Josien Pluim
Generative AI for Synthetic Data Across Multiple Medical Modalities: A Systematic Review of Recent Developments and Challenges
Jul 02, 2024


Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive systematic review of generative models (GANs, VAEs, DMs, and LLMs) used to synthesize various medical data types, including imaging (dermoscopic, mammographic, ultrasound, CT, MRI, and X-ray), text, time-series, and tabular data (EHR). Unlike previous narrowly focused reviews, our study encompasses a broad array of medical data modalities and explores various generative models. Our search strategy queries databases such as Scopus, PubMed, and ArXiv, focusing on recent works from January 2021 to November 2023, excluding reviews and perspectives. This period emphasizes recent advancements beyond GANs, which have been extensively covered previously. The survey reveals insights from three key aspects: (1) Synthesis applications and purpose of synthesis, (2) generation techniques, and (3) evaluation methods. It highlights clinically valid synthesis applications, demonstrating the potential of synthetic data to tackle diverse clinical requirements. While conditional models incorporating class labels, segmentation masks and image translations are prevalent, there is a gap in utilizing prior clinical knowledge and patient-specific context, suggesting a need for more personalized synthesis approaches and emphasizing the importance of tailoring generative approaches to the unique characteristics of medical data. Additionally, there is a significant gap in using synthetic data beyond augmentation, such as for validation and evaluation of downstream medical AI models. The survey uncovers that the lack of standardized evaluation methodologies tailored to medical images is a barrier to clinical application, underscoring the need for in-depth evaluation approaches, benchmarking, and comparative studies to promote openness and collaboration.
Multi-head Attention-based Deep Multiple Instance Learning
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces MAD-MIL, a Multi-head Attention-based Deep Multiple Instance Learning model, designed for weakly supervised Whole Slide Images (WSIs) classification in digital pathology. Inspired by the multi-head attention mechanism of the Transformer, MAD-MIL simplifies model complexity while achieving competitive results against advanced models like CLAM and DS-MIL. Evaluated on the MNIST-BAGS and public datasets, including TUPAC16, TCGA BRCA, TCGA LUNG, and TCGA KIDNEY, MAD-MIL consistently outperforms ABMIL. This demonstrates enhanced information diversity, interpretability, and efficiency in slide representation. The model's effectiveness, coupled with fewer trainable parameters and lower computational complexity makes it a promising solution for automated pathology workflows. Our code is available at https://github.com/tueimage/MAD-MIL.
Pathology Synthesis of 3D Consistent Cardiac MR Im-ages Using 2D VAEs and GANs
Sep 09, 2022



Abstract:We propose a method for synthesizing cardiac MR images with plausible heart shapes and realistic appearances for the purpose of generating labeled data for deep-learning (DL) training. It breaks down the image synthesis into label deformation and label-to-image translation tasks. The former is achieved via latent space interpolation in a VAE model, while the latter is accomplished via a conditional GAN model. We devise an approach for label manipulation in the latent space of the trained VAE model, namely pathology synthesis, aiming to synthesize a series of pseudo-pathological synthetic subjects with characteristics of a desired heart disease. Furthermore, we propose to model the relationship between 2D slices in the latent space of the VAE via estimating the correlation coefficient matrix between the latent vectors and utilizing it to correlate elements of randomly drawn samples before decoding to image space. This simple yet effective approach results in generating 3D consistent subjects from 2D slice-by-slice generations. Such an approach could provide a solution to diversify and enrich the available database of cardiac MR images and to pave the way for the development of generalizable DL-based image analysis algorithms. The code will be available at https://github.com/sinaamirrajab/CardiacPathologySynthesis.
sim2real: Cardiac MR Image Simulation-to-Real Translation via Unsupervised GANs
Aug 09, 2022



Abstract:There has been considerable interest in the MR physics-based simulation of a database of virtual cardiac MR images for the development of deep-learning analysis networks. However, the employment of such a database is limited or shows suboptimal performance due to the realism gap, missing textures, and the simplified appearance of simulated images. In this work we 1) provide image simulation on virtual XCAT subjects with varying anatomies, and 2) propose sim2real translation network to improve image realism. Our usability experiments suggest that sim2real data exhibits a good potential to augment training data and boost the performance of a segmentation algorithm.
PROMISSING: Pruning Missing Values in Neural Networks
Jun 03, 2022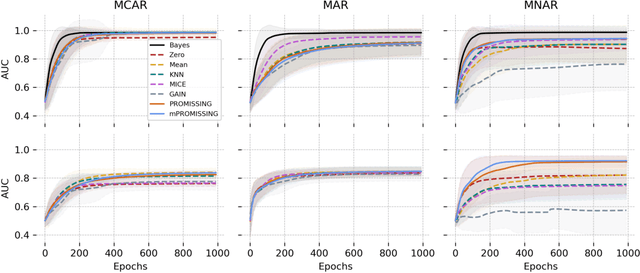
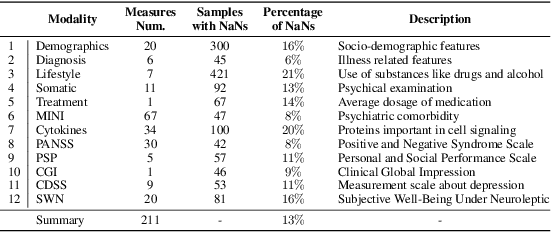
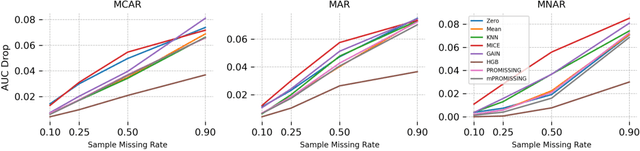
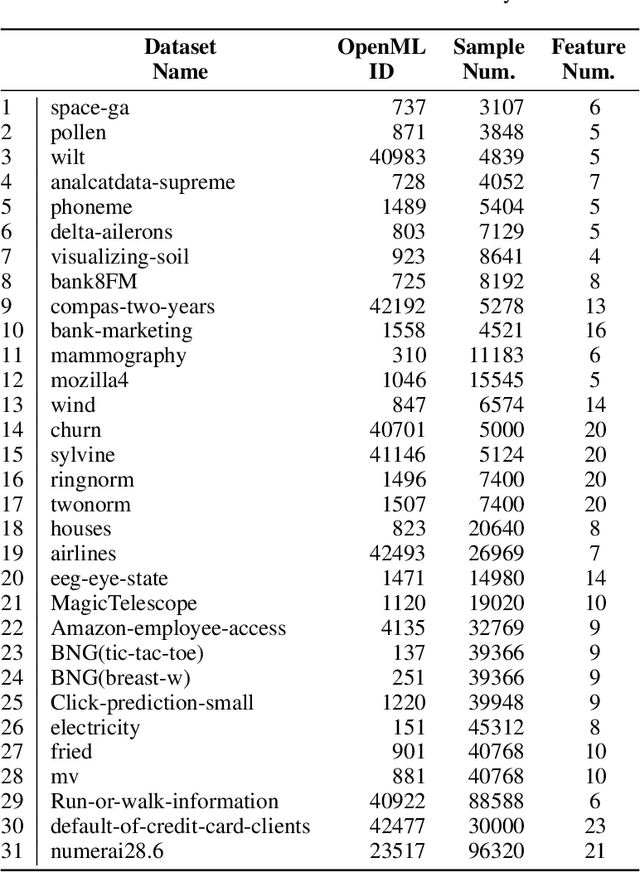
Abstract:While data are the primary fuel for machine learning models, they often suffer from missing values, especially when collected in real-world scenarios. However, many off-the-shelf machine learning models, including artificial neural network models, are unable to handle these missing values directly. Therefore, extra data preprocessing and curation steps, such as data imputation, are inevitable before learning and prediction processes. In this study, we propose a simple and intuitive yet effective method for pruning missing values (PROMISSING) during learning and inference steps in neural networks. In this method, there is no need to remove or impute the missing values; instead, the missing values are treated as a new source of information (representing what we do not know). Our experiments on simulated data, several classification and regression benchmarks, and a multi-modal clinical dataset show that PROMISSING results in similar prediction performance compared to various imputation techniques. In addition, our experiments show models trained using PROMISSING techniques are becoming less decisive in their predictions when facing incomplete samples with many unknowns. This finding hopefully advances machine learning models from being pure predicting machines to more realistic thinkers that can also say "I do not know" when facing incomplete sources of information.
Hybrid Deep Neural Network for Brachial Plexus Nerve Segmentation in Ultrasound Images
Jun 01, 2021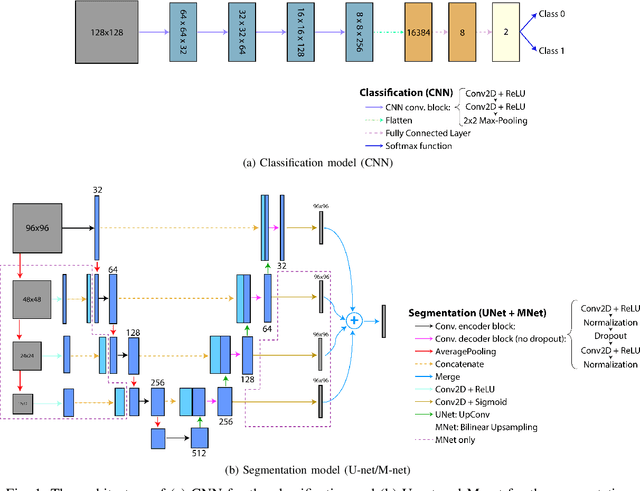
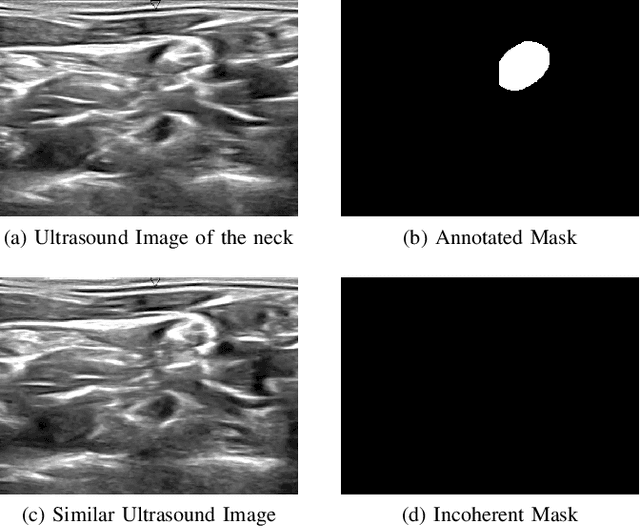
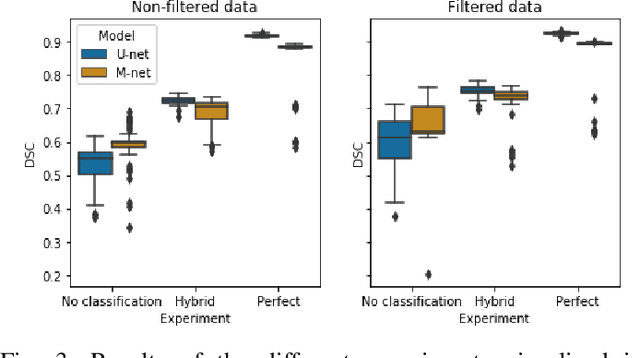

Abstract:Ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia (UGRA) can replace general anesthesia (GA), improving pain control and recovery time. This method can be applied on the brachial plexus (BP) after clavicular surgeries. However, identification of the BP from ultrasound (US) images is difficult, even for trained professionals. To address this problem, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and more advanced deep neural networks (DNNs) can be used for identification and segmentation of the BP nerve region. In this paper, we propose a hybrid model consisting of a classification model followed by a segmentation model to segment BP nerve regions in ultrasound images. A CNN model is employed as a classifier to precisely select the images with the BP region. Then, a U-net or M-net model is used for the segmentation. Our experimental results indicate that the proposed hybrid model significantly improves the segmentation performance over a single segmentation model.
XCAT-GAN for Synthesizing 3D Consistent Labeled Cardiac MR Images on Anatomically Variable XCAT Phantoms
Jul 31, 2020



Abstract:Generative adversarial networks (GANs) have provided promising data enrichment solutions by synthesizing high-fidelity images. However, generating large sets of labeled images with new anatomical variations remains unexplored. We propose a novel method for synthesizing cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) images on a population of virtual subjects with a large anatomical variation, introduced using the 4D eXtended Cardiac and Torso (XCAT) computerized human phantom. We investigate two conditional image synthesis approaches grounded on a semantically-consistent mask-guided image generation technique: 4-class and 8-class XCAT-GANs. The 4-class technique relies on only the annotations of the heart; while the 8-class technique employs a predicted multi-tissue label map of the heart-surrounding organs and provides better guidance for our conditional image synthesis. For both techniques, we train our conditional XCAT-GAN with real images paired with corresponding labels and subsequently at the inference time, we substitute the labels with the XCAT derived ones. Therefore, the trained network accurately transfers the tissue-specific textures to the new label maps. By creating 33 virtual subjects of synthetic CMR images at the end-diastolic and end-systolic phases, we evaluate the usefulness of such data in the downstream cardiac cavity segmentation task under different augmentation strategies. Results demonstrate that even with only 20% of real images (40 volumes) seen during training, segmentation performance is retained with the addition of synthetic CMR images. Moreover, the improvement in utilizing synthetic images for augmenting the real data is evident through the reduction of Hausdorff distance up to 28% and an increase in the Dice score up to 5%, indicating a higher similarity to the ground truth in all dimensions.
4D Semantic Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Image Synthesis on XCAT Anatomical Model
Feb 17, 2020



Abstract:We propose a hybrid controllable image generation method to synthesize anatomically meaningful 3D+t labeled Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR) images. Our hybrid method takes the mechanistic 4D eXtended CArdiac Torso (XCAT) heart model as the anatomical ground truth and synthesizes CMR images via a data-driven Generative Adversarial Network (GAN). We employ the state-of-the-art SPatially Adaptive De-normalization (SPADE) technique for conditional image synthesis to preserve the semantic spatial information of ground truth anatomy. Using the parameterized motion model of the XCAT heart, we generate labels for 25 time frames of the heart for one cardiac cycle at 18 locations for the short axis view. Subsequently, realistic images are generated from these labels, with modality-specific features that are learned from real CMR image data. We demonstrate that style transfer from another cardiac image can be accomplished by using a style encoder network. Due to the flexibility of XCAT in creating new heart models, this approach can result in a realistic virtual population to address different challenges the medical image analysis research community is facing such as expensive data collection. Our proposed method has a great potential to synthesize 4D controllable CMR images with annotations and adaptable styles to be used in various supervised multi-site, multi-vendor applications in medical image analysis.
Exploring the similarity of medical imaging classification problems
Jun 12, 2017



Abstract:Supervised learning is ubiquitous in medical image analysis. In this paper we consider the problem of meta-learning -- predicting which methods will perform well in an unseen classification problem, given previous experience with other classification problems. We investigate the first step of such an approach: how to quantify the similarity of different classification problems. We characterize datasets sampled from six classification problems by performance ranks of simple classifiers, and define the similarity by the inverse of Euclidean distance in this meta-feature space. We visualize the similarities in a 2D space, where meaningful clusters start to emerge, and show that the proposed representation can be used to classify datasets according to their origin with 89.3\% accuracy. These findings, together with the observations of recent trends in machine learning, suggest that meta-learning could be a valuable tool for the medical imaging community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge