Yupeng Hu
StructAlign: Structured Cross-Modal Alignment for Continual Text-to-Video Retrieval
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Continual Text-to-Video Retrieval (CTVR) is a challenging multimodal continual learning setting, where models must incrementally learn new semantic categories while maintaining accurate text-video alignment for previously learned ones, thus making it particularly prone to catastrophic forgetting. A key challenge in CTVR is feature drift, which manifests in two forms: intra-modal feature drift caused by continual learning within each modality, and non-cooperative feature drift across modalities that leads to modality misalignment. To mitigate these issues, we propose StructAlign, a structured cross-modal alignment method for CTVR. First, StructAlign introduces a simplex Equiangular Tight Frame (ETF) geometry as a unified geometric prior to mitigate modality misalignment. Building upon this geometric prior, we design a cross-modal ETF alignment loss that aligns text and video features with category-level ETF prototypes, encouraging the learned representations to form an approximate simplex ETF geometry. In addition, to suppress intra-modal feature drift, we design a Cross-modal Relation Preserving loss, which leverages complementary modalities to preserve cross-modal similarity relations, providing stable relational supervision for feature updates. By jointly addressing non-cooperative feature drift across modalities and intra-modal feature drift, StructAlign effectively alleviates catastrophic forgetting in CTVR. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art continual retrieval approaches.
Omni-R1: Towards the Unified Generative Paradigm for Multimodal Reasoning
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are making significant progress in multimodal reasoning. Early approaches focus on pure text-based reasoning. More recent studies have incorporated multimodal information into the reasoning steps; however, they often follow a single task-specific reasoning pattern, which limits their generalizability across various multimodal tasks. In fact, there are numerous multimodal tasks requiring diverse reasoning skills, such as zooming in on a specific region or marking an object within an image. To address this, we propose unified generative multimodal reasoning, which unifies diverse multimodal reasoning skills by generating intermediate images during the reasoning process. We instantiate this paradigm with Omni-R1, a two-stage SFT+RL framework featuring perception alignment loss and perception reward, thereby enabling functional image generation. Additionally, we introduce Omni-R1-Zero, which eliminates the need for multimodal annotations by bootstrapping step-wise visualizations from text-only reasoning data. Empirical results show that Omni-R1 achieves unified generative reasoning across a wide range of multimodal tasks, and Omni-R1-Zero can match or even surpass Omni-R1 on average, suggesting a promising direction for generative multimodal reasoning.
When Eyes and Ears Disagree: Can MLLMs Discern Audio-Visual Confusion?
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Can Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) discern confused objects that are visually present but audio-absent? To study this, we introduce a new benchmark, AV-ConfuseBench, which simulates an ``Audio-Visual Confusion'' scene by modifying the corresponding sound of an object in the video, e.g., mute the sounding object and ask MLLMs Is there a/an muted-object sound''. Experimental results reveal that MLLMs, such as Qwen2.5-Omni and Gemini 2.5, struggle to discriminate non-existent audio due to visually dominated reasoning. Motivated by this observation, we introduce RL-CoMM, a Reinforcement Learning-based Collaborative Multi-MLLM that is built upon the Qwen2.5-Omni foundation. RL-CoMM includes two stages: 1) To alleviate visually dominated ambiguities, we introduce an external model, a Large Audio Language Model (LALM), as the reference model to generate audio-only reasoning. Then, we design a Step-wise Reasoning Reward function that enables MLLMs to self-improve audio-visual reasoning with the audio-only reference. 2) To ensure an accurate answer prediction, we introduce Answer-centered Confidence Optimization to reduce the uncertainty of potential heterogeneous reasoning differences. Extensive experiments on audio-visual question answering and audio-visual hallucination show that RL-CoMM improves the accuracy by 10~30\% over the baseline model with limited training data. Follow: https://github.com/rikeilong/AVConfusion.
Open Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Factual Image Generation
Oct 26, 2025



Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have achieved remarkable progress in generating photorealistic and prompt-aligned images, but they often produce outputs that contradict verifiable knowledge, especially when prompts involve fine-grained attributes or time-sensitive events. Conventional retrieval-augmented approaches attempt to address this issue by introducing external information, yet they are fundamentally incapable of grounding generation in accurate and evolving knowledge due to their reliance on static sources and shallow evidence integration. To bridge this gap, we introduce ORIG, an agentic open multimodal retrieval-augmented framework for Factual Image Generation (FIG), a new task that requires both visual realism and factual grounding. ORIG iteratively retrieves and filters multimodal evidence from the web and incrementally integrates the refined knowledge into enriched prompts to guide generation. To support systematic evaluation, we build FIG-Eval, a benchmark spanning ten categories across perceptual, compositional, and temporal dimensions. Experiments demonstrate that ORIG substantially improves factual consistency and overall image quality over strong baselines, highlighting the potential of open multimodal retrieval for factual image generation.
Reasoning in the Dark: Interleaved Vision-Text Reasoning in Latent Space
Oct 14, 2025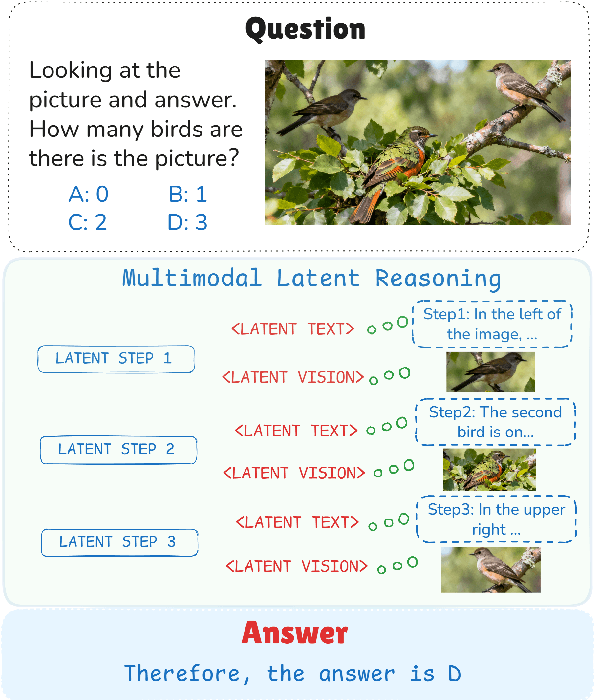
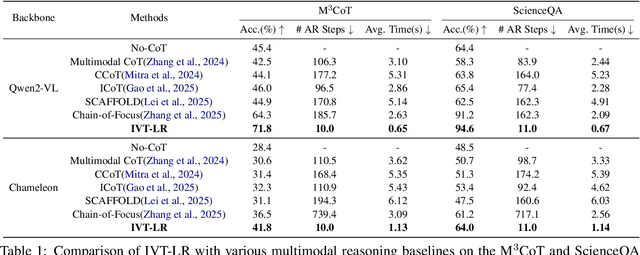
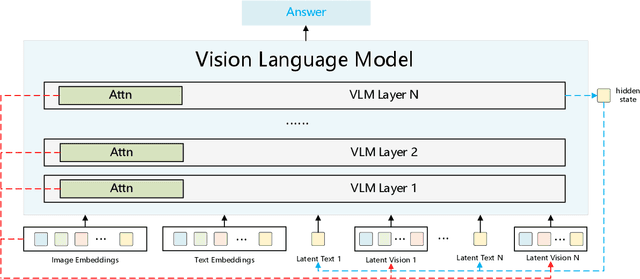
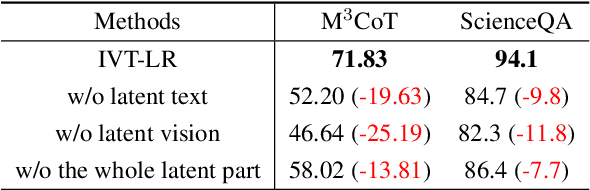
Abstract:Multimodal reasoning aims to enhance the capabilities of MLLMs by incorporating intermediate reasoning steps before reaching the final answer. It has evolved from text-only reasoning to the integration of visual information, enabling the thought process to be conveyed through both images and text. Despite its effectiveness, current multimodal reasoning methods depend on explicit reasoning steps that require labor-intensive vision-text annotations and inherently introduce significant inference latency. To address these issues, we introduce multimodal latent reasoning with the advantages of multimodal representation, reduced annotation, and inference efficiency. To facilicate it, we propose Interleaved Vision-Text Latent Reasoning (IVT-LR), which injects both visual and textual information in the reasoning process within the latent space. Specifically, IVT-LR represents each reasoning step by combining two implicit parts: latent text (the hidden states from the previous step) and latent vision (a set of selected image embeddings). We further introduce a progressive multi-stage training strategy to enable MLLMs to perform the above multimodal latent reasoning steps. Experiments on M3CoT and ScienceQA demonstrate that our IVT-LR method achieves an average performance increase of 5.45% in accuracy, while simultaneously achieving a speed increase of over 5 times compared to existing approaches. Code available at https://github.com/FYYDCC/IVT-LR.
Bilateral Collaboration with Large Vision-Language Models for Open Vocabulary Human-Object Interaction Detection
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Open vocabulary Human-Object Interaction (HOI) detection is a challenging task that detects all <human, verb, object> triplets of interest in an image, even those that are not pre-defined in the training set. Existing approaches typically rely on output features generated by large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to enhance the generalization ability of interaction representations. However, the visual features produced by VLMs are holistic and coarse-grained, which contradicts the nature of detection tasks. To address this issue, we propose a novel Bilateral Collaboration framework for open vocabulary HOI detection (BC-HOI). This framework includes an Attention Bias Guidance (ABG) component, which guides the VLM to produce fine-grained instance-level interaction features according to the attention bias provided by the HOI detector. It also includes a Large Language Model (LLM)-based Supervision Guidance (LSG) component, which provides fine-grained token-level supervision for the HOI detector by the LLM component of the VLM. LSG enhances the ability of ABG to generate high-quality attention bias. We conduct extensive experiments on two popular benchmarks: HICO-DET and V-COCO, consistently achieving superior performance in the open vocabulary and closed settings. The code will be released in Github.
MIST: Towards Multi-dimensional Implicit Bias and Stereotype Evaluation of LLMs via Theory of Mind
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Theory of Mind (ToM) in Large Language Models (LLMs) refers to their capacity for reasoning about mental states, yet failures in this capacity often manifest as systematic implicit bias. Evaluating this bias is challenging, as conventional direct-query methods are susceptible to social desirability effects and fail to capture its subtle, multi-dimensional nature. To this end, we propose an evaluation framework that leverages the Stereotype Content Model (SCM) to reconceptualize bias as a multi-dimensional failure in ToM across Competence, Sociability, and Morality. The framework introduces two indirect tasks: the Word Association Bias Test (WABT) to assess implicit lexical associations and the Affective Attribution Test (AAT) to measure covert affective leanings, both designed to probe latent stereotypes without triggering model avoidance. Extensive experiments on 8 State-of-the-Art LLMs demonstrate our framework's capacity to reveal complex bias structures, including pervasive sociability bias, multi-dimensional divergence, and asymmetric stereotype amplification, thereby providing a more robust methodology for identifying the structural nature of implicit bias.
FineCIR: Explicit Parsing of Fine-Grained Modification Semantics for Composed Image Retrieval
Mar 27, 2025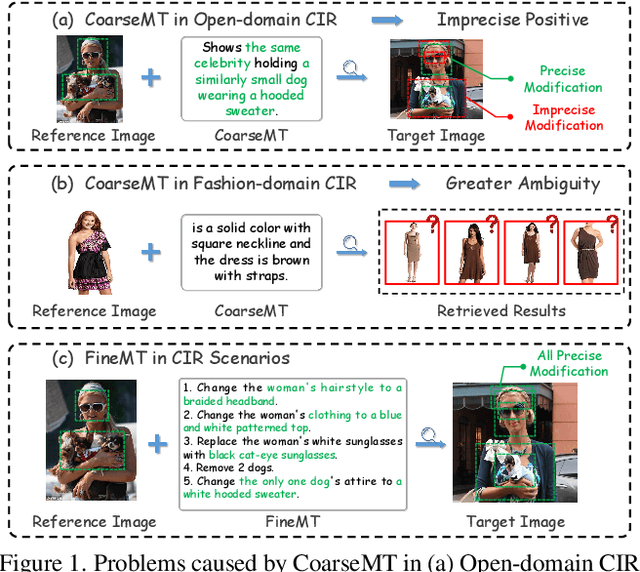
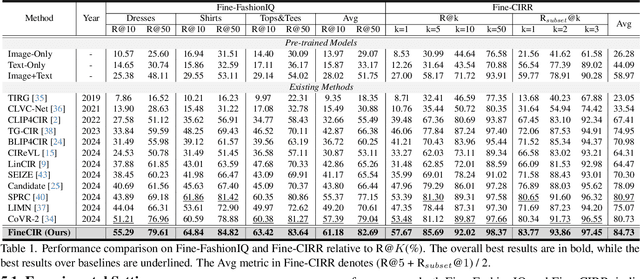
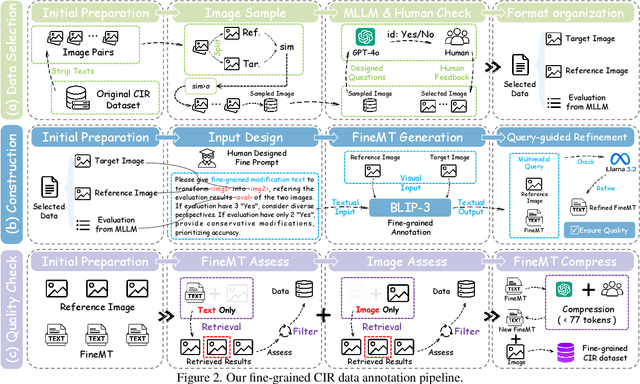
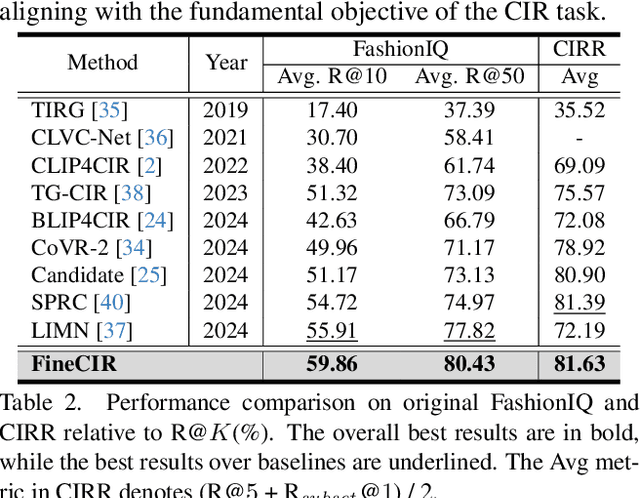
Abstract:Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) facilitates image retrieval through a multimodal query consisting of a reference image and modification text. The reference image defines the retrieval context, while the modification text specifies desired alterations. However, existing CIR datasets predominantly employ coarse-grained modification text (CoarseMT), which inadequately captures fine-grained retrieval intents. This limitation introduces two key challenges: (1) ignoring detailed differences leads to imprecise positive samples, and (2) greater ambiguity arises when retrieving visually similar images. These issues degrade retrieval accuracy, necessitating manual result filtering or repeated queries. To address these limitations, we develop a robust fine-grained CIR data annotation pipeline that minimizes imprecise positive samples and enhances CIR systems' ability to discern modification intents accurately. Using this pipeline, we refine the FashionIQ and CIRR datasets to create two fine-grained CIR datasets: Fine-FashionIQ and Fine-CIRR. Furthermore, we introduce FineCIR, the first CIR framework explicitly designed to parse the modification text. FineCIR effectively captures fine-grained modification semantics and aligns them with ambiguous visual entities, enhancing retrieval precision. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FineCIR consistently outperforms state-of-the-art CIR baselines on both fine-grained and traditional CIR benchmark datasets. Our FineCIR code and fine-grained CIR datasets are available at https://github.com/SDU-L/FineCIR.git.
Fine-grained Textual Inversion Network for Zero-Shot Composed Image Retrieval
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) allows users to search target images with a multimodal query, comprising a reference image and a modification text that describes the user's modification demand over the reference image. Nevertheless, due to the expensive labor cost of training data annotation, recent researchers have shifted to the challenging task of zero-shot CIR (ZS-CIR), which targets fulfilling CIR without annotated triplets. The pioneer ZS-CIR studies focus on converting the CIR task into a standard text-to-image retrieval task by pre-training a textual inversion network that can map a given image into a single pseudo-word token. Despite their significant progress, their coarse-grained textual inversion may be insufficient to capture the full content of the image accurately. To overcome this issue, in this work, we propose a novel Fine-grained Textual Inversion Network for ZS-CIR, named FTI4CIR. In particular, FTI4CIR comprises two main components: fine-grained pseudo-word token mapping and tri-wise caption-based semantic regularization. The former maps the image into a subject-oriented pseudo-word token and several attribute-oriented pseudo-word tokens to comprehensively express the image in the textual form, while the latter works on jointly aligning the fine-grained pseudo-word tokens to the real-word token embedding space based on a BLIP-generated image caption template. Extensive experiments conducted on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method.
Content-aware Balanced Spectrum Encoding in Masked Modeling for Time Series Classification
Dec 17, 2024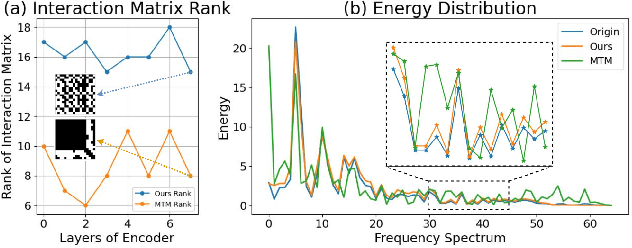
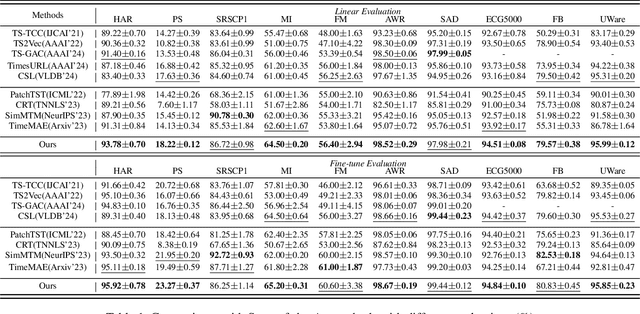
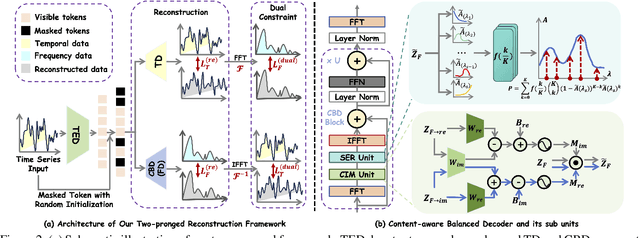
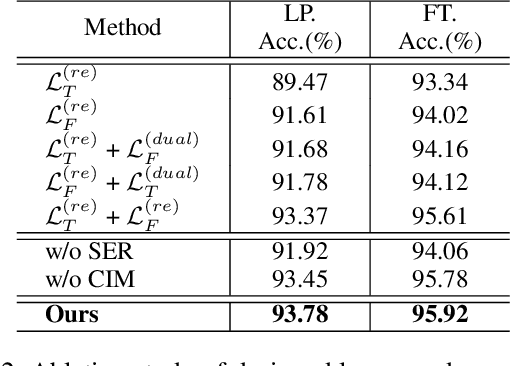
Abstract:Due to the superior ability of global dependency, transformer and its variants have become the primary choice in Masked Time-series Modeling (MTM) towards time-series classification task. In this paper, we experimentally analyze that existing transformer-based MTM methods encounter with two under-explored issues when dealing with time series data: (1) they encode features by performing long-dependency ensemble averaging, which easily results in rank collapse and feature homogenization as the layer goes deeper; (2) they exhibit distinct priorities in fitting different frequency components contained in the time-series, inevitably leading to spectrum energy imbalance of encoded feature. To tackle these issues, we propose an auxiliary content-aware balanced decoder (CBD) to optimize the encoding quality in the spectrum space within masked modeling scheme. Specifically, the CBD iterates on a series of fundamental blocks, and thanks to two tailored units, each block could progressively refine the masked representation via adjusting the interaction pattern based on local content variations of time-series and learning to recalibrate the energy distribution across different frequency components. Moreover, a dual-constraint loss is devised to enhance the mutual optimization of vanilla decoder and our CBD. Extensive experimental results on ten time-series classification datasets show that our method nearly surpasses a bunch of baselines. Meanwhile, a series of explanatory results are showcased to sufficiently demystify the behaviors of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge