Jihua Zhu
Chain-of-Thought Compression Should Not Be Blind: V-Skip for Efficient Multimodal Reasoning via Dual-Path Anchoring
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:While Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning significantly enhances the performance of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), its autoregressive nature incurs prohibitive latency constraints. Current efforts to mitigate this via token compression often fail by blindly applying text-centric metrics to multimodal contexts. We identify a critical failure mode termed Visual Amnesia, where linguistically redundant tokens are erroneously pruned, leading to hallucinations. To address this, we introduce V-Skip that reformulates token pruning as a Visual-Anchored Information Bottleneck (VA-IB) optimization problem. V-Skip employs a dual-path gating mechanism that weighs token importance through both linguistic surprisal and cross-modal attention flow, effectively rescuing visually salient anchors. Extensive experiments on Qwen2-VL and Llama-3.2 families demonstrate that V-Skip achieves a $2.9\times$ speedup with negligible accuracy loss. Specifically, it preserves fine-grained visual details, outperforming other baselines over 30\% on the DocVQA.
Point-SRA: Self-Representation Alignment for 3D Representation Learning
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Masked autoencoders (MAE) have become a dominant paradigm in 3D representation learning, setting new performance benchmarks across various downstream tasks. Existing methods with fixed mask ratio neglect multi-level representational correlations and intrinsic geometric structures, while relying on point-wise reconstruction assumptions that conflict with the diversity of point cloud. To address these issues, we propose a 3D representation learning method, termed Point-SRA, which aligns representations through self-distillation and probabilistic modeling. Specifically, we assign different masking ratios to the MAE to capture complementary geometric and semantic information, while the MeanFlow Transformer (MFT) leverages cross-modal conditional embeddings to enable diverse probabilistic reconstruction. Our analysis further reveals that representations at different time steps in MFT also exhibit complementarity. Therefore, a Dual Self-Representation Alignment mechanism is proposed at both the MAE and MFT levels. Finally, we design a Flow-Conditioned Fine-Tuning Architecture to fully exploit the point cloud distribution learned via MeanFlow. Point-SRA outperforms Point-MAE by 5.37% on ScanObjectNN. On intracranial aneurysm segmentation, it reaches 96.07% mean IoU for arteries and 86.87% for aneurysms. For 3D object detection, Point-SRA achieves 47.3% AP@50, surpassing MaskPoint by 5.12%.
ASCoT: An Adaptive Self-Correction Chain-of-Thought Method for Late-Stage Fragility in LLMs
Aug 07, 2025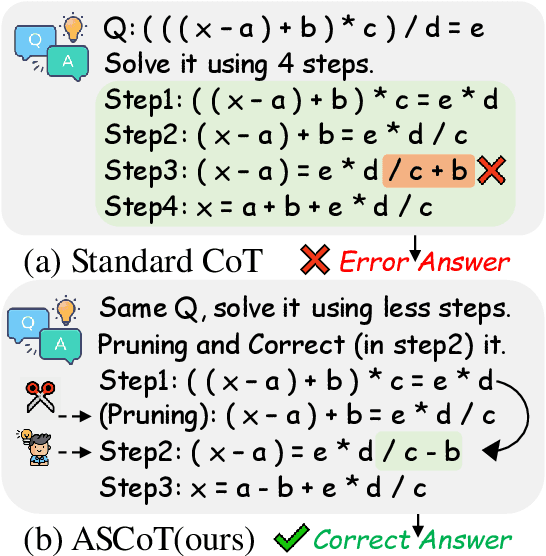
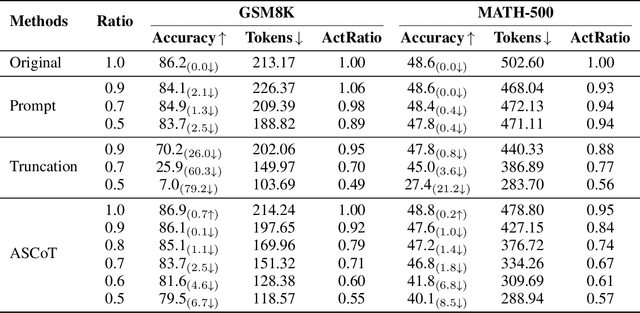
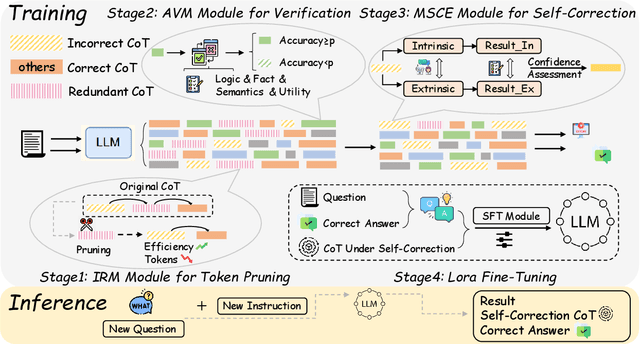
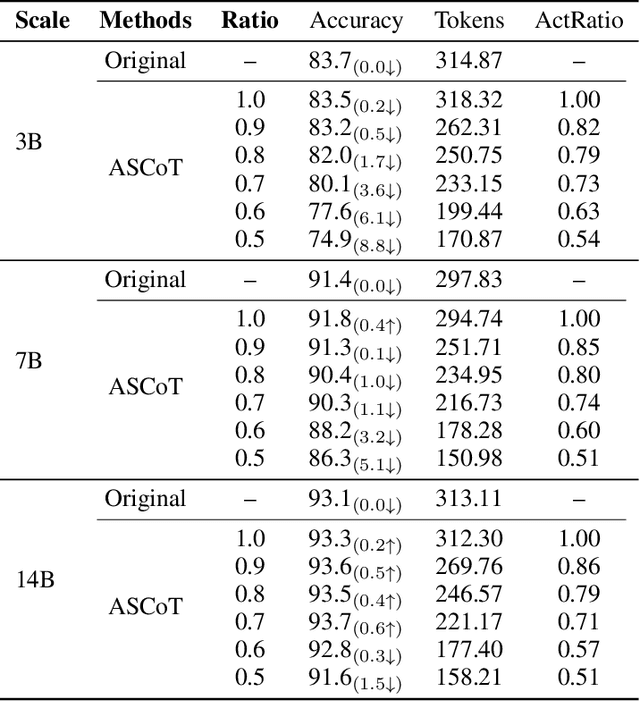
Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has significantly advanced the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), yet the reliability of these reasoning chains remains a critical challenge. A widely held "cascading failure" hypothesis suggests that errors are most detrimental when they occur early in the reasoning process. This paper challenges that assumption through systematic error-injection experiments, revealing a counter-intuitive phenomenon we term "Late-Stage Fragility": errors introduced in the later stages of a CoT chain are significantly more likely to corrupt the final answer than identical errors made at the beginning. To address this specific vulnerability, we introduce the Adaptive Self-Correction Chain-of-Thought (ASCoT) method. ASCoT employs a modular pipeline in which an Adaptive Verification Manager (AVM) operates first, followed by the Multi-Perspective Self-Correction Engine (MSCE). The AVM leverages a Positional Impact Score function I(k) that assigns different weights based on the position within the reasoning chains, addressing the Late-Stage Fragility issue by identifying and prioritizing high-risk, late-stage steps. Once these critical steps are identified, the MSCE applies robust, dual-path correction specifically to the failure parts. Extensive experiments on benchmarks such as GSM8K and MATH demonstrate that ASCoT achieves outstanding accuracy, outperforming strong baselines, including standard CoT. Our work underscores the importance of diagnosing specific failure modes in LLM reasoning and advocates for a shift from uniform verification strategies to adaptive, vulnerability-aware correction mechanisms.
AFBS:Buffer Gradient Selection in Semi-asynchronous Federated Learning
Jun 15, 2025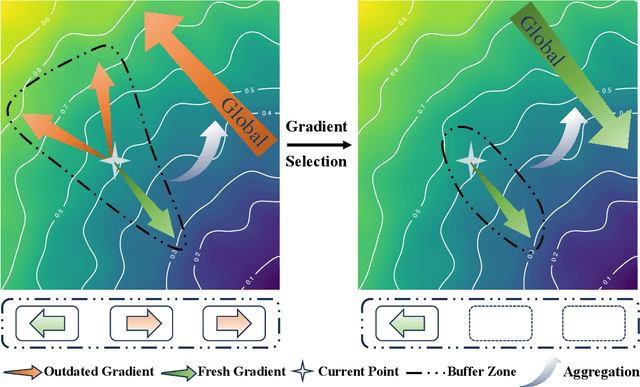



Abstract:Asynchronous federated learning (AFL) accelerates training by eliminating the need to wait for stragglers, but its asynchronous nature introduces gradient staleness, where outdated gradients degrade performance. Existing solutions address this issue with gradient buffers, forming a semi-asynchronous framework. However, this approach struggles when buffers accumulate numerous stale gradients, as blindly aggregating all gradients can harm training. To address this, we propose AFBS (Asynchronous FL Buffer Selection), the first algorithm to perform gradient selection within buffers while ensuring privacy protection. Specifically, the client sends the random projection encrypted label distribution matrix before training, and the server performs client clustering based on it. During training, server scores and selects gradients within each cluster based on their informational value, discarding low-value gradients to enhance semi-asynchronous federated learning. Extensive experiments in highly heterogeneous system and data environments demonstrate AFBS's superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods. Notably, on the most challenging task, CIFAR-100, AFBS improves accuracy by up to 4.8% over the previous best algorithm and reduces the time to reach target accuracy by 75%.
Matching Distance and Geometric Distribution Aided Learning Multiview Point Cloud Registration
May 06, 2025



Abstract:Multiview point cloud registration plays a crucial role in robotics, automation, and computer vision fields. This paper concentrates on pose graph construction and motion synchronization within multiview registration. Previous methods for pose graph construction often pruned fully connected graphs or constructed sparse graph using global feature aggregated from local descriptors, which may not consistently yield reliable results. To identify dependable pairs for pose graph construction, we design a network model that extracts information from the matching distance between point cloud pairs. For motion synchronization, we propose another neural network model to calculate the absolute pose in a data-driven manner, rather than optimizing inaccurate handcrafted loss functions. Our model takes into account geometric distribution information and employs a modified attention mechanism to facilitate flexible and reliable feature interaction. Experimental results on diverse indoor and outdoor datasets confirm the effectiveness and generalizability of our approach. The source code is available at https://github.com/Shi-Qi-Li/MDGD.
HFedCKD: Toward Robust Heterogeneous Federated Learning via Data-free Knowledge Distillation and Two-way Contrast
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Most current federated learning frameworks are modeled as static processes, ignoring the dynamic characteristics of the learning system. Under the limited communication budget of the central server, the flexible model architecture of a large number of clients participating in knowledge transfer requires a lower participation rate, active clients have uneven contributions, and the client scale seriously hinders the performance of FL. We consider a more general and practical federation scenario and propose a system heterogeneous federation method based on data-free knowledge distillation and two-way contrast (HFedCKD). We apply the Inverse Probability Weighted Distillation (IPWD) strategy to the data-free knowledge transfer framework. The generator completes the data features of the nonparticipating clients. IPWD implements a dynamic evaluation of the prediction contribution of each client under different data distributions. Based on the antibiased weighting of its prediction loss, the weight distribution of each client is effectively adjusted to fairly integrate the knowledge of participating clients. At the same time, the local model is split into a feature extractor and a classifier. Through differential contrast learning, the feature extractor is aligned with the global model in the feature space, while the classifier maintains personalized decision-making capabilities. HFedCKD effectively alleviates the knowledge offset caused by a low participation rate under data-free knowledge distillation and improves the performance and stability of the model. We conduct extensive experiments on image and IoT datasets to comprehensively evaluate and verify the generalization and robustness of the proposed HFedCKD framework.
Variable-frame CNNLSTM for Breast Nodule Classification using Ultrasound Videos
Feb 17, 2025



Abstract:The intersection of medical imaging and artificial intelligence has become an important research direction in intelligent medical treatment, particularly in the analysis of medical images using deep learning for clinical diagnosis. Despite the advances, existing keyframe classification methods lack extraction of time series features, while ultrasonic video classification based on three-dimensional convolution requires uniform frame numbers across patients, resulting in poor feature extraction efficiency and model classification performance. This study proposes a novel video classification method based on CNN and LSTM, introducing NLP's long and short sentence processing scheme into video classification for the first time. The method reduces CNN-extracted image features to 1x512 dimension, followed by sorting and compressing feature vectors for LSTM training. Specifically, feature vectors are sorted by patient video frame numbers and populated with padding value 0 to form variable batches, with invalid padding values compressed before LSTM training to conserve computing resources. Experimental results demonstrate that our variable-frame CNNLSTM method outperforms other approaches across all metrics, showing improvements of 3-6% in F1 score and 1.5% in specificity compared to keyframe methods. The variable-frame CNNLSTM also achieves better accuracy and precision than equal-frame CNNLSTM. These findings validate the effectiveness of our approach in classifying variable-frame ultrasound videos and suggest potential applications in other medical imaging modalities.
Advancing the Understanding of Fine-Grained 3D Forest Structures using Digital Cousins and Simulation-to-Reality: Methods and Datasets
Jan 07, 2025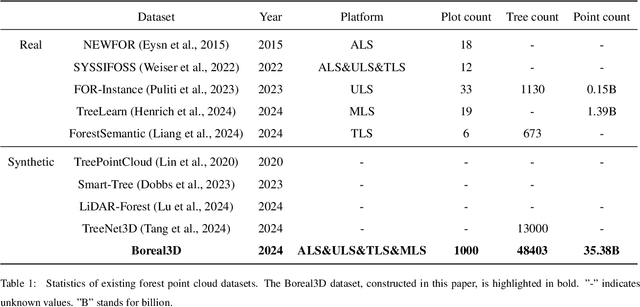
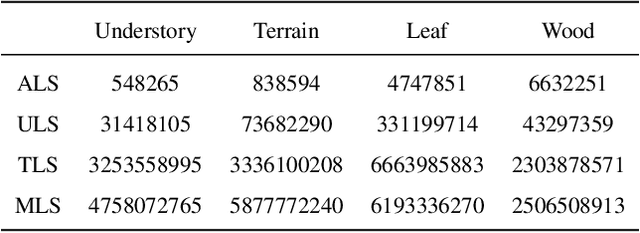
Abstract:Understanding and analyzing the spatial semantics and structure of forests is essential for accurate forest resource monitoring and ecosystem research. However, the lack of large-scale and annotated datasets has limited the widespread use of advanced intelligent techniques in this field. To address this challenge, a fully automated synthetic data generation and processing framework based on the concepts of Digital Cousins and Simulation-to-Reality (Sim2Real) is proposed, offering versatility and scalability to any size and platform. Using this process, we created the Boreal3D, the world's largest forest point cloud dataset. It includes 1000 highly realistic and structurally diverse forest plots across four different platforms, totaling 48,403 trees and over 35.3 billion points. Each point is labeled with semantic, instance, and viewpoint information, while each tree is described with structural parameters such as diameter, crown width, leaf area, and total volume. We designed and conducted extensive experiments to evaluate the potential of Boreal3D in advancing fine-grained 3D forest structure analysis in real-world applications. The results demonstrate that with certain strategies, models pre-trained on synthetic data can significantly improve performance when applied to real forest datasets. Especially, the findings reveal that fine-tuning with only 20% of real-world data enables the model to achieve performance comparable to models trained exclusively on entire real-world data, highlighting the value and potential of our proposed framework. The Boreal3D dataset, and more broadly, the synthetic data augmentation framework, is poised to become a critical resource for advancing research in large-scale 3D forest scene understanding and structural parameter estimation.
SYKI-SVC: Advancing Singing Voice Conversion with Post-Processing Innovations and an Open-Source Professional Testset
Jan 06, 2025Abstract:Singing voice conversion aims to transform a source singing voice into that of a target singer while preserving the original lyrics, melody, and various vocal techniques. In this paper, we propose a high-fidelity singing voice conversion system. Our system builds upon the SVCC T02 framework and consists of three key components: a feature extractor, a voice converter, and a post-processor. The feature extractor utilizes the ContentVec and Whisper models to derive F0 contours and extract speaker-independent linguistic features from the input singing voice. The voice converter then integrates the extracted timbre, F0, and linguistic content to synthesize the target speaker's waveform. The post-processor augments high-frequency information directly from the source through simple and effective signal processing to enhance audio quality. Due to the lack of a standardized professional dataset for evaluating expressive singing conversion systems, we have created and made publicly available a specialized test set. Comparative evaluations demonstrate that our system achieves a remarkably high level of naturalness, and further analysis confirms the efficacy of our proposed system design.
TPFL: A Trustworthy Personalized Federated Learning Framework via Subjective Logic
Oct 16, 2024Abstract:Federated learning (FL) enables collaborative model training across distributed clients while preserving data privacy. Despite its widespread adoption, most FL approaches focusing solely on privacy protection fall short in scenarios where trustworthiness is crucial, necessitating advancements in secure training, dependable decision-making mechanisms, robustness on corruptions, and enhanced performance with Non-IID data. To bridge this gap, we introduce Trustworthy Personalized Federated Learning (TPFL) framework designed for classification tasks via subjective logic in this paper. Specifically, TPFL adopts a unique approach by employing subjective logic to construct federated models, providing probabilistic decisions coupled with an assessment of uncertainty rather than mere probability assignments. By incorporating a trainable heterogeneity prior to the local training phase, TPFL effectively mitigates the adverse effects of data heterogeneity. Model uncertainty and instance uncertainty are further utilized to ensure the safety and reliability of the training and inference stages. Through extensive experiments on widely recognized federated learning benchmarks, we demonstrate that TPFL not only achieves competitive performance compared with advanced methods but also exhibits resilience against prevalent malicious attacks, robustness on domain shifts, and reliability in high-stake scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge