Yinghui Quan
School of Electronic Engineering, Xidian University
A Unified Anti-Jamming Design in Complex Environments Based on Cross-Modal Fusion and Intelligent Decision-Making
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:With the rapid development of radar jamming systems, especially digital radio frequency memory (DRFM), the electromagnetic environment has become increasingly complex. In recent years, most existing studies have focused solely on either jamming recognition or anti-jamming strategy design. In this paper, we propose a unified framework that integrates interference recognition with intelligent anti-jamming strategy selection. Specifically, time-frequency (TF) features of radar echoes are first extracted using both Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) and Smoothed Pseudo Wigner-Ville Distribution (SPWVD). A feature fusion method is then designed to effectively combine these two types of time-frequency representations. The fused TF features are further combined with time-domain features of the radar echoes through a cross-modal fusion module based on an attention mechanism. Finally, the recognition results, together with information obtained from the passive radar, are fed into a Deep Q-Network (DQN)-based intelligent anti-jamming strategy network to select jamming suppression waveforms. The key jamming parameters obtained by the passive radar provide essential information for intelligent decision-making, enabling the generation of more effective strategies tailored to specific jamming types. The proposed method demonstrates improvements in both jamming type recognition accuracy and the stability of anti-jamming strategy selection under complex environments. Experimental results show that our method achieves superior performance compared to Support Vector Machines (SVM), VGG-16, and 2D-CNN methods, with respective improvements of 1.41%, 2.5%, and 14.51% in overall accuracy. Moreover, in comparison with the SARSA algorithm, the designed algorithm achieves faster reward convergence and more stable strategy generation.
Monopulse Parameter Estimation based on MIMO-STCA Radar in the Presence of Multiple Mainlobe Jammings
May 10, 2025Abstract:The monopulse technique is characterized by its high accuracy in angle estimation and simplicity in engineering implementation. However, in the complex electromagnetic environment, the presence of the mainlobe jamming (MLJ) greatly degrades the accuracy of angle estimation. Conventional methods of jamming suppression often lead to significant deviations in monopulse ratio while suppressing MLJ. Additionally, the monopulse technique based on traditional radar cannot jointly estimate the target's range. In this paper, the four-channel adaptive beamforming (ABF) algorithm is proposed, which adds a delta-delta channel based on conventional sum-difference-difference three-channel to suppress a single MLJ. Moreover, considering the suppression of multiple MLJs and sidelobe jammings (SLJs), the row-column ABF algorithm is proposed. This algorithm utilizes more spatial degrees of freedom (DOFs) to suppress multiple jammings by the row-column adaptive beamforming at the subarray level. The key ideal of both algorithms is to suppress MLJ with null along one spatial direction while keeping the sum and difference beampatterns undistorted along another spatial direction. Therefore, the monopulse ratio remains undistorted while suppressing the MLJ, ensuring the accuracy of monopulse parameter estimation. Furthermore, by utilizing the additional degrees of freedom (DOFs) in the range domain provided by the multiple-input multiple-output space-time coding array (MIMO-STCA) radar, joint angle-range estimation can be achieved through the monopulse technique. Simulation results highlight the effectiveness of the proposed methods in suppressing multiple MLJs and enhancing the accuracy of monopulse parameter estimation, as verified by the low root mean square error (RMSE) in the parameter estimation results.
A Deep Learning-Based Supervised Transfer Learning Framework for DOA Estimation with Array Imperfections
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:In practical scenarios, processes such as sensor design, manufacturing, and installation will introduce certain errors. Furthermore, mutual interference occurs when the sensors receive signals. These defects in array systems are referred to as array imperfections, which can significantly degrade the performance of Direction of Arrival (DOA) estimation. In this study, we propose a deep-learning based transfer learning approach, which effectively mitigates the degradation of deep-learning based DOA estimation performance caused by array imperfections. In the proposed approach, we highlight three major contributions. First, we propose a Vision Transformer (ViT) based method for DOA estimation, which achieves excellent performance in scenarios with low signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) and limited snapshots. Second, we introduce a transfer learning framework that extends deep learning models from ideal simulation scenarios to complex real-world scenarios with array imperfections. By leveraging prior knowledge from ideal simulation data, the proposed transfer learning framework significantly improves deep learning-based DOA estimation performance in the presence of array imperfections, without the need for extensive real-world data. Finally, we incorporate visualization and evaluation metrics to assess the performance of DOA estimation algorithms, which allow for a more thorough evaluation of algorithms and further validate the proposed method. Our code can be accessed at https://github.com/zzb-nice/DOA_est_Master.
CompetitorFormer: Competitor Transformer for 3D Instance Segmentation
Nov 21, 2024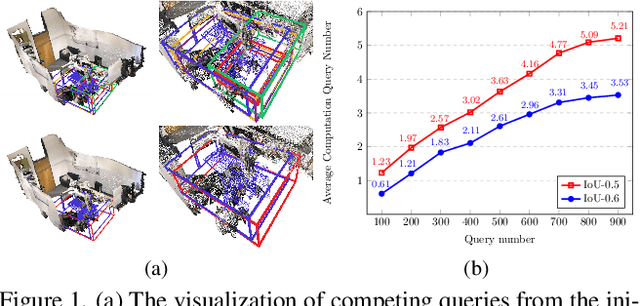
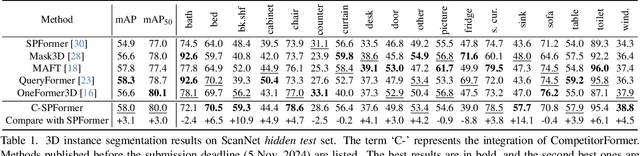
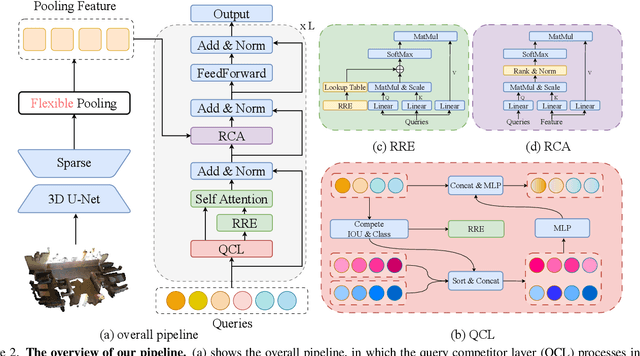
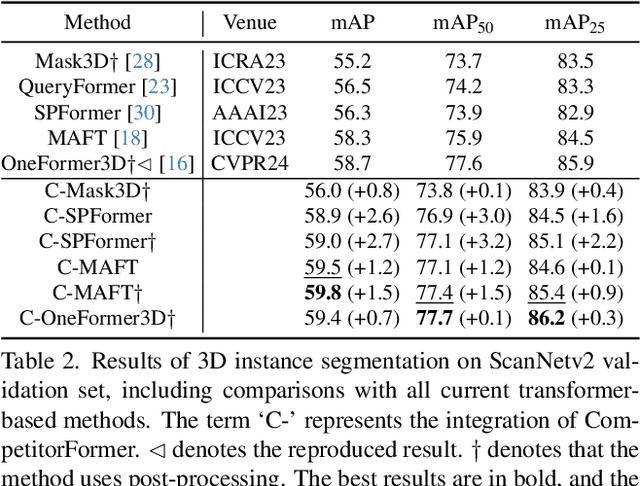
Abstract:Transformer-based methods have become the dominant approach for 3D instance segmentation. These methods predict instance masks via instance queries, ranking them by classification confidence and IoU scores to select the top prediction as the final outcome. However, it has been observed that the current models employ a fixed and higher number of queries than the instances present within a scene. In such instances, multiple queries predict the same instance, yet only a single query is ultimately optimized. The close scores of queries in the lower-level decoders make it challenging for the dominant query to distinguish itself rapidly, which ultimately impairs the model's accuracy and convergence efficiency. This phenomenon is referred to as inter-query competition. To address this challenge, we put forth a series of plug-and-play competition-oriented designs, collectively designated as the CompetitorFormer, with the aim of reducing competition and facilitating a dominant query. Experiments showed that integrating our designs with state-of-the-art frameworks consistently resulted in significant performance improvements in 3D instance segmentation across a range of datasets.
Efficiently Expanding Receptive Fields: Local Split Attention and Parallel Aggregation for Enhanced Large-scale Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation
Sep 03, 2024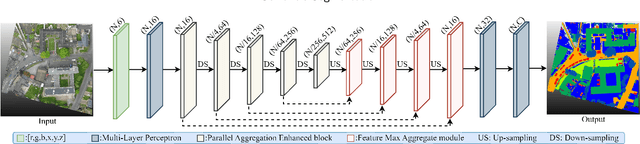
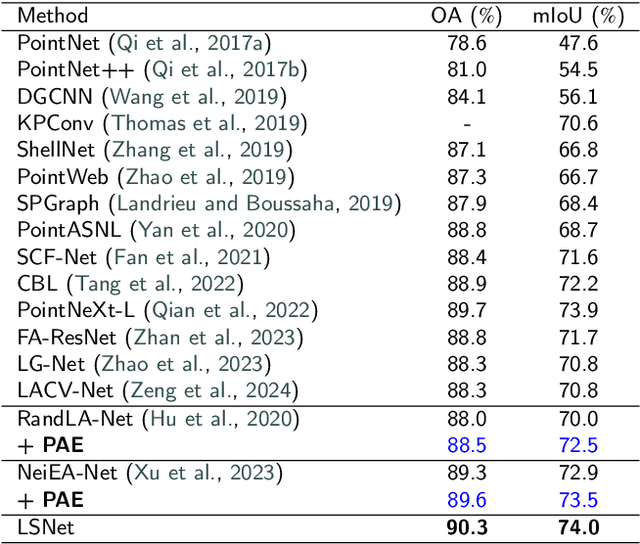
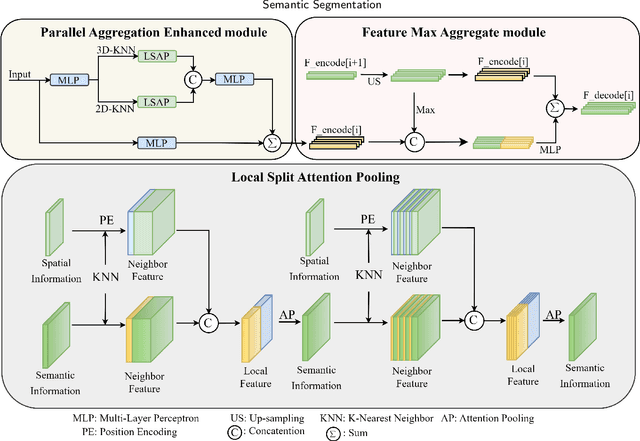
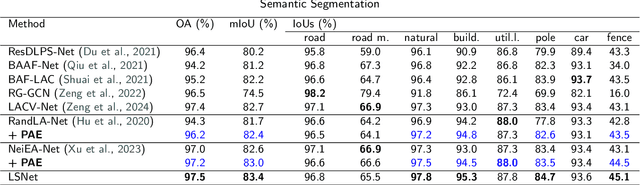
Abstract:Expanding the receptive field in a deep learning model for large-scale 3D point cloud segmentation is an effective technique for capturing rich contextual information, which consequently enhances the network's ability to learn meaningful features. However, this often leads to increased computational complexity and risk of overfitting, challenging the efficiency and effectiveness of the learning paradigm. To address these limitations, we propose the Local Split Attention Pooling (LSAP) mechanism to effectively expand the receptive field through a series of local split operations, thus facilitating the acquisition of broader contextual knowledge. Concurrently, it optimizes the computational workload associated with attention-pooling layers to ensure a more streamlined processing workflow. Based on LSAP, a Parallel Aggregation Enhancement (PAE) module is introduced to enable parallel processing of data using both 2D and 3D neighboring information to further enhance contextual representations within the network. In light of the aforementioned designs, we put forth a novel framework, designated as LSNet, for large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation. Extensive evaluations demonstrated the efficacy of seamlessly integrating the proposed PAE module into existing frameworks, yielding significant improvements in mean intersection over union (mIoU) metrics, with a notable increase of up to 11%. Furthermore, LSNet demonstrated superior performance compared to state-of-the-art semantic segmentation networks on three benchmark datasets, including S3DIS, Toronto3D, and SensatUrban. It is noteworthy that our method achieved a substantial speedup of approximately 38.8% compared to those employing similar-sized receptive fields, which serves to highlight both its computational efficiency and practical utility in real-world large-scale scenes.
Scaling and Masking: A New Paradigm of Data Sampling for Image and Video Quality Assessment
Jan 05, 2024



Abstract:Quality assessment of images and videos emphasizes both local details and global semantics, whereas general data sampling methods (e.g., resizing, cropping or grid-based fragment) fail to catch them simultaneously. To address the deficiency, current approaches have to adopt multi-branch models and take as input the multi-resolution data, which burdens the model complexity. In this work, instead of stacking up models, a more elegant data sampling method (named as SAMA, scaling and masking) is explored, which compacts both the local and global content in a regular input size. The basic idea is to scale the data into a pyramid first, and reduce the pyramid into a regular data dimension with a masking strategy. Benefiting from the spatial and temporal redundancy in images and videos, the processed data maintains the multi-scale characteristics with a regular input size, thus can be processed by a single-branch model. We verify the sampling method in image and video quality assessment. Experiments show that our sampling method can improve the performance of current single-branch models significantly, and achieves competitive performance to the multi-branch models without extra model complexity. The source code will be available at https://github.com/Sissuire/SAMA.
A Novel Granular-Based Bi-Clustering Method of Deep Mining the Co-Expressed Genes
May 12, 2020


Abstract:Traditional clustering methods are limited when dealing with huge and heterogeneous groups of gene expression data, which motivates the development of bi-clustering methods. Bi-clustering methods are used to mine bi-clusters whose subsets of samples (genes) are co-regulated under their test conditions. Studies show that mining bi-clusters of consistent trends and trends with similar degrees of fluctuations from the gene expression data is essential in bioinformatics research. Unfortunately, traditional bi-clustering methods are not fully effective in discovering such bi-clusters. Therefore, we propose a novel bi-clustering method by involving here the theory of Granular Computing. In the proposed scheme, the gene data matrix, considered as a group of time series, is transformed into a series of ordered information granules. With the information granules we build a characteristic matrix of the gene data to capture the fluctuation trend of the expression value between consecutive conditions to mine the ideal bi-clusters. The experimental results are in agreement with the theoretical analysis, and show the excellent performance of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge