviate from the expected patterns, exhibiting reward-hacking effect even without a reward model. This undesired consequence exposes a fundamental limitation in contrastive alignment, which we characterize as likelihood underdetermination. In this work, we revisit direct preference optimization (DPO) -- the seminal direct alignment method -- and demonstrate that its loss theoretically admits a decomposed reformulation. The reformulated loss not only broadens applicability to a wider range of feedback types, but also provides novel insights into the underlying cause of likelihood underdetermination. Specifically, the standard DPO implementation implicitly oversimplifies a regularizer in the reformulated loss, and reinstating its complete version effectively resolves the underdetermination issue. Leveraging these findings, we introduce PRoximalized PReference Optimization (PRO), a unified method to align with diverse feeback types, eliminating likelihood underdetermination through an efficient approximation of the complete regularizer. Comprehensive experiments show the superiority of PRO over existing methods in scenarios involving pairwise, binary and scalar feedback.
UltraVSR: Achieving Ultra-Realistic Video Super-Resolution with Efficient One-Step Diffusion Space
May 26, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have shown great potential in generating realistic image detail. However, adapting these models to video super-resolution (VSR) remains challenging due to their inherent stochasticity and lack of temporal modeling. In this paper, we propose UltraVSR, a novel framework that enables ultra-realistic and temporal-coherent VSR through an efficient one-step diffusion space. A central component of UltraVSR is the Degradation-aware Restoration Schedule (DRS), which estimates a degradation factor from the low-resolution input and transforms iterative denoising process into a single-step reconstruction from from low-resolution to high-resolution videos. This design eliminates randomness from diffusion noise and significantly speeds up inference. To ensure temporal consistency, we propose a lightweight yet effective Recurrent Temporal Shift (RTS) module, composed of an RTS-convolution unit and an RTS-attention unit. By partially shifting feature components along the temporal dimension, these two units collaboratively facilitate effective feature propagation, fusion, and alignment across neighboring frames, without relying on explicit temporal layers. The RTS module is integrated into a pretrained text-to-image diffusion model and is further enhanced through Spatio-temporal Joint Distillation (SJD), which improves temporal coherence while preserving realistic details. Additionally, we introduce a Temporally Asynchronous Inference (TAI) strategy to capture long-range temporal dependencies under limited memory constraints. Extensive experiments show that UltraVSR achieves state-of-the-art performance, both qualitatively and quantitatively, in a single sampling step.
GUI-explorer: Autonomous Exploration and Mining of Transition-aware Knowledge for GUI Agent
May 22, 2025Abstract:GUI automation faces critical challenges in dynamic environments. MLLMs suffer from two key issues: misinterpreting UI components and outdated knowledge. Traditional fine-tuning methods are costly for app-specific knowledge updates. We propose GUI-explorer, a training-free GUI agent that incorporates two fundamental mechanisms: (1) Autonomous Exploration of Function-aware Trajectory. To comprehensively cover all application functionalities, we design a Function-aware Task Goal Generator that automatically constructs exploration goals by analyzing GUI structural information (e.g., screenshots and activity hierarchies). This enables systematic exploration to collect diverse trajectories. (2) Unsupervised Mining of Transition-aware Knowledge. To establish precise screen-operation logic, we develop a Transition-aware Knowledge Extractor that extracts effective screen-operation logic through unsupervised analysis the state transition of structured interaction triples (observation, action, outcome). This eliminates the need for human involvement in knowledge extraction. With a task success rate of 53.7% on SPA-Bench and 47.4% on AndroidWorld, GUI-explorer shows significant improvements over SOTA agents. It requires no parameter updates for new apps. GUI-explorer is open-sourced and publicly available at https://github.com/JiuTian-VL/GUI-explorer.
Conditioning Matters: Training Diffusion Policies is Faster Than You Think
May 16, 2025Abstract:Diffusion policies have emerged as a mainstream paradigm for building vision-language-action (VLA) models. Although they demonstrate strong robot control capabilities, their training efficiency remains suboptimal. In this work, we identify a fundamental challenge in conditional diffusion policy training: when generative conditions are hard to distinguish, the training objective degenerates into modeling the marginal action distribution, a phenomenon we term loss collapse. To overcome this, we propose Cocos, a simple yet general solution that modifies the source distribution in the conditional flow matching to be condition-dependent. By anchoring the source distribution around semantics extracted from condition inputs, Cocos encourages stronger condition integration and prevents the loss collapse. We provide theoretical justification and extensive empirical results across simulation and real-world benchmarks. Our method achieves faster convergence and higher success rates than existing approaches, matching the performance of large-scale pre-trained VLAs using significantly fewer gradient steps and parameters. Cocos is lightweight, easy to implement, and compatible with diverse policy architectures, offering a general-purpose improvement to diffusion policy training.
EmbodiedMAE: A Unified 3D Multi-Modal Representation for Robot Manipulation
May 15, 2025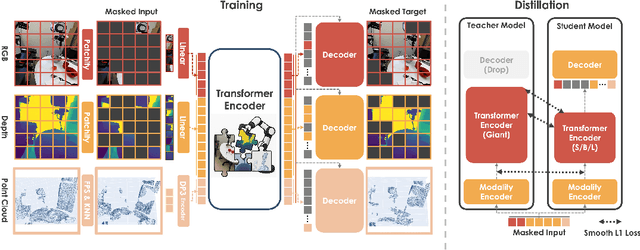
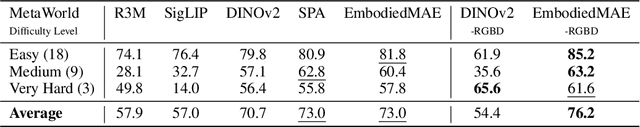

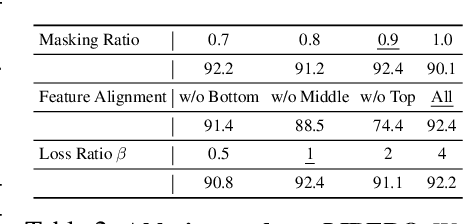
Abstract:We present EmbodiedMAE, a unified 3D multi-modal representation for robot manipulation. Current approaches suffer from significant domain gaps between training datasets and robot manipulation tasks, while also lacking model architectures that can effectively incorporate 3D information. To overcome these limitations, we enhance the DROID dataset with high-quality depth maps and point clouds, constructing DROID-3D as a valuable supplement for 3D embodied vision research. Then we develop EmbodiedMAE, a multi-modal masked autoencoder that simultaneously learns representations across RGB, depth, and point cloud modalities through stochastic masking and cross-modal fusion. Trained on DROID-3D, EmbodiedMAE consistently outperforms state-of-the-art vision foundation models (VFMs) in both training efficiency and final performance across 70 simulation tasks and 20 real-world robot manipulation tasks on two robot platforms. The model exhibits strong scaling behavior with size and promotes effective policy learning from 3D inputs. Experimental results establish EmbodiedMAE as a reliable unified 3D multi-modal VFM for embodied AI systems, particularly in precise tabletop manipulation settings where spatial perception is critical.
Ergodic Generative Flows
May 06, 2025Abstract:Generative Flow Networks (GFNs) were initially introduced on directed acyclic graphs to sample from an unnormalized distribution density. Recent works have extended the theoretical framework for generative methods allowing more flexibility and enhancing application range. However, many challenges remain in training GFNs in continuous settings and for imitation learning (IL), including intractability of flow-matching loss, limited tests of non-acyclic training, and the need for a separate reward model in imitation learning. The present work proposes a family of generative flows called Ergodic Generative Flows (EGFs) which are used to address the aforementioned issues. First, we leverage ergodicity to build simple generative flows with finitely many globally defined transformations (diffeomorphisms) with universality guarantees and tractable flow-matching loss (FM loss). Second, we introduce a new loss involving cross-entropy coupled to weak flow-matching control, coined KL-weakFM loss. It is designed for IL training without a separate reward model. We evaluate IL-EGFs on toy 2D tasks and real-world datasets from NASA on the sphere, using the KL-weakFM loss. Additionally, we conduct toy 2D reinforcement learning experiments with a target reward, using the FM loss.
DeCo: Task Decomposition and Skill Composition for Zero-Shot Generalization in Long-Horizon 3D Manipulation
May 01, 2025Abstract:Generalizing language-conditioned multi-task imitation learning (IL) models to novel long-horizon 3D manipulation tasks remains a significant challenge. To address this, we propose DeCo (Task Decomposition and Skill Composition), a model-agnostic framework compatible with various multi-task IL models, designed to enhance their zero-shot generalization to novel, compositional, long-horizon 3D manipulation tasks. DeCo first decomposes IL demonstrations into a set of modular atomic tasks based on the physical interaction between the gripper and objects, and constructs an atomic training dataset that enables models to learn a diverse set of reusable atomic skills during imitation learning. At inference time, DeCo leverages a vision-language model (VLM) to parse high-level instructions for novel long-horizon tasks, retrieve the relevant atomic skills, and dynamically schedule their execution; a spatially-aware skill-chaining module then ensures smooth, collision-free transitions between sequential skills. We evaluate DeCo in simulation using DeCoBench, a benchmark specifically designed to assess zero-shot generalization of multi-task IL models in compositional long-horizon 3D manipulation. Across three representative multi-task IL models (RVT-2, 3DDA, and ARP), DeCo achieves success rate improvements of 66.67%, 21.53%, and 57.92%, respectively, on 12 novel compositional tasks. Moreover, in real-world experiments, a DeCo-enhanced model trained on only 6 atomic tasks successfully completes 9 novel long-horizon tasks, yielding an average success rate improvement of 53.33% over the base multi-task IL model. Video demonstrations are available at: https://deco226.github.io.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge