Haoran Gong
School of Software Engineering, Xian Jiaotong University
Advancing the Understanding of Fine-Grained 3D Forest Structures using Digital Cousins and Simulation-to-Reality: Methods and Datasets
Jan 07, 2025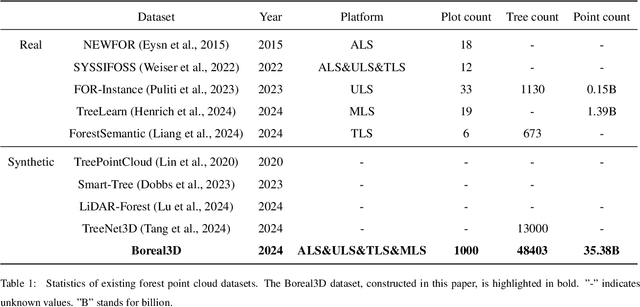
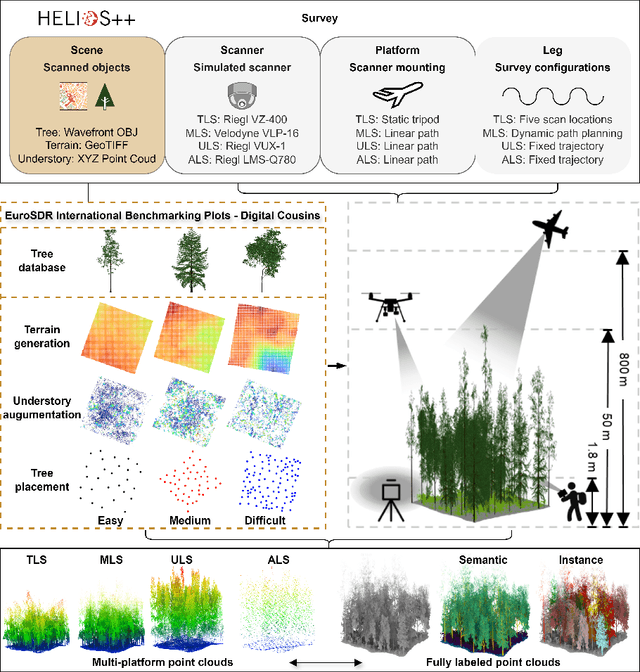
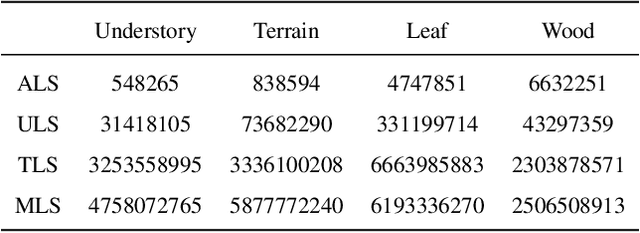
Abstract:Understanding and analyzing the spatial semantics and structure of forests is essential for accurate forest resource monitoring and ecosystem research. However, the lack of large-scale and annotated datasets has limited the widespread use of advanced intelligent techniques in this field. To address this challenge, a fully automated synthetic data generation and processing framework based on the concepts of Digital Cousins and Simulation-to-Reality (Sim2Real) is proposed, offering versatility and scalability to any size and platform. Using this process, we created the Boreal3D, the world's largest forest point cloud dataset. It includes 1000 highly realistic and structurally diverse forest plots across four different platforms, totaling 48,403 trees and over 35.3 billion points. Each point is labeled with semantic, instance, and viewpoint information, while each tree is described with structural parameters such as diameter, crown width, leaf area, and total volume. We designed and conducted extensive experiments to evaluate the potential of Boreal3D in advancing fine-grained 3D forest structure analysis in real-world applications. The results demonstrate that with certain strategies, models pre-trained on synthetic data can significantly improve performance when applied to real forest datasets. Especially, the findings reveal that fine-tuning with only 20% of real-world data enables the model to achieve performance comparable to models trained exclusively on entire real-world data, highlighting the value and potential of our proposed framework. The Boreal3D dataset, and more broadly, the synthetic data augmentation framework, is poised to become a critical resource for advancing research in large-scale 3D forest scene understanding and structural parameter estimation.
CompetitorFormer: Competitor Transformer for 3D Instance Segmentation
Nov 21, 2024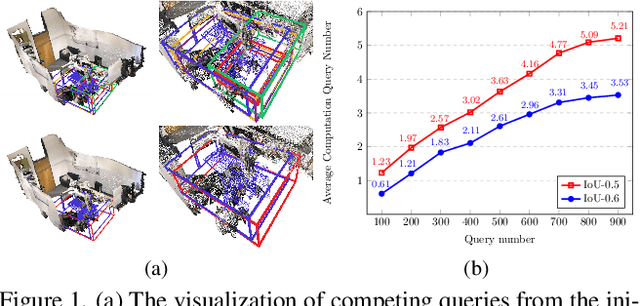
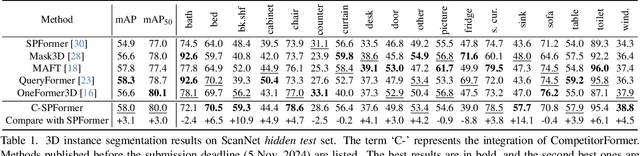
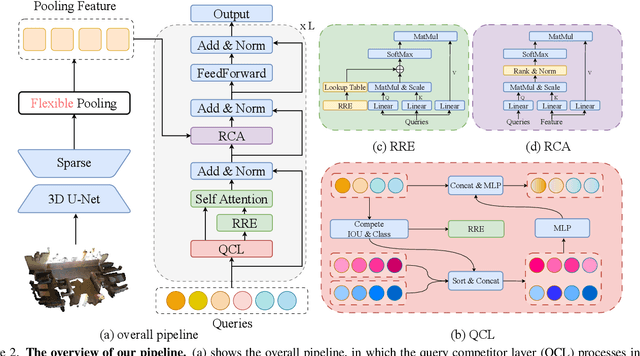
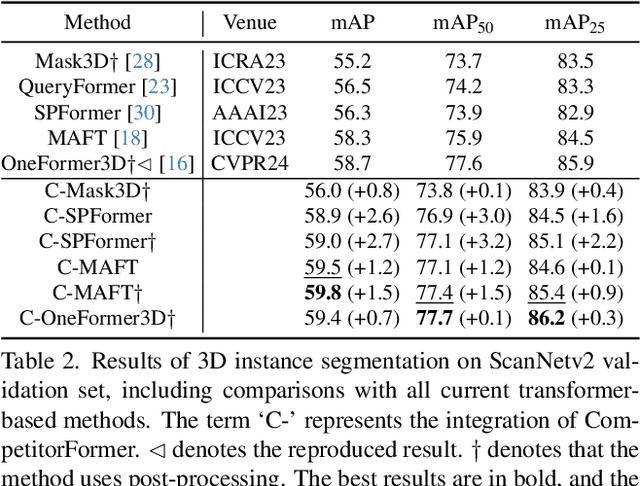
Abstract:Transformer-based methods have become the dominant approach for 3D instance segmentation. These methods predict instance masks via instance queries, ranking them by classification confidence and IoU scores to select the top prediction as the final outcome. However, it has been observed that the current models employ a fixed and higher number of queries than the instances present within a scene. In such instances, multiple queries predict the same instance, yet only a single query is ultimately optimized. The close scores of queries in the lower-level decoders make it challenging for the dominant query to distinguish itself rapidly, which ultimately impairs the model's accuracy and convergence efficiency. This phenomenon is referred to as inter-query competition. To address this challenge, we put forth a series of plug-and-play competition-oriented designs, collectively designated as the CompetitorFormer, with the aim of reducing competition and facilitating a dominant query. Experiments showed that integrating our designs with state-of-the-art frameworks consistently resulted in significant performance improvements in 3D instance segmentation across a range of datasets.
Enhanced Semantic Segmentation for Large-Scale and Imbalanced Point Clouds
Sep 21, 2024



Abstract:Semantic segmentation of large-scale point clouds is of significant importance in environment perception and scene understanding. However, point clouds collected from real-world environments are usually imbalanced and small-sized objects are prone to be under-sampled or misclassified due to their low occurrence frequency, thereby reducing the overall accuracy of semantic segmentation. In this study, we propose the Multilateral Cascading Network (MCNet) for large-scale and sample-imbalanced point cloud scenes. To increase the frequency of small-sized objects, we introduce the semantic-weighted sampling module, which incorporates a probability parameter into the collected data group. To facilitate feature learning, we propose a Multilateral Cascading Attention Enhancement (MCAE) module to learn complex local features through multilateral cascading operations and attention mechanisms. To promote feature fusion, we propose a Point Cross Stage Partial (P-CSP) module to combine global and local features, optimizing the integration of valuable feature information across multiple scales. Finally, we introduce the neighborhood voting module to integrate results at the output layer. Our proposed method demonstrates either competitive or superior performance relative to state-of-the-art approaches across three widely recognized benchmark datasets: S3DIS, Toronto3D, and SensatUrban with mIoU scores of 74.0\%, 82.9\% and 64.5\%, respectively. Notably, our work yielded consistent optimal results on the under-sampled semantic categories, thereby demonstrating exceptional performance in the recognition of small-sized objects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge