Yujie Dun
LDM-RSIC: Exploring Distortion Prior with Latent Diffusion Models for Remote Sensing Image Compression
Jun 06, 2024Abstract:Deep learning-based image compression algorithms typically focus on designing encoding and decoding networks and improving the accuracy of entropy model estimation to enhance the rate-distortion (RD) performance. However, few algorithms leverage the compression distortion prior from existing compression algorithms to improve RD performance. In this paper, we propose a latent diffusion model-based remote sensing image compression (LDM-RSIC) method, which aims to enhance the final decoding quality of RS images by utilizing the generated distortion prior from a LDM. Our approach consists of two stages. In the first stage, a self-encoder learns prior from the high-quality input image. In the second stage, the prior is generated through an LDM, conditioned on the decoded image of an existing learning-based image compression algorithm, to be used as auxiliary information for generating the texture-rich enhanced image. To better utilize the prior, a channel attention and gate-based dynamic feature attention module (DFAM) is embedded into a Transformer-based multi-scale enhancement network (MEN) for image enhancement. Extensive experiments demonstrate the proposed LDM-RSIC significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art traditional and learning-based image compression algorithms in terms of both subjective perception and objective metrics. Additionally, we use the LDM-based scheme to improve the traditional image compression algorithm JPEG2000 and obtain 32.00% bit savings on the DOTA testing set. The code will be available at https://github.com/mlkk518/LDM-RSIC.
Division Gets Better: Learning Brightness-Aware and Detail-Sensitive Representations for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Jul 18, 2023Abstract:Low-light image enhancement strives to improve the contrast, adjust the visibility, and restore the distortion in color and texture. Existing methods usually pay more attention to improving the visibility and contrast via increasing the lightness of low-light images, while disregarding the significance of color and texture restoration for high-quality images. Against above issue, we propose a novel luminance and chrominance dual branch network, termed LCDBNet, for low-light image enhancement, which divides low-light image enhancement into two sub-tasks, e.g., luminance adjustment and chrominance restoration. Specifically, LCDBNet is composed of two branches, namely luminance adjustment network (LAN) and chrominance restoration network (CRN). LAN takes responsibility for learning brightness-aware features leveraging long-range dependency and local attention correlation. While CRN concentrates on learning detail-sensitive features via multi-level wavelet decomposition. Finally, a fusion network is designed to blend their learned features to produce visually impressive images. Extensive experiments conducted on seven benchmark datasets validate the effectiveness of our proposed LCDBNet, and the results manifest that LCDBNet achieves superior performance in terms of multiple reference/non-reference quality evaluators compared to other state-of-the-art competitors. Our code and pretrained model will be available.
Learning Data-Driven Vector-Quantized Degradation Model for Animation Video Super-Resolution
Mar 17, 2023

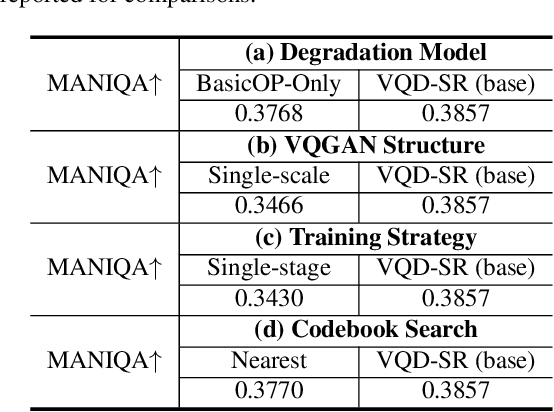
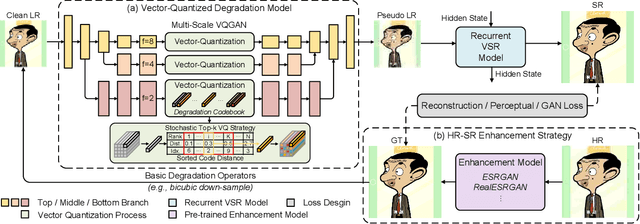
Abstract:Existing real-world video super-resolution (VSR) methods focus on designing a general degradation pipeline for open-domain videos while ignoring data intrinsic characteristics which strongly limit their performance when applying to some specific domains (e.g. animation videos). In this paper, we thoroughly explore the characteristics of animation videos and leverage the rich priors in real-world animation data for a more practical animation VSR model. In particular, we propose a multi-scale Vector-Quantized Degradation model for animation video Super-Resolution (VQD-SR) to decompose the local details from global structures and transfer the degradation priors in real-world animation videos to a learned vector-quantized codebook for degradation modeling. A rich-content Real Animation Low-quality (RAL) video dataset is collected for extracting the priors. We further propose a data enhancement strategy for high-resolution (HR) training videos based on our observation that existing HR videos are mostly collected from the Web which contains conspicuous compression artifacts. The proposed strategy is valid to lift the upper bound of animation VSR performance, regardless of the specific VSR model. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed VQD-SR over state-of-the-art methods, through extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations of the latest animation video super-resolution benchmark.
Diversity Regularized Interests Modeling for Recommender Systems
Mar 23, 2021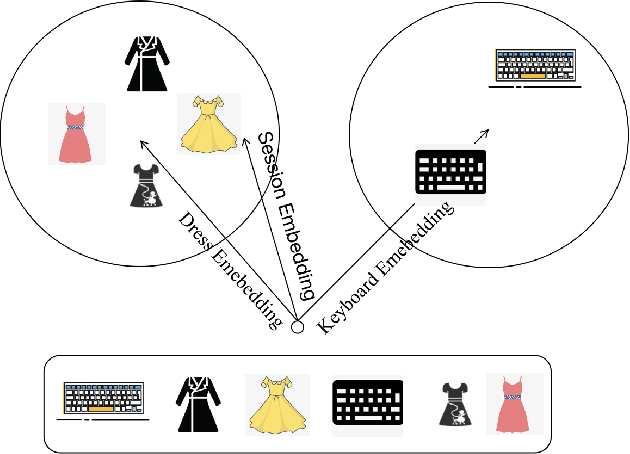
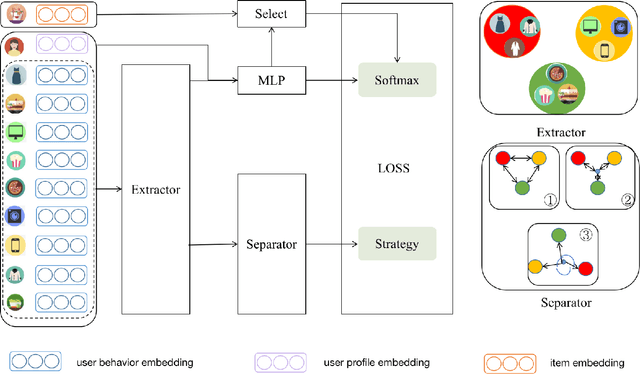
Abstract:With the rapid development of E-commerce and the increase in the quantity of items, users are presented with more items hence their interests broaden. It is increasingly difficult to model user intentions with traditional methods, which model the user's preference for an item by combining a single user vector and an item vector. Recently, some methods are proposed to generate multiple user interest vectors and achieve better performance compared to traditional methods. However, empirical studies demonstrate that vectors generated from these multi-interests methods are sometimes homogeneous, which may lead to sub-optimal performance. In this paper, we propose a novel method of Diversity Regularized Interests Modeling (DRIM) for Recommender Systems. We apply a capsule network in a multi-interest extractor to generate multiple user interest vectors. Each interest of the user should have a certain degree of distinction, thus we introduce three strategies as the diversity regularized separator to separate multiple user interest vectors. Experimental results on public and industrial data sets demonstrate the ability of the model to capture different interests of a user and the superior performance of the proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge