Chang Sun
Omni-directional attention mechanism based on Mamba for speech separation
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Mamba, a selective state-space model (SSM), has emerged as an efficient alternative to Transformers for speech modeling, enabling long-sequence processing with linear complexity. While effective in speech separation, existing approaches, whether in the time or time-frequency domain, typically decompose the input along a single dimension into short one-dimensional sequences before processing them with Mamba, which restricts it to local 1D modeling and limits its ability to capture global dependencies across the 2D spectrogram. In this work, we propose an efficient omni-directional attention (OA) mechanism built upon unidirectional Mamba, which models global dependencies from ten different directions on the spectrogram. We expand the proposed mechanism into two baseline separation models and evaluate on three public datasets. Experimental results show that our approach consistently achieves significant performance gains over the baselines while preserving linear complexity, outperforming existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) systems.
JetFormer: A Scalable and Efficient Transformer for Jet Tagging from Offline Analysis to FPGA Triggers
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:We present JetFormer, a versatile and scalable encoder-only Transformer architecture for particle jet tagging at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). Unlike prior approaches that are often tailored to specific deployment regimes, JetFormer is designed to operate effectively across the full spectrum of jet tagging scenarios, from high-accuracy offline analysis to ultra-low-latency online triggering. The model processes variable-length sets of particle features without relying on input of explicit pairwise interactions, yet achieves competitive or superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods. On the large-scale JetClass dataset, a large-scale JetFormer matches the accuracy of the interaction-rich ParT model (within 0.7%) while using 37.4% fewer FLOPs, demonstrating its computational efficiency and strong generalization. On benchmark HLS4ML 150P datasets, JetFormer consistently outperforms existing models such as MLPs, Deep Sets, and Interaction Networks by 3-4% in accuracy. To bridge the gap to hardware deployment, we further introduce a hardware-aware optimization pipeline based on multi-objective hyperparameter search, yielding compact variants like JetFormer-tiny suitable for FPGA-based trigger systems with sub-microsecond latency requirements. Through structured pruning and quantization, we show that JetFormer can be aggressively compressed with minimal accuracy loss. By unifying high-performance modeling and deployability within a single architectural framework, JetFormer provides a practical pathway for deploying Transformer-based jet taggers in both offline and online environments at the LHC. Code is available at https://github.com/walkieq/JetFormer.
VALLR-Pin: Uncertainty-Factorized Visual Speech Recognition for Mandarin with Pinyin Guidance
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Visual speech recognition (VSR) aims to transcribe spoken content from silent lip-motion videos and is particularly challenging in Mandarin due to severe viseme ambiguity and pervasive homophones. We propose VALLR-Pin, a two-stage Mandarin VSR framework that extends the VALLR architecture by explicitly incorporating Pinyin as an intermediate representation. In the first stage, a shared visual encoder feeds dual decoders that jointly predict Mandarin characters and their corresponding Pinyin sequences, encouraging more robust visual-linguistic representations. In the second stage, an LLM-based refinement module takes the predicted Pinyin sequence together with an N-best list of character hypotheses to resolve homophone-induced ambiguities. To further adapt the LLM to visual recognition errors, we fine-tune it on synthetic instruction data constructed from model-generated Pinyin-text pairs, enabling error-aware correction. Experiments on public Mandarin VSR benchmarks demonstrate that VALLR-Pin consistently improves transcription accuracy under multi-speaker conditions, highlighting the effectiveness of combining phonetic guidance with lightweight LLM refinement.
VALLR-Pin: Dual-Decoding Visual Speech Recognition for Mandarin with Pinyin-Guided LLM Refinement
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Visual Speech Recognition aims to transcribe spoken words from silent lip-motion videos. This task is particularly challenging for Mandarin, as visemes are highly ambiguous and homophones are prevalent. We propose VALLR-Pin, a novel two-stage framework that extends the recent VALLR architecture from English to Mandarin. First, a shared video encoder feeds into dual decoders, which jointly predict both Chinese character sequences and their standard Pinyin romanization. The multi-task learning of character and phonetic outputs fosters robust visual-semantic representations. During inference, the text decoder generates multiple candidate transcripts. We construct a prompt by concatenating the Pinyin output with these candidate Chinese sequences and feed it to a large language model to resolve ambiguities and refine the transcription. This provides the LLM with explicit phonetic context to correct homophone-induced errors. Finally, we fine-tune the LLM on synthetic noisy examples: we generate imperfect Pinyin-text pairs from intermediate VALLR-Pin checkpoints using the training data, creating instruction-response pairs for error correction. This endows the LLM with awareness of our model's specific error patterns. In summary, VALLR-Pin synergizes visual features with phonetic and linguistic context to improve Mandarin lip-reading performance.
AIE4ML: An End-to-End Framework for Compiling Neural Networks for the Next Generation of AMD AI Engines
Dec 17, 2025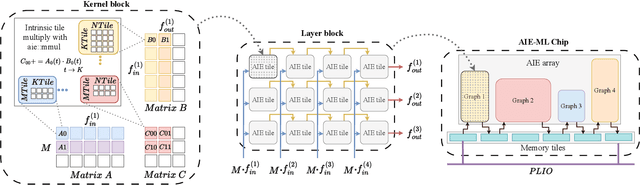
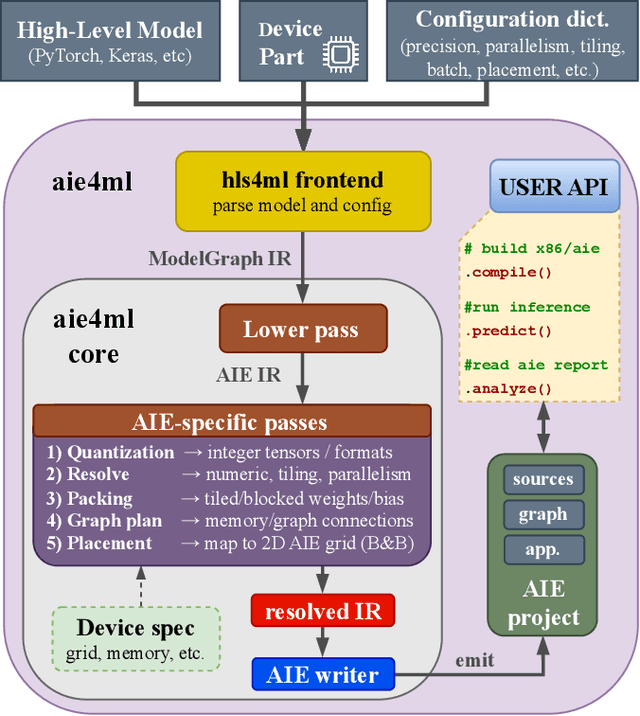
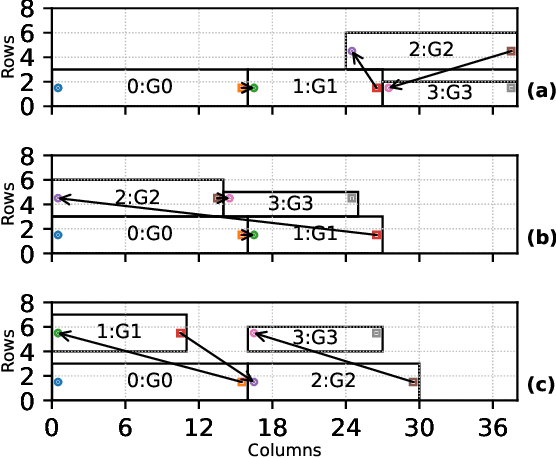
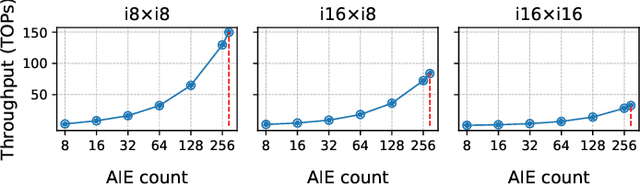
Abstract:Efficient AI inference on AMD's Versal AI Engine (AIE) is challenging due to tightly coupled VLIW execution, explicit datapaths, and local memory management. Prior work focused on first-generation AIE kernel optimizations, without tackling full neural network execution across the 2D array. In this work, we present AIE4ML, the first comprehensive framework for converting AI models automatically into optimized firmware targeting the AIE-ML generation devices, also with forward compatibility for the newer AIE-MLv2 architecture. At the single-kernel level, we attain performance close to the architectural peak. At the graph and system levels, we provide a structured parallelization method that can scale across the 2D AIE-ML fabric and exploit its dedicated memory tiles to stay entirely on-chip throughout the model execution. As a demonstration, we designed a generalized and highly efficient linear-layer implementation with intrinsic support for fused bias addition and ReLU activation. Also, as our framework necessitates the generation of multi-layer implementations, our approach systematically derives deterministic, compact, and topology-optimized placements tailored to the physical 2D grid of the device through a novel graph placement and search algorithm. Finally, the framework seamlessly accepts quantized models imported from high-level tools such as hls4ml or PyTorch while preserving bit-exactness. In layer scaling benchmarks, we achieve up to 98.6% efficiency relative to the single-kernel baseline, utilizing 296 of 304 AIE tiles (97.4%) of the device with entirely on-chip data movement. With evaluations across real-world model topologies, we demonstrate that AIE4ML delivers GPU-class throughput under microsecond latency constraints, making it a practical companion for ultra-low-latency environments such as trigger systems in particle physics experiments.
RINO: Renormalization Group Invariance with No Labels
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:A common challenge with supervised machine learning (ML) in high energy physics (HEP) is the reliance on simulations for labeled data, which can often mismodel the underlying collision or detector response. To help mitigate this problem of domain shift, we propose RINO (Renormalization Group Invariance with No Labels), a self-supervised learning approach that can instead pretrain models directly on collision data, learning embeddings invariant to renormalization group flow scales. In this work, we pretrain a transformer-based model on jets originating from quantum chromodynamic (QCD) interactions from the JetClass dataset, emulating real QCD-dominated experimental data, and then finetune on the JetNet dataset -- emulating simulations -- for the task of identifying jets originating from top quark decays. RINO demonstrates improved generalization from the JetNet training data to JetClass data compared to supervised training on JetNet from scratch, demonstrating the potential for RINO pretraining on real collision data followed by fine-tuning on small, high-quality MC datasets, to improve the robustness of ML models in HEP.
Bilateral Collaboration with Large Vision-Language Models for Open Vocabulary Human-Object Interaction Detection
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Open vocabulary Human-Object Interaction (HOI) detection is a challenging task that detects all <human, verb, object> triplets of interest in an image, even those that are not pre-defined in the training set. Existing approaches typically rely on output features generated by large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to enhance the generalization ability of interaction representations. However, the visual features produced by VLMs are holistic and coarse-grained, which contradicts the nature of detection tasks. To address this issue, we propose a novel Bilateral Collaboration framework for open vocabulary HOI detection (BC-HOI). This framework includes an Attention Bias Guidance (ABG) component, which guides the VLM to produce fine-grained instance-level interaction features according to the attention bias provided by the HOI detector. It also includes a Large Language Model (LLM)-based Supervision Guidance (LSG) component, which provides fine-grained token-level supervision for the HOI detector by the LLM component of the VLM. LSG enhances the ability of ABG to generate high-quality attention bias. We conduct extensive experiments on two popular benchmarks: HICO-DET and V-COCO, consistently achieving superior performance in the open vocabulary and closed settings. The code will be released in Github.
Adapting Lightweight Vision Language Models for Radiological Visual Question Answering
Jun 17, 2025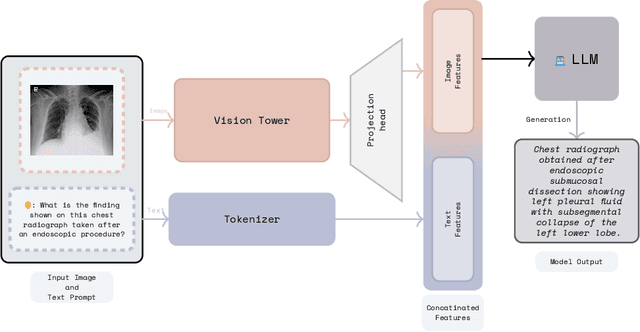
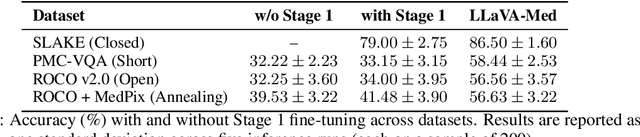
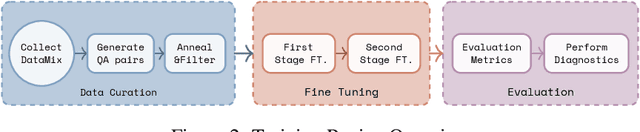
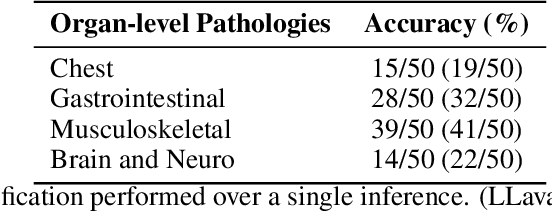
Abstract:Recent advancements in vision-language systems have improved the accuracy of Radiological Visual Question Answering (VQA) Models. However, some challenges remain across each stage of model development: limited expert-labeled images hinders data procurement at scale; the intricate and nuanced patterns of radiological images make modeling inherently difficult; and the lack of evaluation evaluation efforts makes it difficult to identify cases where the model might be ill-conditioned. In this study, we fine-tune a lightweight 3B parameter vision-language model for Radiological VQA, demonstrating that small models, when appropriately tuned with curated data, can achieve robust performance across both open- and closed-ended questions. We propose a cost-effective training pipeline from synthetic question-answer pair generation to multi-stage fine-tuning on specialised radiological domain-targeted datasets (e.g., ROCO v2.0, MedPix v2.0). Our results show that despite operating at a fraction of the scale of state-of-the-art models such as LLaVA-Med, our model achieves promising performance given its small parameter size and the limited scale of training data. We introduce a lightweight saliency-based diagnostic tool that enables domain experts to inspect VQA model performance and identify ill-conditioned failure modes through saliency analysis.
LPCM: Learning-based Predictive Coding for LiDAR Point Cloud Compression
May 26, 2025Abstract:Since the data volume of LiDAR point clouds is very huge, efficient compression is necessary to reduce their storage and transmission costs. However, existing learning-based compression methods do not exploit the inherent angular resolution of LiDAR and ignore the significant differences in the correlation of geometry information at different bitrates. The predictive geometry coding method in the geometry-based point cloud compression (G-PCC) standard uses the inherent angular resolution to predict the azimuth angles. However, it only models a simple linear relationship between the azimuth angles of neighboring points. Moreover, it does not optimize the quantization parameters for residuals on each coordinate axis in the spherical coordinate system. We propose a learning-based predictive coding method (LPCM) with both high-bitrate and low-bitrate coding modes. LPCM converts point clouds into predictive trees using the spherical coordinate system. In high-bitrate coding mode, we use a lightweight Long-Short-Term Memory-based predictive (LSTM-P) module that captures long-term geometry correlations between different coordinates to efficiently predict and compress the elevation angles. In low-bitrate coding mode, where geometry correlation degrades, we introduce a variational radius compression (VRC) module to directly compress the point radii. Then, we analyze why the quantization of spherical coordinates differs from that of Cartesian coordinates and propose a differential evolution (DE)-based quantization parameter selection method, which improves rate-distortion performance without increasing coding time. Experimental results on the LiDAR benchmark \textit{SemanticKITTI} and the MPEG-specified \textit{Ford} datasets show that LPCM outperforms G-PCC and other learning-based methods.
Fast Jet Tagging with MLP-Mixers on FPGAs
Mar 05, 2025
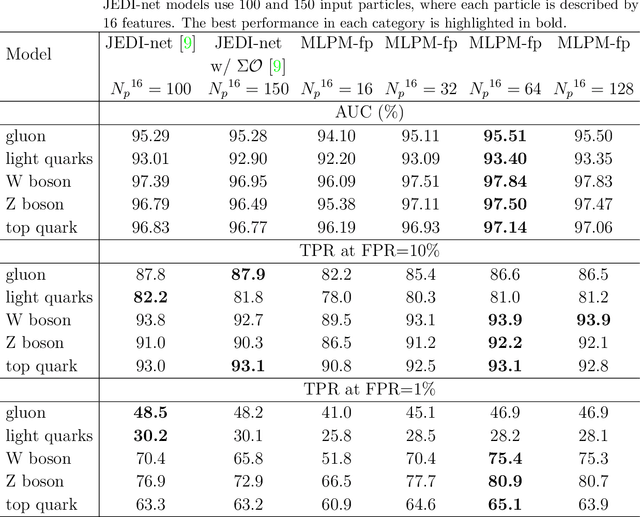
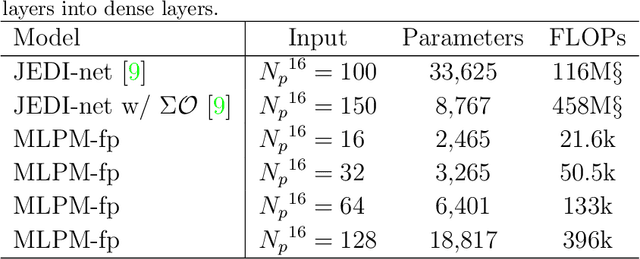
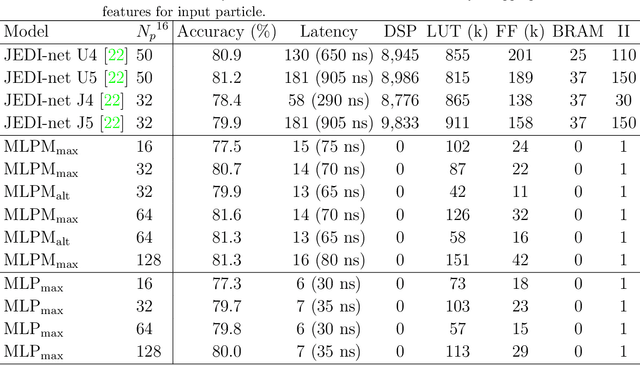
Abstract:We explore the innovative use of MLP-Mixer models for real-time jet tagging and establish their feasibility on resource-constrained hardware like FPGAs. MLP-Mixers excel in processing sequences of jet constituents, achieving state-of-the-art performance on datasets mimicking Large Hadron Collider conditions. By using advanced optimization techniques such as High-Granularity Quantization and Distributed Arithmetic, we achieve unprecedented efficiency. These models match or surpass the accuracy of previous architectures, reduce hardware resource usage by up to 97%, double the throughput, and half the latency. Additionally, non-permutation-invariant architectures enable smart feature prioritization and efficient FPGA deployment, setting a new benchmark for machine learning in real-time data processing at particle colliders.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge