Huake Wang
A Unified Anti-Jamming Design in Complex Environments Based on Cross-Modal Fusion and Intelligent Decision-Making
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:With the rapid development of radar jamming systems, especially digital radio frequency memory (DRFM), the electromagnetic environment has become increasingly complex. In recent years, most existing studies have focused solely on either jamming recognition or anti-jamming strategy design. In this paper, we propose a unified framework that integrates interference recognition with intelligent anti-jamming strategy selection. Specifically, time-frequency (TF) features of radar echoes are first extracted using both Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) and Smoothed Pseudo Wigner-Ville Distribution (SPWVD). A feature fusion method is then designed to effectively combine these two types of time-frequency representations. The fused TF features are further combined with time-domain features of the radar echoes through a cross-modal fusion module based on an attention mechanism. Finally, the recognition results, together with information obtained from the passive radar, are fed into a Deep Q-Network (DQN)-based intelligent anti-jamming strategy network to select jamming suppression waveforms. The key jamming parameters obtained by the passive radar provide essential information for intelligent decision-making, enabling the generation of more effective strategies tailored to specific jamming types. The proposed method demonstrates improvements in both jamming type recognition accuracy and the stability of anti-jamming strategy selection under complex environments. Experimental results show that our method achieves superior performance compared to Support Vector Machines (SVM), VGG-16, and 2D-CNN methods, with respective improvements of 1.41%, 2.5%, and 14.51% in overall accuracy. Moreover, in comparison with the SARSA algorithm, the designed algorithm achieves faster reward convergence and more stable strategy generation.
Mainlobe Jamming Suppression Using MIMO-STCA Radar
May 14, 2025Abstract:Radar jamming suppression, particularly against mainlobe jamming, has become a critical focus in modern radar systems. This article investigates advanced mainlobe jamming suppression techniques utilizing a novel multiple-input multiple-output space-time coding array (MIMO-STCA) radar. Extending the capabilities of traditional MIMO radar, the MIMO-STCA framework introduces additional degrees of freedom (DoFs) in the range domain through the utilization of transmit time delays, offering enhanced resilience against interference. One of the key challenges in mainlobe jamming scenarios is the difficulty in obtaining interference-plus-noise samples that are free from target signal contamination. To address this, the study introduces a cumulative sampling-based non-homogeneous sample selection (CS-NHSS) algorithm to remove target-contaminated samples, ensuring accurate interference-plus-noise covariance matrix estimation and effective noise subspace separation. Building on this, the subsequent step is to apply the proposed noise subspace-based jamming mitigation (NSJM) algorithm, which leverages the orthogonality between noise and jamming subspace for effective jamming mitigation. However, NSJM performance can degrade due to spatial frequency mismatches caused by DoA or range quantization errors. To overcome this limitation, the study further proposes the robust jamming mitigation via noise subspace (RJNS) algorithm, incorporating adaptive beampattern control to achieve a flat-top mainlobe and broadened nulls, enhancing both anti-jamming effectiveness and robustness under non-ideal conditions. Simulation results verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms. Significant improvements in mainlobe jamming suppression are demonstrated through transmit-receive beampattern analysis and enhanced signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) curve.
Monopulse Parameter Estimation based on MIMO-STCA Radar in the Presence of Multiple Mainlobe Jammings
May 10, 2025Abstract:The monopulse technique is characterized by its high accuracy in angle estimation and simplicity in engineering implementation. However, in the complex electromagnetic environment, the presence of the mainlobe jamming (MLJ) greatly degrades the accuracy of angle estimation. Conventional methods of jamming suppression often lead to significant deviations in monopulse ratio while suppressing MLJ. Additionally, the monopulse technique based on traditional radar cannot jointly estimate the target's range. In this paper, the four-channel adaptive beamforming (ABF) algorithm is proposed, which adds a delta-delta channel based on conventional sum-difference-difference three-channel to suppress a single MLJ. Moreover, considering the suppression of multiple MLJs and sidelobe jammings (SLJs), the row-column ABF algorithm is proposed. This algorithm utilizes more spatial degrees of freedom (DOFs) to suppress multiple jammings by the row-column adaptive beamforming at the subarray level. The key ideal of both algorithms is to suppress MLJ with null along one spatial direction while keeping the sum and difference beampatterns undistorted along another spatial direction. Therefore, the monopulse ratio remains undistorted while suppressing the MLJ, ensuring the accuracy of monopulse parameter estimation. Furthermore, by utilizing the additional degrees of freedom (DOFs) in the range domain provided by the multiple-input multiple-output space-time coding array (MIMO-STCA) radar, joint angle-range estimation can be achieved through the monopulse technique. Simulation results highlight the effectiveness of the proposed methods in suppressing multiple MLJs and enhancing the accuracy of monopulse parameter estimation, as verified by the low root mean square error (RMSE) in the parameter estimation results.
LDM-RSIC: Exploring Distortion Prior with Latent Diffusion Models for Remote Sensing Image Compression
Jun 06, 2024Abstract:Deep learning-based image compression algorithms typically focus on designing encoding and decoding networks and improving the accuracy of entropy model estimation to enhance the rate-distortion (RD) performance. However, few algorithms leverage the compression distortion prior from existing compression algorithms to improve RD performance. In this paper, we propose a latent diffusion model-based remote sensing image compression (LDM-RSIC) method, which aims to enhance the final decoding quality of RS images by utilizing the generated distortion prior from a LDM. Our approach consists of two stages. In the first stage, a self-encoder learns prior from the high-quality input image. In the second stage, the prior is generated through an LDM, conditioned on the decoded image of an existing learning-based image compression algorithm, to be used as auxiliary information for generating the texture-rich enhanced image. To better utilize the prior, a channel attention and gate-based dynamic feature attention module (DFAM) is embedded into a Transformer-based multi-scale enhancement network (MEN) for image enhancement. Extensive experiments demonstrate the proposed LDM-RSIC significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art traditional and learning-based image compression algorithms in terms of both subjective perception and objective metrics. Additionally, we use the LDM-based scheme to improve the traditional image compression algorithm JPEG2000 and obtain 32.00% bit savings on the DOTA testing set. The code will be available at https://github.com/mlkk518/LDM-RSIC.
Dual Degradation-Inspired Deep Unfolding Network for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Aug 05, 2023



Abstract:Although low-light image enhancement has achieved great stride based on deep enhancement models, most of them mainly stress on enhancement performance via an elaborated black-box network and rarely explore the physical significance of enhancement models. Towards this issue, we propose a Dual degrAdation-inSpired deep Unfolding network, termed DASUNet, for low-light image enhancement. Specifically, we construct a dual degradation model (DDM) to explicitly simulate the deterioration mechanism of low-light images. It learns two distinct image priors via considering degradation specificity between luminance and chrominance spaces. To make the proposed scheme tractable, we design an alternating optimization solution to solve the proposed DDM. Further, the designed solution is unfolded into a specified deep network, imitating the iteration updating rules, to form DASUNet. Local and long-range information are obtained by prior modeling module (PMM), inheriting the advantages of convolution and Transformer, to enhance the representation capability of dual degradation priors. Additionally, a space aggregation module (SAM) is presented to boost the interaction of two degradation models. Extensive experiments on multiple popular low-light image datasets validate the effectiveness of DASUNet compared to canonical state-of-the-art low-light image enhancement methods. Our source code and pretrained model will be publicly available.
Division Gets Better: Learning Brightness-Aware and Detail-Sensitive Representations for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Jul 18, 2023Abstract:Low-light image enhancement strives to improve the contrast, adjust the visibility, and restore the distortion in color and texture. Existing methods usually pay more attention to improving the visibility and contrast via increasing the lightness of low-light images, while disregarding the significance of color and texture restoration for high-quality images. Against above issue, we propose a novel luminance and chrominance dual branch network, termed LCDBNet, for low-light image enhancement, which divides low-light image enhancement into two sub-tasks, e.g., luminance adjustment and chrominance restoration. Specifically, LCDBNet is composed of two branches, namely luminance adjustment network (LAN) and chrominance restoration network (CRN). LAN takes responsibility for learning brightness-aware features leveraging long-range dependency and local attention correlation. While CRN concentrates on learning detail-sensitive features via multi-level wavelet decomposition. Finally, a fusion network is designed to blend their learned features to produce visually impressive images. Extensive experiments conducted on seven benchmark datasets validate the effectiveness of our proposed LCDBNet, and the results manifest that LCDBNet achieves superior performance in terms of multiple reference/non-reference quality evaluators compared to other state-of-the-art competitors. Our code and pretrained model will be available.
Sparsity and Coefficient Permutation Based Two-Domain AMP for Image Block Compressed Sensing
May 22, 2023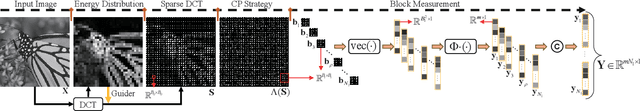

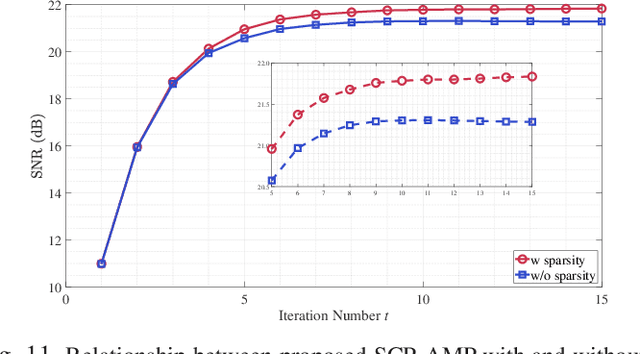
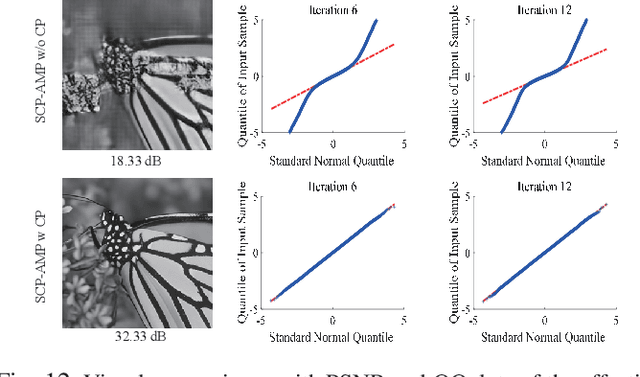
Abstract:The learned denoising-based approximate message passing (LDAMP) algorithm has attracted great attention for image compressed sensing (CS) tasks. However, it has two issues: first, its global measurement model severely restricts its applicability to high-dimensional images, and its block-based measurement method exhibits obvious block artifacts; second, the denoiser in the LDAMP is too simple, and existing denoisers have limited ability in detail recovery. In this paper, to overcome the issues and develop a high-performance LDAMP method for image block compressed sensing (BCS), we propose a novel sparsity and coefficient permutation-based AMP (SCP-AMP) method consisting of the block-based sampling and the two-domain reconstruction modules. In the sampling module, SCP-AMP adopts a discrete cosine transform (DCT) based sparsity strategy to reduce the impact of the high-frequency coefficient on the reconstruction, followed by a coefficient permutation strategy to avoid block artifacts. In the reconstruction module, a two-domain AMP method with DCT domain noise correction and pixel domain denoising is proposed for iterative reconstruction. Regarding the denoiser, we proposed a multi-level deep attention network (MDANet) to enhance the texture details by employing multi-level features and multiple attention mechanisms. Extensive experiments demonstrated that the proposed SCP-AMP method achieved better reconstruction accuracy than other state-of-the-art BCS algorithms in terms of both visual perception and objective metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge